1hkb
From Proteopedia
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | [[Image:1hkb. | + | {{Seed}} |
| + | [[Image:1hkb.png|left|200px]] | ||
<!-- | <!-- | ||
| Line 9: | Line 10: | ||
{{STRUCTURE_1hkb| PDB=1hkb | SCENE= }} | {{STRUCTURE_1hkb| PDB=1hkb | SCENE= }} | ||
| - | + | ===CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF RECOMBINANT HUMAN BRAIN HEXOKINASE TYPE I COMPLEXED WITH GLUCOSE AND GLUCOSE-6-PHOSPHATE=== | |
| - | + | <!-- | |
| - | + | The line below this paragraph, {{ABSTRACT_PUBMED_9493266}}, adds the Publication Abstract to the page | |
| + | (as it appears on PubMed at http://www.pubmed.gov), where 9493266 is the PubMed ID number. | ||
| + | --> | ||
| + | {{ABSTRACT_PUBMED_9493266}} | ||
==About this Structure== | ==About this Structure== | ||
| Line 34: | Line 38: | ||
[[Category: Glycolysis]] | [[Category: Glycolysis]] | ||
[[Category: Phosphotransferase]] | [[Category: Phosphotransferase]] | ||
| - | ''Page seeded by [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca OCA ] on | + | |
| + | ''Page seeded by [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca OCA ] on Tue Jul 1 08:18:33 2008'' | ||
Revision as of 05:18, 1 July 2008
| |||||||||
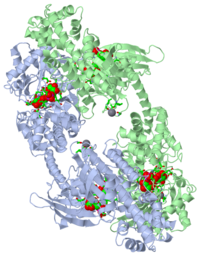
| 1hkb, resolution 2.80Å () | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligands: | , , | ||||||||
| Activity: | Hexokinase, with EC number 2.7.1.1 | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| |||||||||
| Resources: | FirstGlance, OCA, RCSB, PDBsum | ||||||||
| Coordinates: | save as pdb, mmCIF, xml | ||||||||
CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF RECOMBINANT HUMAN BRAIN HEXOKINASE TYPE I COMPLEXED WITH GLUCOSE AND GLUCOSE-6-PHOSPHATE
BACKGROUND: Hexokinase I is the pacemaker of glycolysis in brain tissue. The type I isozyme exhibits unique regulatory properties in that physiological levels of phosphate relieve potent inhibition by the product, glucose-6-phosphate (Gluc-6-P). The 100 kDa polypeptide chain of hexokinase I consists of a C-terminal (catalytic) domain and an N-terminal (regulatory) domain. Structures of ligated hexokinase I should provide a basis for understanding mechanisms of catalysis and regulation at an atomic level. RESULTS: The complex of human hexokinase I with glucose and Gluc-6-P (determined to 2.8 A resolution) is a dimer with twofold molecular symmetry. The N- and C-terminal domains of one monomer interact with the C- and N-terminal domains, respectively, of the symmetry-related monomer. The two domains of a monomer are connected by a single alpha helix and each have the fold of yeast hexokinase. Salt links between a possible cation-binding loop of the N-terminal domain and a loop of the C-terminal domain may be important to regulation. Each domain binds single glucose and Gluc-6-P molecules in proximity to each other. The 6-phosphoryl group of bound Gluc-6-P at the C-terminal domain occupies the putative binding site for ATP, whereas the 6-phosphoryl group at the N-terminal domain may overlap the binding site for phosphate. CONCLUSIONS: The binding synergism of glucose and Gluc-6-P probably arises out of the mutual stabilization of a common (glucose-bound) conformation of hexokinase I. Conformational changes in the N-terminal domain in response to glucose, phosphate, and/or Gluc-6-P may influence the binding of ATP to the C-terminal domain.
The mechanism of regulation of hexokinase: new insights from the crystal structure of recombinant human brain hexokinase complexed with glucose and glucose-6-phosphate., Aleshin AE, Zeng C, Bourenkov GP, Bartunik HD, Fromm HJ, Honzatko RB, Structure. 1998 Jan 15;6(1):39-50. PMID:9493266
From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine.
About this Structure
1HKB is a Single protein structure of sequence from Homo sapiens. Full crystallographic information is available from OCA.
Reference
The mechanism of regulation of hexokinase: new insights from the crystal structure of recombinant human brain hexokinase complexed with glucose and glucose-6-phosphate., Aleshin AE, Zeng C, Bourenkov GP, Bartunik HD, Fromm HJ, Honzatko RB, Structure. 1998 Jan 15;6(1):39-50. PMID:9493266
Page seeded by OCA on Tue Jul 1 08:18:33 2008