We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Ceramidase
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
Refs <ref name="Okino">PMID:9603946</ref>, <ref name="Inoue">PMID:19088069</ref> , <ref name="Reverse">PMID:10832092</ref> | Refs <ref name="Okino">PMID:9603946</ref>, <ref name="Inoue">PMID:19088069</ref> , <ref name="Reverse">PMID:10832092</ref> | ||
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
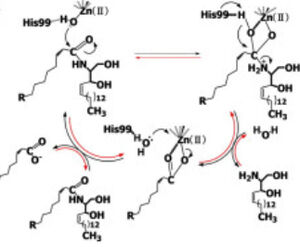
| - | CerN consists of two domains: a catalytic domain near the N-terminal and an immunoglobulin-fold domain near the C-terminal.<ref name="Inoue">PMID:19088069</ref> Three β-sheets, each formed from four β-strands, compose a β-prism fold at the center of the N-terminal domain.<ref name="Inoue">PMID:19088069</ref> Surrounding the β-prism fold are 11 α-helices, forming an <scene name='91/910024/Bprism/3'>α+ β 2-layer sandwich fold</scene>.<ref name="Inoue">PMID:19088069</ref> The immunoglobulin-like C-terminal domain is composed of two β-sheets, containing four β-strands each, forming a <scene name='91/910024/Igfold/1'>β-sandwich fold</scene>.<ref name="Inoue">PMID:19088069</ref> Between the N- and C-terminal domains is a magnesium/calcium ion binding site that links together the two domains.<ref name="Inoue">PMID:19088069</ref> His37, Asp579, Asp581, and Thr854 interact with divalent cations within the <scene name='91/910024/Mg_bs/1'>magnesium/calcium ion binding site</scene>.<ref name="Inoue">PMID:19088069</ref> A <scene name='91/910024/Zinc_bs/3'>second metal-binding site containing a zinc ion</scene> is located within the N-terminal domain active site, where it is coordinated by His97, His204, Glu411, and a water molecule.<ref name="Inoue">PMID:19088069</ref> | + | CerN consists of two domains: a <scene name='91/910024/Domains/1'>catalytic domain near the N-terminal and an immunoglobulin-fold domain near the C-terminal</scene>.<ref name="Inoue">PMID:19088069</ref> Three β-sheets, each formed from four β-strands, compose a β-prism fold at the center of the N-terminal domain.<ref name="Inoue">PMID:19088069</ref> Surrounding the β-prism fold are 11 α-helices, forming an <scene name='91/910024/Bprism/3'>α+ β 2-layer sandwich fold</scene>.<ref name="Inoue">PMID:19088069</ref> The immunoglobulin-like C-terminal domain is composed of two β-sheets, containing four β-strands each, forming a <scene name='91/910024/Igfold/1'>β-sandwich fold</scene>.<ref name="Inoue">PMID:19088069</ref> Between the N- and C-terminal domains is a magnesium/calcium ion binding site that links together the two domains.<ref name="Inoue">PMID:19088069</ref> His37, Asp579, Asp581, and Thr854 interact with divalent cations within the <scene name='91/910024/Mg_bs/1'>magnesium/calcium ion binding site</scene>.<ref name="Inoue">PMID:19088069</ref> A <scene name='91/910024/Zinc_bs/3'>second metal-binding site containing a zinc ion</scene> is located within the N-terminal domain active site, where it is coordinated by His97, His204, Glu411, and a water molecule.<ref name="Inoue">PMID:19088069</ref> |
Revision as of 19:57, 30 April 2022
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ 1.00 1.01 1.02 1.03 1.04 1.05 1.06 1.07 1.08 1.09 1.10 1.11 1.12 1.13 1.14 1.15 1.16 1.17 Inoue T, Okino N, Kakuta Y, Hijikata A, Okano H, Goda HM, Tani M, Sueyoshi N, Kambayashi K, Matsumura H, Kai Y, Ito M. Mechanistic insights into the hydrolysis and synthesis of ceramide by neutral ceramidase. J Biol Chem. 2009 Apr 3;284(14):9566-77. Epub 2008 Dec 16. PMID:19088069 doi:10.1074/jbc.M808232200
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 Okino N, Tani M, Imayama S, Ito M. Purification and characterization of a novel ceramidase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Biol Chem. 1998 Jun 5;273(23):14368-73. PMID:9603946
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Kita K, Okino N, Ito M. Reverse hydrolysis reaction of a recombinant alkaline ceramidase of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2000 May 31;1485(2-3):111-20. doi:, 10.1016/s1388-1981(00)00029-9. PMID:10832092 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/s1388-1981(00)00029-9