This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
GLUT1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | == | + | ==Facilitated glucose transporter 1, Solute Carrier Family 2 (''Homo sapiens'')== |
<StructureSection load='4pyp' size='340' side='right' caption='Crystal structure 4PYP from PDB' scene=''> | <StructureSection load='4pyp' size='340' side='right' caption='Crystal structure 4PYP from PDB' scene=''> | ||
Revision as of 16:31, 27 April 2022
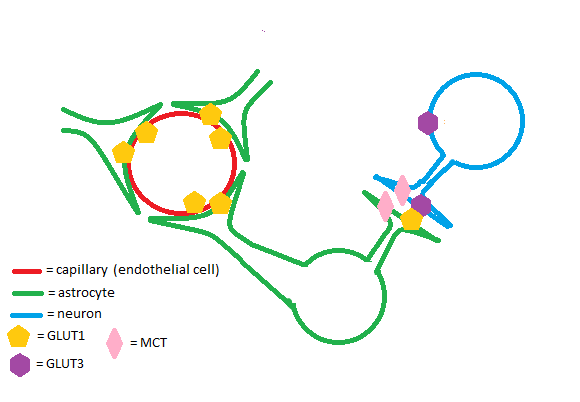
Facilitated glucose transporter 1, Solute Carrier Family 2 (Homo sapiens)
| |||||||||||
References
Pragallapati S, Manyam R. Glucose transporter 1 in health and disease. J Oral Maxillofac Pathol. 2019 Sep-Dec;23(3):443-449. doi: 10.4103/jomfp.JOMFP_22_18. PMID: 31942129; PMCID: PMC6948067.
Koepsell H. Glucose transporters in brain in health and disease. Pflugers Arch. 2020 Sep;472(9):1299-1343. doi: 10.1007/s00424-020-02441-x. Epub 2020 Aug 13. PMID: 32789766; PMCID: PMC7462931.
Asano T, Katagiri H, Takata K, Lin JL, Ishihara H, Inukai K, Tsukuda K, Kikuchi M, Hirano H, Yazaki Y, et al. The role of N-glycosylation of GLUT1 for glucose transport activity. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 25;266(36):24632-6. PMID: 1761560.