This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
User:Ann Taylor/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | |||
--> | --> | ||
{{STRUCTURE_1d66| PDB=1d66 | SCENE= }} | {{STRUCTURE_1d66| PDB=1d66 | SCENE= }} | ||
| Line 9: | Line 8: | ||
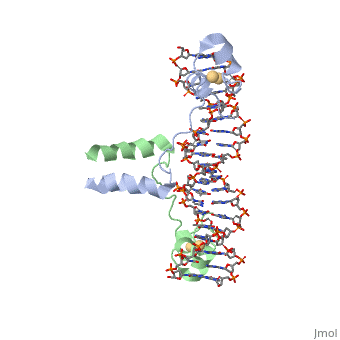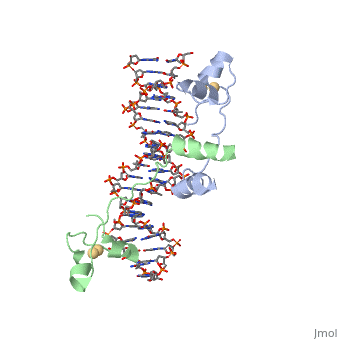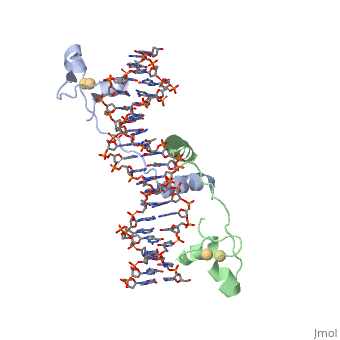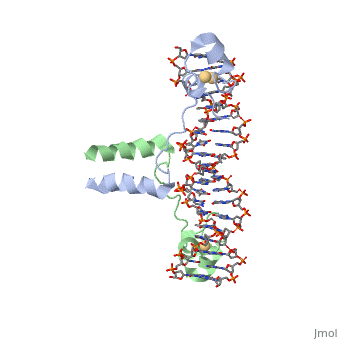
==Dimer== | ==Dimer== | ||
| + | The protein binds as a <scene name='92/925552/Dimer/1'>dimer</scene> to a symmetrical 17-base-pair sequence. | ||
The protein binds as a <scene name='92/925538/Dimer/2'>dimer</scene> to a symmetrical 17-base-pair sequence. | The protein binds as a <scene name='92/925538/Dimer/2'>dimer</scene> to a symmetrical 17-base-pair sequence. | ||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
There is a compact <scene name='92/925538/Metal_binding_domain/5'>metal binding domain</scene> (residues 8-40), an <scene name='92/925538/Extended_linker/4'>extended linker</scene> (41-49), and an <scene name='92/925538/Alpha-helical_dimerization/2'>alpha-helical dimerization element</scene> (50-64). | There is a compact <scene name='92/925538/Metal_binding_domain/5'>metal binding domain</scene> (residues 8-40), an <scene name='92/925538/Extended_linker/4'>extended linker</scene> (41-49), and an <scene name='92/925538/Alpha-helical_dimerization/2'>alpha-helical dimerization element</scene> (50-64). | ||
| - | + | Each subunit fold into three distinct modules: a compact, <scene name='92/925552/Metal_binding_domain/1'>metal binding domain</scene> (residues 8-40), an <scene name='92/925552/Extended_linker/1'>extended linker</scene> (41-49), and an <scene name='92/925552/Alpha-helical_dimerization/1'>alpha-helical dimerization</scene> element (50-64). | |
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
A small, Zn(2+)-containing domain recognizes a conserved CCG triplet at each end of the site through direct contacts with the major groove. The metal binding domain contains <scene name='92/925538/Cysteine_metal_binding/3'>cysteine residues</scene> that coordinate to the metal as shown as cadmium. | A small, Zn(2+)-containing domain recognizes a conserved CCG triplet at each end of the site through direct contacts with the major groove. The metal binding domain contains <scene name='92/925538/Cysteine_metal_binding/3'>cysteine residues</scene> that coordinate to the metal as shown as cadmium. | ||
| - | + | The cadmium is coordinated to this domain via interactions with several <scene name='92/925552/Cysteine_coordination_sites/1'>cysteine residues</scene>. | |
==DNA/protein interaction== | ==DNA/protein interaction== | ||
| - | + | Gal4 also contains an upstream activating sequence (<scene name='92/925552/Uas/1'>UAS</scene>) adjacent to that of the promoter region. This sequence works much like an enhancer regions that are common in Eukaryotic genes. | |
| + | |||
| + | <scene name='92/925538/Dna_protein_interaction/3'>The DNA-Protein Interaction</scene> with all of the base pairs within 5 angstroms of the protein highlighted illustrates that the protein interacts with both strands of the UAS. | ||
Revision as of 02:46, 22 September 2022
-->
| |||||||||
| 1d66, resolution 2.70Å () | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligands: | |||||||||
| |||||||||
| |||||||||
| Resources: | FirstGlance, OCA, RCSB, PDBsum | ||||||||
| Coordinates: | save as pdb, mmCIF, xml | ||||||||
Contents |
Evaluating scenes representing the same structure
This sandbox compiles several student-generated scenes that illustrate properties of the Gal4 repressor.
Dimer
The protein binds as a to a symmetrical 17-base-pair sequence. The protein binds as a to a symmetrical 17-base-pair sequence.
Domains
There is a compact (residues 8-40), an (41-49), and an (50-64).
Each subunit fold into three distinct modules: a compact, (residues 8-40), an (41-49), and an element (50-64).
Metal binding
A small, Zn(2+)-containing domain recognizes a conserved CCG triplet at each end of the site through direct contacts with the major groove. The metal binding domain contains that coordinate to the metal as shown as cadmium.
The cadmium is coordinated to this domain via interactions with several .
DNA/protein interaction
Gal4 also contains an upstream activating sequence () adjacent to that of the promoter region. This sequence works much like an enhancer regions that are common in Eukaryotic genes.
with all of the base pairs within 5 angstroms of the protein highlighted illustrates that the protein interacts with both strands of the UAS.