| Classification
GLUT proteins, encoded by the SLC2 genes, are part of the Major Facilitator Superfamily (MFS) of substrate transporters. Structural elements characteristic of GLUT proteins are twelve transmembrane domains, one N-linked glycosylation site, and lengths of about five-hundred amino acids.[1] GLUT proteins transport a variety of monosaccharides that enable cellular respiration and are thus abundant in the body. Referencing the CATH classification database, the MFS superfamily has 23,982 unique species and 134 characteristic domains. GLUT1 has two highly-conserved ATP-binding domains known as Walker motifs A and B.[2] A third ATP-binding domain is less conserved. According to UniProt, these specific sequences in the GLUT1 transporter are shared among glucose transporters in several different organisms.
Function
GLUT1 is a glucose transporter expressed by all cells in the body to maintain adequate baseline glucose uptake. Some examples of tissues that express GLUT1 at high rates include: the placenta and fetal tissues, epithelial cells of the retina and mammary gland, and the brain.[3]
Brain
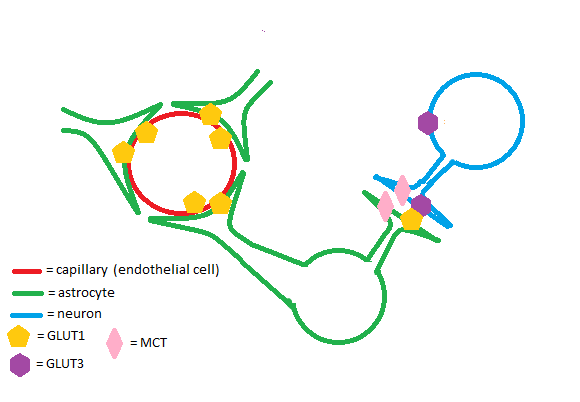
The GLUT1 transporter works synergistically with other solute carriers in the brain. Astrocytes and endothelial cells of brain capillaries primarily express GLUT1; neurons primarily express Glut3. GLUT1 has a relatively high Km and is upregulated in times of hypoglycemia in the brain to ensure adequate glucose uptake. Glut3 has a low Km to ensure a steady supply of glucose for neurons even when extracellular glucose concentrations are low.[4] Astrocytes are cells of the brain that enable glycogen storage; as a result, they are of great metabolic importance in brain function. GLUT1, Glut3, and monocarboxylate transporters (MCTs) work in conjunction to regulate transport of energy-providing molecules such as glucose and lactate in the brain.[5]
Pregnancy
The GLUT1 transporter is highly expressed in both the placenta and the developing embryo/fetus.[6] During pregnancy, there is no significant fetal gluconeogenesis in humans.[7] High GLUT1 expression in the fetoplacental tissues ensures that the fetus receives a steady supply of glucose.
Retina
GLUT1 is the most abundant glucose transporter in the retina. Retinal pigmented epithelium and retinal capillary endothelium, the tissues that comprise the retina-brain barrier, express GLUT1.[8] The retina has a consistently high energy requirement due to abundance of energy-consuming enzymes such as Sodium-Potassium ATPase. Studies on mice have shown that GLUT1 knockout leads to photoreceptor cell death - a greater effect was noted in cone cells versus rod cells.[9]
Disease
GLUT1 Deficiency Syndrome
GLUT1 deficiency syndrome is a autosomal-dominant genetic condition which involves a mutation in SLC2A1, the gene that codes for the GLUT1 transporter. Symptoms of GLUT1 deficiency syndrome develop within the first few months of life and manifest themselves neurologically. Symptoms can include seizures, involuntary eye movements, microcephaly, developmental delays, intellectual disabilities, spasticity, or ataxia.[10]
Cancer
Oncogenes such as Ras and Src have been linked to upregulation of GLUT1 in rat tumors. Many studies have shown that GLUT1 is upregulated in malignancies of the breast.[11] Upregulation of the GLUT1 transporter has been shown to increase cell proliferation in some types of breast cancer.[12] GLUT1 upregulation is thought to play a role in malignant cell proliferation in some types of tumors.[13]
Diabetes
Diabetes and Pregnancy
GLUT1 has been shown to be upregulated in the placental tissue of mothers with both pregestational and gestational diabetes, even when the mother's glycemic control is considered good. It is hypothesized that fetal hyperglycemia due to increased glucose transporter expression increases the risk of offspring developing type I or type II diabetes.[14]
Diabetic Retinopathy
GLUT1 has been found to be upregulated in retinal tissue of diabetic mice. Studies on mice show that GLUT1 overexpression plays a key role in development of diabetic retinopathy.[15] While it has been proven that hyperglycemia causes diabetic retinopathy in humans, at this point more research is necessary to determine if GLUT1 plays a direct role in diabetic retinopathy.
Alzheimer's Disease
A handful of glucose transporters, including GLUT1, have been shown to be downregulated in Alzheimer's disease.[16] Potential therapeutic solutions to glucose transporter deficiency in conditions such as Alzheimer's include glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) analog treatment. Although GLP-1 agonists have been proven to increase insulin secretion by the pancreas in type II diabetes mellitus[17], it is unclear how they affect glucose transporter kinetics in the brain.
Structural highlights
The GLUT1 transporter has one known site at Asn 45. Varied molecular weights of the GLUT1 transporter suggest glycosylation is dependent on cell type. This glycosylation site is thought to be important for increasing glucose binding to the extracellular portion of the transporter. Mutations in the GLUT1 transporter from Asn 45 to an Asp, Tyr, or Gln residue have been shown to increase the Km of the enzyme.[18] In addition, samples of both bovine capillaries and choroid plexus cells show differences in GLUT1 molecular weight attributable to N-linked glycosylation.[19] This evidence suggests that GLUT1 glycosylation may differ by tissue type to serve certain functions.
GLUT1 and Glut3 have a that are predicted to stabilize the "outward" conformation of both proteins, allowing extracellular glucose binding.[20] These motifs are referred to as the "A" and "SP" motifs. The implications of this finding are that these two motifs may play a key role in conformational changes involved in glucose import. The sequence of the A motif, from residue 84 to residue 93, is G-L-F-V-N-R-F-G-R-R. The sequence of the SP motif, from residue 208 to residue 212, is P-E-S-P-R.
has a and is proposed to be comprised of . In the structure 4pyp, these residues are Gly27, Thr30, Ile164, Val165, Ile168, and Phe291. This hydrophobic pocket has been proposed to facilitate substrate binding and unbinding between the "occluded" and "inward-open" conformations.[21] In this crystal structure, acts as a glucose analog that binds the hydrophobic pocket.[22]
The GLUT1 transporter also has three ATP-binding sites. The lone is proposed to be comprised of the residues Gly111, Phe112, Ser113, Lys114, Leu115, Gly116, Lys117, and Ser118. This is a domain consistent with Walker Motif A (G-X-X-G/X-X-G-K-T/X). The is one of two in the cytoplasmic portion of the protein. The residues comprising this ATP-binding site are Lys225, Ser226, Val227, Leu228, and Lys229. The , also localized to the cytoplasm, is comprised of the amino acids Gly332, Arg 333, Arg334, Thr335, Leu336, His337, and Leu338. This sequence is consistent with Walker Motif B (G-X-X-X-L-X-X).[23] As mentioned earlier in this page, both Walker motifs A and B are highly conserved. Some studies on GLUT1 show that ATP binding to the cytosolic domains causes C-terminus binding to the C-terminal side of the intracellular loop of the protein, preventing substrate import. ATP binding is not known to have any effects when binding extracellularly.[24]
Several types of GLUT1 inhibitors exist, one being cytochalasin b. Two Trp residues, Trp388 and Trp412, are thought to play a major role in via hydrophobic interactions.[25]
There is at least one known amino acid substitution in GLUT1 that can cause GLUT1 deficiency syndrome. causes transmembrane helix #4 to become kinked, blocking substrate transport. Arg126 is the amino acid most often mutated in GLUT1 deficiency syndrome.[26]
GLUT1, and other glucose transporters, have an . The ICH domain of GLUT1 may play a role in stabilizing the outward-facing conformation of the enzyme based on computer modeling in MODELLER.[27] Two residues of interest in the ICH domain are Arg212 and Asp240. These residues are hypothesized to participate in hydrogen bonding between the ICH domain and transmembrane domains of the protein with the cumulative effect of stabilizing the outward-facing conformation.
References
- ↑ Mueckler M, Thorens B. The SLC2 (GLUT) family of membrane transporters. Mol Aspects Med. 2013 Apr-Jun;34(2-3):121-38. doi: 10.1016/j.mam.2012.07.001. PMID:23506862 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.mam.2012.07.001
- ↑ Salas-Burgos A, Iserovich P, Zuniga F, Vera JC, Fischbarg J. Predicting the three-dimensional structure of the human facilitative glucose transporter glut1 by a novel evolutionary homology strategy: insights on the molecular mechanism of substrate migration, and binding sites for glucose and inhibitory molecules. Biophys J. 2004 Nov;87(5):2990-9. Epub 2004 Aug 23. PMID:15326030 doi:10.1529/biophysj.104.047886
- ↑ Pragallapati S, Manyam R. Glucose transporter 1 in health and disease. J Oral Maxillofac Pathol. 2019 Sep-Dec;23(3):443-449. doi:, 10.4103/jomfp.JOMFP_22_18. PMID:31942129 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.4103/jomfp.JOMFP_22_18
- ↑ Koepsell H. Glucose transporters in brain in health and disease. Pflugers Arch. 2020 Sep;472(9):1299-1343. doi: 10.1007/s00424-020-02441-x. Epub, 2020 Aug 13. PMID:32789766 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00424-020-02441-x
- ↑ Alberini CM, Cruz E, Descalzi G, Bessieres B, Gao V. Astrocyte glycogen and lactate: New insights into learning and memory mechanisms. Glia. 2018 Jun;66(6):1244-1262. doi: 10.1002/glia.23250. Epub 2017 Oct 27. PMID:29076603 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/glia.23250
- ↑ Illsley NP, Baumann MU. Human placental glucose transport in fetoplacental growth and metabolism. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2020 Feb 1;1866(2):165359. doi:, 10.1016/j.bbadis.2018.12.010. Epub 2018 Dec 26. PMID:30593896 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.bbadis.2018.12.010
- ↑ Borges MH, Pullockaran J, Catalano PM, Baumann MU, Zamudio S, Illsley NP. Human placental GLUT1 glucose transporter expression and the fetal insulin-like growth factor axis in pregnancies complicated by diabetes. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2019 Sep 1;1865(9):2411-2419. doi:, 10.1016/j.bbadis.2019.06.002. Epub 2019 Jun 5. PMID:31175930 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.bbadis.2019.06.002
- ↑ Liu H, Prokosch V. Energy Metabolism in the Inner Retina in Health and Glaucoma. Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 1;22(7). pii: ijms22073689. doi: 10.3390/ijms22073689. PMID:33916246 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/ijms22073689
- ↑ Swarup A, Samuels IS, Bell BA, Han JYS, Du J, Massenzio E, Abel ED, Boesze-Battaglia K, Peachey NS, Philp NJ. Modulating GLUT1 expression in retinal pigment epithelium decreases glucose levels in the retina: impact on photoreceptors and Muller glial cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2019 Jan 1;316(1):C121-C133. doi:, 10.1152/ajpcell.00410.2018. Epub 2018 Nov 21. PMID:30462537 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1152/ajpcell.00410.2018
- ↑ Wang D, Pascual JM, De Vivo D. Glucose Transporter Type 1 Deficiency Syndrome PMID:20301603
- ↑ Macheda ML, Rogers S, Best JD. Molecular and cellular regulation of glucose transporter (GLUT) proteins in cancer. J Cell Physiol. 2005 Mar;202(3):654-62. doi: 10.1002/jcp.20166. PMID:15389572 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/jcp.20166
- ↑ Oh S, Kim H, Nam K, Shin I. Glut1 promotes cell proliferation, migration and invasion by regulating epidermal growth factor receptor and integrin signaling in triple-negative breast cancer cells. BMB Rep. 2017 Mar;50(3):132-137. doi: 10.5483/bmbrep.2017.50.3.189. PMID:27931517 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.5483/bmbrep.2017.50.3.189
- ↑ Zambrano A, Molt M, Uribe E, Salas M. Glut 1 in Cancer Cells and the Inhibitory Action of Resveratrol as A Potential Therapeutic Strategy. Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jul 9;20(13). pii: ijms20133374. doi: 10.3390/ijms20133374. PMID:31324056 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/ijms20133374
- ↑ Gaither K, Quraishi AN, Illsley NP. Diabetes alters the expression and activity of the human placental GLUT1 glucose transporter. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1999 Feb;84(2):695-701. doi: 10.1210/jcem.84.2.5438. PMID:10022440 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1210/jcem.84.2.5438
- ↑ Holoman NC, Aiello JJ, Trobenter TD, Tarchick MJ, Kozlowski MR, Makowski ER, De Vivo DC, Singh C, Sears JE, Samuels IS. Reduction of Glut1 in the Neural Retina But Not the RPE Alleviates Polyol Accumulation and Normalizes Early Characteristics of Diabetic Retinopathy. J Neurosci. 2021 Apr 7;41(14):3275-3299. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2010-20.2021., Epub 2021 Feb 23. PMID:33622781 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2010-20.2021
- ↑ Gejl M, Brock B, Egefjord L, Vang K, Rungby J, Gjedde A. Blood-Brain Glucose Transfer in Alzheimer's disease: Effect of GLP-1 Analog Treatment. Sci Rep. 2017 Dec 13;7(1):17490. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-17718-y. PMID:29235507 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-17718-y
- ↑ Filippatos TD, Panagiotopoulou TV, Elisaf MS. Adverse Effects of GLP-1 Receptor Agonists. Rev Diabet Stud. 2014 Fall-Winter;11(3-4):202-30. doi: 10.1900/RDS.2014.11.202., Epub 2015 Feb 10. PMID:26177483 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1900/RDS.2014.11.202
- ↑ Asano T, Katagiri H, Takata K, Lin JL, Ishihara H, Inukai K, Tsukuda K, Kikuchi M, Hirano H, Yazaki Y, et al.. The role of N-glycosylation of GLUT1 for glucose transport activity. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 25;266(36):24632-6. PMID:1761560
- ↑ Kumagai AK, Dwyer KJ, Pardridge WM. Differential glycosylation of the GLUT1 glucose transporter in brain capillaries and choroid plexus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1994 Jul 13;1193(1):24-30. doi:, 10.1016/0005-2736(94)90328-x. PMID:8038191 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0005-2736(94)90328-x
- ↑ Custodio TF, Paulsen PA, Frain KM, Pedersen BP. Structural comparison of GLUT1 to GLUT3 reveal transport regulation mechanism in sugar porter family. Life Sci Alliance. 2021 Feb 3;4(4). pii: 4/4/e202000858. doi:, 10.26508/lsa.202000858. Print 2021 Apr. PMID:33536238 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.26508/lsa.202000858
- ↑ Ung PM, Song W, Cheng L, Zhao X, Hu H, Chen L, Schlessinger A. Inhibitor Discovery for the Human GLUT1 from Homology Modeling and Virtual Screening. ACS Chem Biol. 2016 Jul 15;11(7):1908-16. doi: 10.1021/acschembio.6b00304. Epub, 2016 May 11. PMID:27128978 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/acschembio.6b00304
- ↑ Deng D, Xu C, Sun P, Wu J, Yan C, Hu M, Yan N. Crystal structure of the human glucose transporter GLUT1. Nature. 2014 Jun 5;510(7503):121-5. doi: 10.1038/nature13306. Epub 2014 May 18. PMID:24847886 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nature13306
- ↑ Liu Q, Vera JC, Peng H, Golde DW. The predicted ATP-binding domains in the hexose transporter GLUT1 critically affect transporter activity. Biochemistry. 2001 Jul 3;40(26):7874-81. doi: 10.1021/bi002850x. PMID:11425315 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/bi002850x
- ↑ Sage JM, Cura AJ, Lloyd KP, Carruthers A. Caffeine inhibits glucose transport by binding at the GLUT1 nucleotide-binding site. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2015 May 15;308(10):C827-34. doi:, 10.1152/ajpcell.00001.2015. Epub 2015 Feb 25. PMID:25715702 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1152/ajpcell.00001.2015
- ↑ MacLeod KE, Hanisch RC, Lewis RG. Evaluation of gel permeation chromatography for clean up of human adipose tissue samples for GC/MS analysis of pesticides and other chemicals. J Anal Toxicol. 1982 Jan-Feb;6(1):38-40. doi: 10.1093/jat/6.1.38. PMID:7078104 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/jat/6.1.38
- ↑ Pascual JM, Wang D, Yang R, Shi L, Yang H, De Vivo DC. Structural signatures and membrane helix 4 in GLUT1: inferences from human blood-brain glucose transport mutants. J Biol Chem. 2008 Jun 13;283(24):16732-42. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M801403200. Epub 2008, Apr 3. PMID:18387950 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M801403200
- ↑ Park MS. Molecular Dynamics Simulations of the Human Glucose Transporter GLUT1. PLoS One. 2015 Apr 28;10(4):e0125361. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0125361., eCollection 2015. PMID:25919356 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0125361
|

