GLUT1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
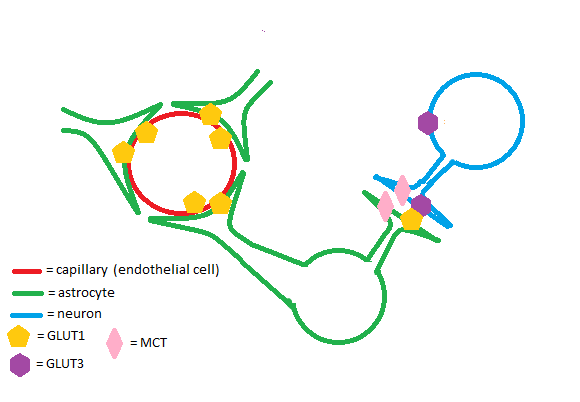
| - | The GLUT1 is an insulin-independent glucose transporter expressed by all cells in the body to maintain adequate baseline glucose uptake. Tissues that express GLUT1 at high concentrations include (but are not limited to): the placenta and fetal tissues, epithelial cells of the retina and mammary gland, and the brain.<ref>PMID:31942129</ref> | + | The GLUT1 is an '''insulin-independent''' glucose transporter expressed by all cells in the body to maintain adequate baseline glucose uptake. Tissues that express GLUT1 at high concentrations include (but are not limited to): the placenta and fetal tissues, epithelial cells of the retina and mammary gland, and the brain.<ref>PMID:31942129</ref> |
===Brain=== | ===Brain=== | ||
Revision as of 18:44, 28 April 2022
Facilitated Glucose Transporter 1, Solute Carrier Family 2, Homo sapiens
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Pragallapati S, Manyam R. Glucose transporter 1 in health and disease. J Oral Maxillofac Pathol. 2019 Sep-Dec;23(3):443-449. doi:, 10.4103/jomfp.JOMFP_22_18. PMID:31942129 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.4103/jomfp.JOMFP_22_18
- ↑ Koepsell H. Glucose transporters in brain in health and disease. Pflugers Arch. 2020 Sep;472(9):1299-1343. doi: 10.1007/s00424-020-02441-x. Epub, 2020 Aug 13. PMID:32789766 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00424-020-02441-x
- ↑ Illsley NP, Baumann MU. Human placental glucose transport in fetoplacental growth and metabolism. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2020 Feb 1;1866(2):165359. doi:, 10.1016/j.bbadis.2018.12.010. Epub 2018 Dec 26. PMID:30593896 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.bbadis.2018.12.010
- ↑ Borges MH, Pullockaran J, Catalano PM, Baumann MU, Zamudio S, Illsley NP. Human placental GLUT1 glucose transporter expression and the fetal insulin-like growth factor axis in pregnancies complicated by diabetes. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2019 Sep 1;1865(9):2411-2419. doi:, 10.1016/j.bbadis.2019.06.002. Epub 2019 Jun 5. PMID:31175930 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.bbadis.2019.06.002
- ↑ Macheda ML, Rogers S, Best JD. Molecular and cellular regulation of glucose transporter (GLUT) proteins in cancer. J Cell Physiol. 2005 Mar;202(3):654-62. doi: 10.1002/jcp.20166. PMID:15389572 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/jcp.20166
- ↑ Oh S, Kim H, Nam K, Shin I. Glut1 promotes cell proliferation, migration and invasion by regulating epidermal growth factor receptor and integrin signaling in triple-negative breast cancer cells. BMB Rep. 2017 Mar;50(3):132-137. doi: 10.5483/bmbrep.2017.50.3.189. PMID:27931517 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.5483/bmbrep.2017.50.3.189
- ↑ Asano T, Katagiri H, Takata K, Lin JL, Ishihara H, Inukai K, Tsukuda K, Kikuchi M, Hirano H, Yazaki Y, et al.. The role of N-glycosylation of GLUT1 for glucose transport activity. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 25;266(36):24632-6. PMID:1761560