Putative kinase, PDB ID 3HDT, shows limited activity as a cytidylate kinase, utilizing ATP and dCMP as ligands.
Introduction
Kinases (or phosphotransferases) facilitate the transfer of a phosphate group from one molecule to another and are involved in cell growth and signaling. The goal of this research is to study a protein (PDB ID 3HDT) with unknown function and elucidate its potential substrates. This work uses in silico techniques to characterize the protein before biochemical assays were used to test for kinase activity. This research is part of the BASIL project that involved performing in silico and in vitro modules to make predictions and study the function of this protein.
In silico anaylsis
We used a variety of in silico tools to find similarities between 3HDT and other amino acid sequences, protein families, and 3-dimensional structures of known proteins in the PDB. Below are the recorded results and information from each database. From this information, a function was hypothesized for 3HDT and potential substrates such as dCMP were selected for kinase assays.
BLASTp
Beginning with BLASTp[1], we queried the FASTA sequence for our protein, PDB ID 3HDT. Our query sequence aligned with the NK superfamily and showed a high degree of overlap indicating that this protein is likely a member. The importance of this is that the cytidylate kinase family is a member of the NK superfamily, supporting our hypothesis that 3HDT is a cytidylate kinase. Additionally, the query hits showed several cytidylate kinase-like family proteins almost completely aligning with our protein, 3HDT.

BLASTp alignment showing a hit with cytidylate kinase-like family, part of the NK superfamily.

Query hits 1-2 show proteins with unknown function while 3-6 match a cytidylate kinase-like family protein.
Pfam
We used 3HDT's FASTA sequence to search in Pfam[2] for protein families that 3HDT may belong to. Pfam predicted that 3HDT is part of the cytidylate kinase-like family which concurs with the BLASTp results shown previously. Also shown below are domains commonly associated with the sequence queried.

Pfam query aligned with a cytidylate kinase-like family.
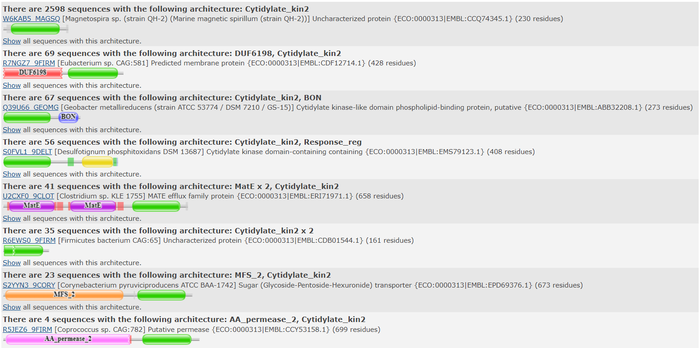
Top domain results from Pfam.
DALI
Two of the top results from our DALI[3] query (both cytidylate kinases) show a high structural resemblance with 3HDT when overlaid in DALI’s viewer. It is also worth noting that the majority of the results from our DALI query consisted of cytidylate kinases. This information helped us hypothesize the function (cytidylate kinase) of 3HDT due to the structural similarity between the proteins (structure of the protein = function) indicating a similarity in function between these kinases and our protein.
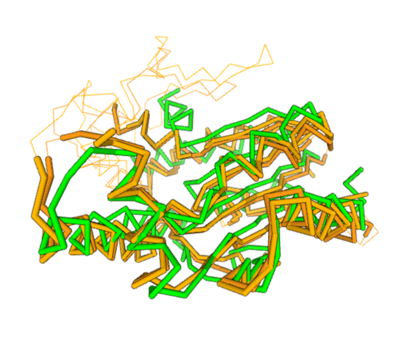
Spatial alignment of putative kinase 3HDT (green) with two cytidylate kinases: 7L4A (dark brown) and 1KDO (light brown).
Docking
We used POCASA[4] to determine potential binding pockets within 3HDT before using PyRx[5] to dock dCMP into the protein. PyMOL[6] was then used to visualize the binding pockets with dCMP and other various ligands docked in 3HDT. This (in purple) is a region within 3HDT where the substrate dCMP could bind as indicated by POCASA. This area was also where dCMP bound with the highest affinity in PyRx. The (Gly21, Ser22, Gly23, Val27, Thr 142, Gln149, Arg150, Thr197, Leu200, Thr201) interact within that area to help hold the substrate in place with hydrophobic interactions. Also, there are two residues, within the active site containing dCMP and cofactor ATP that are important in substrate binding. They interact with the substrate forming hydrogen bonds with the oxygens on the phosphate groups and the 6-membered ring. The program LIGPLOT[7] was instrumental in discovering these specific interactions between various residues and ligands. However, the PyRx and LIGPLOT results may be inaccurate due to an issue in the docking process where we were unsuccessful in getting PyRx to recognize where the ATP cofactor was bound before docking our substrate into the protein.
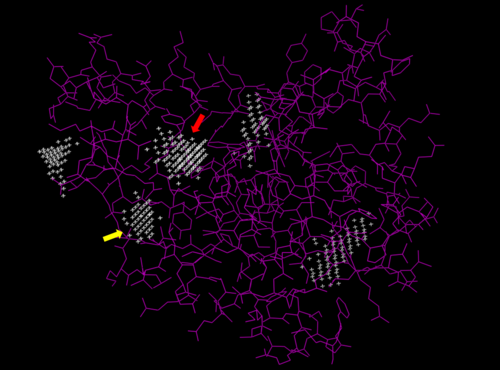
Predicted binding pockets for 3HDT represented by the white stippling.
Some of the predicted binding pockets were areas where ATP (red arrow) and dCMP (yellow arrow) bound with the highest affinity in PyRx.
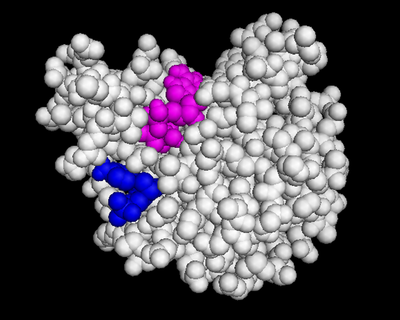
dCMP (purple) docked with 3HDT and cofactor ATP (pink). Visualized in PyMOL.
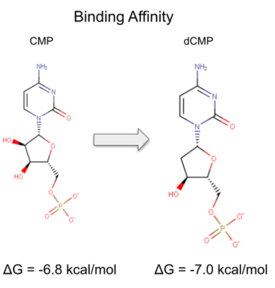
Binding affinity was increased when a hydroxyl group was removed from the ribose ring on CMP to make dCMP.
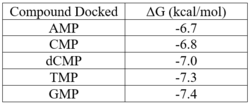
Binding affinities for compounds docked using PyRx.
Laboratory Experiments
Plasmid Analysis
BL21-Gold E.Coli were transformed with a plasmid containing the gene for 3HDT to produce our protein of interest. A pMCSG19 vector with ampicillin resistance was inserted into the cells via heat shock and incubated on a plate containing carbenicillin. To ensure we inserted the gene of interest the plasmid was digested with Xho1 and Nde1 before gel electrophoresis was run to verify its identity. The vector was 6,441 bp with the insert being an additional 660 bp for a total of 7,101 bp. This is approximately the size of the combined bands in lane five, demonstrating that we had the correct plasmid and could move forward with protein over-expression and purification.
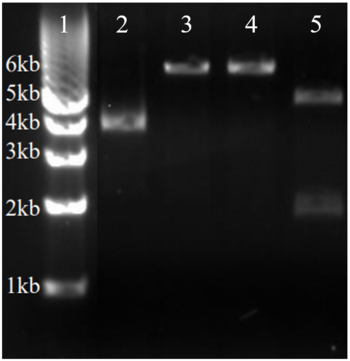
Lane one contains ladder. Lane two contains pDNA without enzyme. Lane three contains pDNA + Xho1. Lane four contains pDNA + Nde1. Lane 5 contains pDNA + Xho1 + Nde1. Image has been modified to only show lanes of interest.
Coupled kinase assay
Two rounds of coupled kinase assays were run using 3HDT with ATP and dCMP as substrates. Various concentrations of dCMP between 5-10mM were used in a total of 8 assays. In the first round of assays (3 assays) 45.6ng of 3HDT and increasing concentrations of 5.0, 7.5, and 10.0mM of dCMP were added to wells each containing 100μL total. A concentration of 7.5mM dCMP resulted in the highest specific activity (0.377 U/mg) while increasing the substrate concentration to 10mM slightly lowered specific activity to 0.348 U/mg. When we repeated the first three kinase assays (5.0, 7.5, 10.0mM dCMP), there were discrepancies in the results indicating a potential experimental error such improper mixing, bubbles being present in the well, or too much time passing between adding substrate to the well and measuring absorbance in the plate reader. Additionally, the protein in the second round of assays was older (original protein but approximately a week had passed from time of over-expression) which could have affected the specific activity in those trials due to the protein starting to expire/decrease in function.
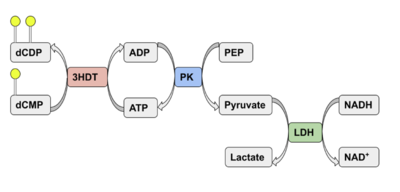
Coupled kinase assay diagram with enzymes shown in color and phosphates in yellow. Phosphorylation of dCMP is measured indirectly through the conversion of NADH to NAD+. Background hydrolysis of NADH is measured and subtracted from the conversion rate in the presence of dCMP to produce specific activity values.

Data table showing all eight coupled kinase assays with 3HDT and dCMP along with their specific activity values.
SDS-PAGE
SDS-PAGE results for our purified protein sample are shown below. The first lane (left) contains a size standard and the second lane (right) contains our protein sample. The band in the second lane (right) at ~70kD is not the protein of interest (3HDT) but contains a metal binding protein. The mass of 3HDT is approximately 25.79 kD, which matches the faint band at ~26kD, indicating that our protein of interest was present.

Results from SDS-PAGE with purified protein sample.
Conclusion/Future Experiments
Our protein, 3HDT, was confirmed to be present using SDS-PAGE and showed activity during coupled kinase assays. While this confirms that 3HDT is a kinase, the true substrate was likely not dCMP due to the low specific activity values. Further research should be done with molecules such as TMP and GMP in the future to narrow down potential nucleotide substrates or elucidate other types of compounds to be considered as ligands for 3HDT. Additionally, in the future we would like to repeat the protein purification process to try and get a higher protein concentration than what we achieved as the low concentration may have affected our coupled kinase assay results.