|
|
| Line 3: |
Line 3: |
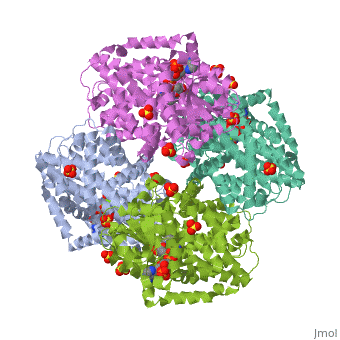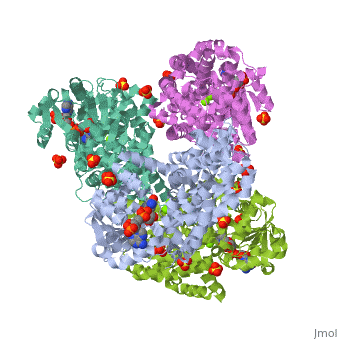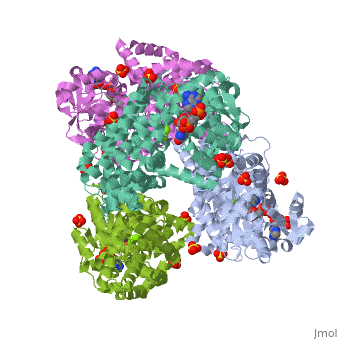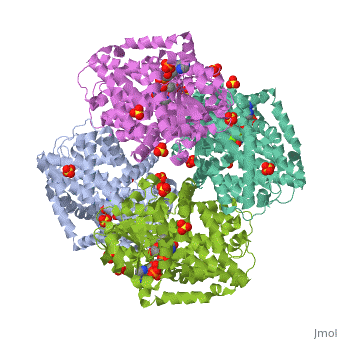
| | <StructureSection load='3ulk' size='340' side='right'caption='[[3ulk]], [[Resolution|resolution]] 2.30Å' scene=''> | | <StructureSection load='3ulk' size='340' side='right'caption='[[3ulk]], [[Resolution|resolution]] 2.30Å' scene=''> |
| | == Structural highlights == | | == Structural highlights == |
| - | <table><tr><td colspan='2'>[[3ulk]] is a 2 chain structure with sequence from [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ecoli Ecoli]. Full crystallographic information is available from [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocashort?id=3ULK OCA]. For a <b>guided tour on the structure components</b> use [https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=3ULK FirstGlance]. <br> | + | <table><tr><td colspan='2'>[[3ulk]] is a 2 chain structure with sequence from [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Escherichia_coli_K-12 Escherichia coli K-12]. Full crystallographic information is available from [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocashort?id=3ULK OCA]. For a <b>guided tour on the structure components</b> use [https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=3ULK FirstGlance]. <br> |
| - | </td></tr><tr id='ligand'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Ligand|Ligands:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat" id="ligandDat"><scene name='pdbligand=MG:MAGNESIUM+ION'>MG</scene>, <scene name='pdbligand=NDP:NADPH+DIHYDRO-NICOTINAMIDE-ADENINE-DINUCLEOTIDE+PHOSPHATE'>NDP</scene>, <scene name='pdbligand=SO4:SULFATE+ION'>SO4</scene></td></tr> | + | </td></tr><tr id='method'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Empirical_models|Method:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat" id="methodDat">X-ray diffraction, [[Resolution|Resolution]] 2.3Å</td></tr> |
| - | <tr id='NonStdRes'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Non-Standard_Residue|NonStd Res:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><scene name='pdbligand=CSX:S-OXY+CYSTEINE'>CSX</scene></td></tr> | + | <tr id='ligand'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Ligand|Ligands:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat" id="ligandDat"><scene name='pdbligand=CSX:S-OXY+CYSTEINE'>CSX</scene>, <scene name='pdbligand=MG:MAGNESIUM+ION'>MG</scene>, <scene name='pdbligand=NDP:NADPH+DIHYDRO-NICOTINAMIDE-ADENINE-DINUCLEOTIDE+PHOSPHATE'>NDP</scene>, <scene name='pdbligand=SO4:SULFATE+ION'>SO4</scene></td></tr> |
| - | <tr id='related'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Related_structure|Related:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><div style='overflow: auto; max-height: 3em;'>[[1yrl|1yrl]], [[1yve|1yve]], [[3fr7|3fr7]], [[3fr8|3fr8]]</div></td></tr>
| + | |
| - | <tr id='gene'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Gene|Gene:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat">ilvC ([https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Taxonomy/Browser/wwwtax.cgi?mode=Info&srchmode=5&id=83333 ECOLI])</td></tr>
| + | |
| - | <tr id='activity'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Activity:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ketol-acid_reductoisomerase Ketol-acid reductoisomerase], with EC number [https://www.brenda-enzymes.info/php/result_flat.php4?ecno=1.1.1.86 1.1.1.86] </span></td></tr>
| + | |
| | <tr id='resources'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Resources:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=3ulk FirstGlance], [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocaids?id=3ulk OCA], [https://pdbe.org/3ulk PDBe], [https://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=3ulk RCSB], [https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbsum/3ulk PDBsum], [https://prosat.h-its.org/prosat/prosatexe?pdbcode=3ulk ProSAT]</span></td></tr> | | <tr id='resources'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Resources:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=3ulk FirstGlance], [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocaids?id=3ulk OCA], [https://pdbe.org/3ulk PDBe], [https://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=3ulk RCSB], [https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbsum/3ulk PDBsum], [https://prosat.h-its.org/prosat/prosatexe?pdbcode=3ulk ProSAT]</span></td></tr> |
| | </table> | | </table> |
| | + | == Function == |
| | + | [https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/ILVC_ECOLI ILVC_ECOLI] |
| | <div style="background-color:#fffaf0;"> | | <div style="background-color:#fffaf0;"> |
| | == Publication Abstract from PubMed == | | == Publication Abstract from PubMed == |
| Line 28: |
Line 27: |
| | __TOC__ | | __TOC__ |
| | </StructureSection> | | </StructureSection> |
| - | [[Category: Ecoli]] | + | [[Category: Escherichia coli K-12]] |
| - | [[Category: Ketol-acid reductoisomerase]]
| + | |
| | [[Category: Large Structures]] | | [[Category: Large Structures]] |
| - | [[Category: Guddat, L W]] | + | [[Category: Guddat LW]] |
| - | [[Category: Lonhienne, T G.A]] | + | [[Category: Lonhienne TGA]] |
| - | [[Category: Schenk, G]] | + | [[Category: Schenk G]] |
| - | [[Category: Winzor, D J]] | + | [[Category: Winzor DJ]] |
| - | [[Category: Wong, S H]] | + | [[Category: Wong SH]] |
| - | [[Category: Acetolactate]]
| + | |
| - | [[Category: Branched-chain amino acid biosynthesis]]
| + | |
| - | [[Category: Oxidoreductase]]
| + | |
| - | [[Category: Reductoisomerase]]
| + | |
| - | [[Category: Rossmann fold]]
| + | |
| Structural highlights
Function
ILVC_ECOLI
Publication Abstract from PubMed
Ketol-acid reductoisomerase (KARI) is the second enzyme in the branched-chain amino acid biosynthesis pathway, which is found in plants, fungi and bacteria but not in animals. This difference in metabolism between animals and microorganisms makes KARI an attractive target for the development of antimicrobial agents. Herein we report the crystal structure of Escherichia coli KARI in complex with Mg(2+) and NADPH at 2.3A resolution. Ultracentrifugation studies confirm that the enzyme exists as a tetramer in solution, and isothermal titration calorimetry shows that the binding of Mg(2+) increases structural disorder while the binding of NADPH increases the structural rigidity of the enzyme. Comparison of the structure of the E. coli KARI-Mg(2+)-NADPH complex with that of enzyme in the absence of cofactors shows that the binding of Mg(2+) and NADPH opens the interface between the N- and C-domains, thereby allowing access for the substrates to bind: the existence of only a small opening between the domains in the crystal structure of the unliganded enzyme signifies restricted access to the active site. This observation contrasts with that in the plant enzyme, where the N-domain can rotate freely with respect to the C-domain until the binding of Mg(2+) and/or NADPH stabilizes the relative positions of these domains. Support is thereby provided for the idea that plant and bacterial KARIs have evolved different mechanisms of induced fit to prepare the active site for catalysis.
Bacterial and Plant Ketol-Acid Reductoisomerases Have Different Mechanisms of Induced Fit during the Catalytic Cycle.,Wong SH, Lonhienne TG, Winzor DJ, Schenk G, Guddat LW J Mol Biol. 2012 Oct 2. pii: S0022-2836(12)00783-8. doi:, 10.1016/j.jmb.2012.09.018. PMID:23036858[1]
From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine.
See Also
References
- ↑ Wong SH, Lonhienne TG, Winzor DJ, Schenk G, Guddat LW. Bacterial and Plant Ketol-Acid Reductoisomerases Have Different Mechanisms of Induced Fit during the Catalytic Cycle. J Mol Biol. 2012 Oct 2. pii: S0022-2836(12)00783-8. doi:, 10.1016/j.jmb.2012.09.018. PMID:23036858 doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2012.09.018
|