User:Max Hideki Oliveira Homma/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
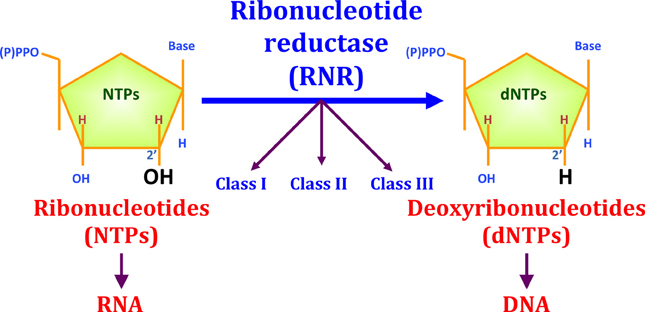
Several microorganisms are able to encode RNRs of different classes. In the case of Escherichia coli, RNR Ia is preferentially expressed in the growth phase under aerobic conditions, while RNR III is mainly expressed under anaerobic conditions. Furthermore, in environments with low iron availability or when there is biofilm formation, E. coli tends to preferentially express RNR Ib. | Several microorganisms are able to encode RNRs of different classes. In the case of Escherichia coli, RNR Ia is preferentially expressed in the growth phase under aerobic conditions, while RNR III is mainly expressed under anaerobic conditions. Furthermore, in environments with low iron availability or when there is biofilm formation, E. coli tends to preferentially express RNR Ib. | ||
| - | |||
== Geral structure of RNR Ia == | == Geral structure of RNR Ia == | ||
| Line 35: | Line 34: | ||
== R2 subunit and cofactor == | == R2 subunit and cofactor == | ||
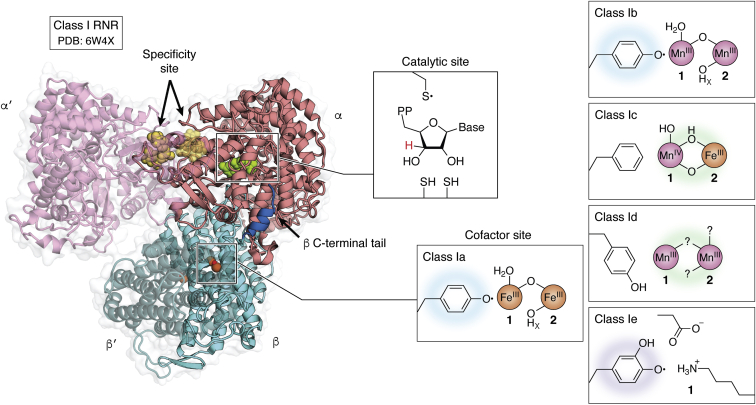
| + | In Ia RNRs, the cofactor binding site is located on the R2 subunit, also known as β. The β subunit may be associated with the α protein in dimeric or oligomeric forms, and there may be one or more β subunits in the same enzyme. | ||
| + | |||
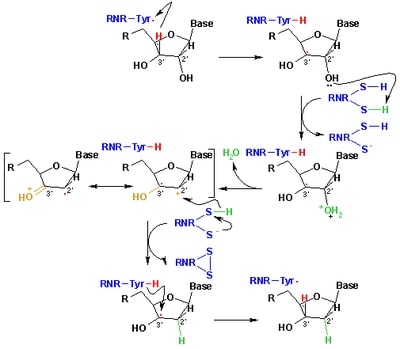
| + | It contains the essential metal cofactor binding site for the initiation of nucleotide reduction, the ionic transition that occurs with the metallofactor at the β subunit site promotes the formation of the radical that will later be transferred through long-range radical transfer to the alpha subunit, where it will generate the thiol radical at the active site of the enzyme, where the two cysteine loops reduce NTP. | ||
| + | |||
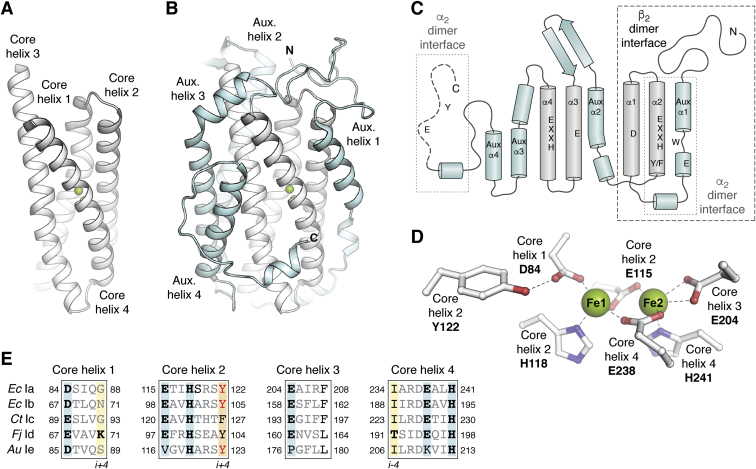
| + | The R2 protein has a binding site for two Iron atoms on each of its two identical protomers and a nearby potential tyrosyl radical site (Y122 in E.coli). The general structure of the protein is mainly α-helix and each of the di-iron centers are coordinated by aspartate (D84), two histidines (H118 and H241) and three glutamate residues (E115, E204 and E238) that are brought together within a bundle of four helices. This structure is conserved in all subclasses of RNR I, with very few exceptions. | ||
| + | |||
| + | All β subunits belong to the ferritin structural superfamily, with a core composed of a package of four central helices that connect to assemble the active oxidant. In class Ia, this core unit is symmetrical, with two α-helix pairs arranged in a head-to-tail direction to sink the Metallocofactor, FeIII-O-FeIII in this class, into the β structure and protect it from the solvent. Each of the helices in the pair confer a linker region with the cofactor. In addition to cofactor protection, the helical structure also provides second-sphere side chains that contribute to cofactor assembly and reactivity. | ||
| + | [[Image:RNR4.jpg]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Regulation == | ||
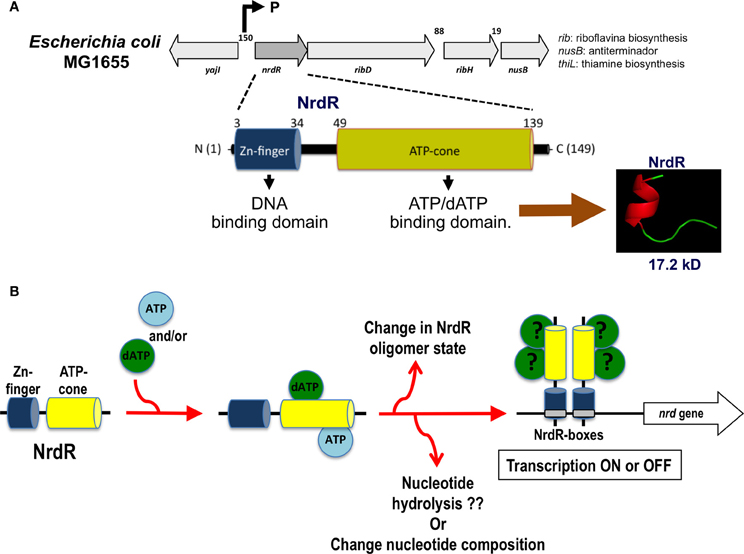
| + | The regulation of RNRs is very refined and occurs at several levels. In microorganisms, a transcription factor, called NrdR, was identified, which is capable of binding to NrdR-box, a consensus sequence present in the promoters of nrd genes, which encode RNRs. The NrdR is composed of two domains, the Zn-finger, which binds to DNA, and the ATP-cone, which has ATP and/or dATP binding sites. Although its regulatory mechanism has not been fully elucidated, it is proposed that the binding of dATP to the ATP-cone causes NrdR to dimerize and interact more with the NrdR-boxes sequences, leading to reduced transcription of nrd genes. | ||
| + | [[Image:RNR5.jpg]] | ||
| + | |||
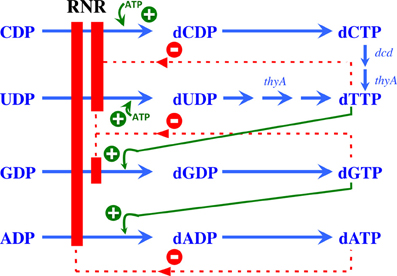
| + | The activity of the already translated RNR is also finely regulated. Although RNRs are capable of reducing the 4 ribonucleotides, the binding of dATP (or ATP), dGTP, dCTP and dUTP to the S site of the R1 subunit changes which ribonucleotide will be preferentially reduced by the enzyme. For example, in Ia RNRs, the binding of dATP or ATP to the S site causes the enzyme to reduce CDP and UDP while inhibiting the reduction of ADP. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:RNR6.jpg]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | In addition to the S site, the A site is also capable of regulating RNR Ia activity. In this sense, ATP binding to this site will stimulate the general activity of the enzyme, while dATP will inhibit it. However, because dATP binds with a much higher affinity to the S site than to the A site, its inhibitory effect is only significant when this molecule is in high concentrations. | ||
| + | Due to the cellular importance of RNRs and the possibility of regulating their activity, inhibitors of these enzymes have been used for therapeutic purposes. Inhibition of Ia RNRs seems to be a particularly interesting strategy in the fight against cancer, as it leads to the interruption of cell proliferation. An alternative R2 subunit, called p53R2, was also identified in mammalian cells, which is associated with the DNA repair system and is often not functioning correctly in cancer cells. | ||
| + | Inhibitors of Ia RNRs can be divided into three main groups. The first group consists of inhibitors that bind to the R1 subunit, either at the active site or at allosteric sites. The second group comprises inhibitors that act on the R2 subunit, usually being iron-chelating or radical-scavenging compounds. Finally, the third group is composed of inhibitors that form hairpins with the mRNA transcribed from the nrd genes, preventing their translation. In addition to these three groups, there are also inhibitors that prevent the union between the R1 and R2 subunits. | ||
| + | |||
Revision as of 14:46, 13 June 2022
</math>==Your Heading Here (maybe something like 'Structure')==
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Hanson, R. M., Prilusky, J., Renjian, Z., Nakane, T. and Sussman, J. L. (2013), JSmol and the Next-Generation Web-Based Representation of 3D Molecular Structure as Applied to Proteopedia. Isr. J. Chem., 53:207-216. doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/ijch.201300024
- ↑ Herraez A. Biomolecules in the computer: Jmol to the rescue. Biochem Mol Biol Educ. 2006 Jul;34(4):255-61. doi: 10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644. PMID:21638687 doi:10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644