Sandbox reserved 1752
From Proteopedia
| Line 63: | Line 63: | ||
<Structure load='4g7O' size='350' frame='true' align='right' caption='Insert caption here' scene='Insert optional scene name here' /> | <Structure load='4g7O' size='350' frame='true' align='right' caption='Insert caption here' scene='Insert optional scene name here' /> | ||
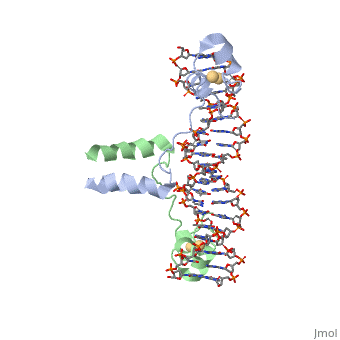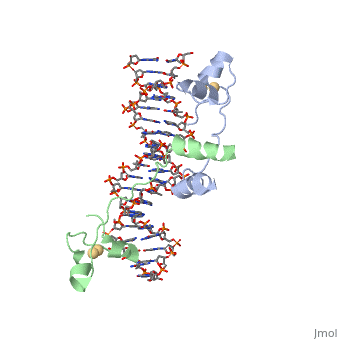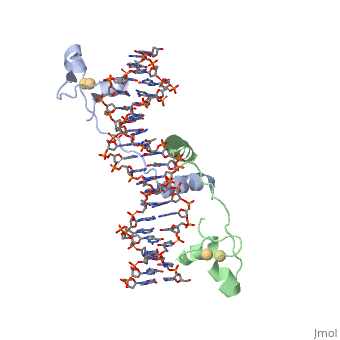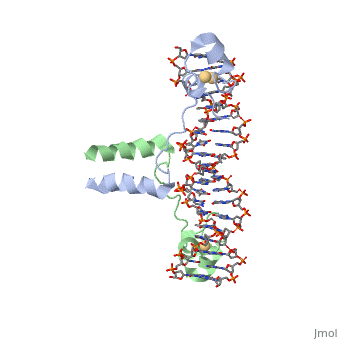
| - | UvrD, also known as Helicase II, is one of many components responsible in repairing DNA damage. UvrD is involved in nucleotide excision repair (NER) and transcription-coupled DNA repair (TCR repair). TCR repair occurs during transcription when Helicase II binds to a RNA polymerase (RNAP) and slides backwards in order to fix the mismatched nucleotide. One of the main structural components of how UvrD binds to RNAP is by having a Tudor-domain like fold. This helps better explain the UvrD-RNAP interaction, which is a better explanation than just having nucleic-acid affinity. A main cause in damage to DNA, which requires for nucleotide excision repair is from UV radiation, which can come from multiple sources, including sunlight and UV light from tanning beds. | + | <scene name='92/925553/Uvrd/1'>UvrD</scene>, also known as Helicase II, is one of many components responsible in repairing DNA damage. UvrD is involved in nucleotide excision repair (NER) and transcription-coupled DNA repair (TCR repair). TCR repair occurs during transcription when Helicase II binds to a RNA polymerase (RNAP) and slides backwards in order to fix the mismatched nucleotide. One of the main structural components of how UvrD binds to RNAP is by having a Tudor-domain like fold. This helps better explain the UvrD-RNAP interaction, which is a better explanation than just having nucleic-acid affinity. A main cause in damage to DNA, which requires for nucleotide excision repair is from UV radiation, which can come from multiple sources, including sunlight and UV light from tanning beds. |
== UvrD Binding Site for DNA == | == UvrD Binding Site for DNA == | ||
Revision as of 03:34, 4 October 2022
Contents |
DNA RECOGNITION BY GAL4: STRUCTURE OF A PROTEIN/DNA COMPLEX
| |||||||||||
UvrD
|
, also known as Helicase II, is one of many components responsible in repairing DNA damage. UvrD is involved in nucleotide excision repair (NER) and transcription-coupled DNA repair (TCR repair). TCR repair occurs during transcription when Helicase II binds to a RNA polymerase (RNAP) and slides backwards in order to fix the mismatched nucleotide. One of the main structural components of how UvrD binds to RNAP is by having a Tudor-domain like fold. This helps better explain the UvrD-RNAP interaction, which is a better explanation than just having nucleic-acid affinity. A main cause in damage to DNA, which requires for nucleotide excision repair is from UV radiation, which can come from multiple sources, including sunlight and UV light from tanning beds.