Sandbox reserved 1752
From Proteopedia
| Line 75: | Line 75: | ||
== UvrD Tudor-Domain == | == UvrD Tudor-Domain == | ||
| + | What is a Tudor Domain? | ||
| + | It is a methyl-lysine and methyl arginine binding domain present in proteins. | ||
| + | <scene name='92/925553/Tudor_domain/1'>Tudor Domain</scene> | ||
Revision as of 15:51, 4 October 2022
Contents |
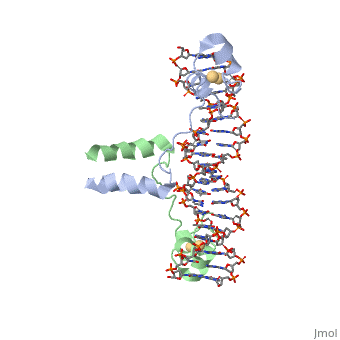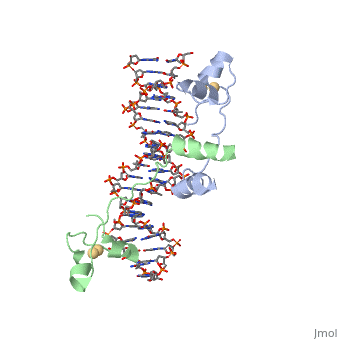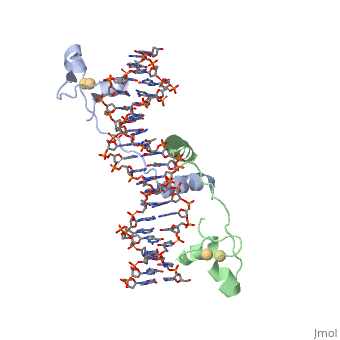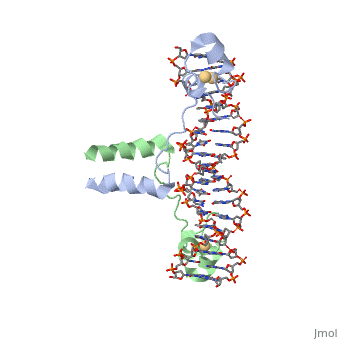
DNA RECOGNITION BY GAL4: STRUCTURE OF A PROTEIN/DNA COMPLEX
| |||||||||||
UvrD
|
, also known as Helicase II, is one of many components responsible in repairing DNA damage. UvrD is involved in nucleotide excision repair (NER) and transcription-coupled DNA repair (TCR repair). TCR repair occurs during transcription when Helicase II binds to a RNA polymerase (RNAP) and slides backwards in order to fix the mismatched nucleotide. One of the main structural components of how UvrD binds to RNAP is by having a Tudor-domain like fold. This helps better explain the UvrD-RNAP interaction, which is a better explanation than just having nucleic-acid affinity. A main cause in damage to DNA, which requires for nucleotide excision repair is from UV radiation, which can come from multiple sources, including sunlight and UV light from tanning beds.
UvrD Binding Site for DNA
UvrD Binding Site for RNAP
UvrD-dependent binding for RNA polymerase is necessary for the backtracking over DNA to repair the mismatched nucleotide. The C-terminal Domain or CTD is an important structure that is thought of to be an important in the interaction between UvrD and RNAP.
UvrD Tudor-Domain
What is a Tudor Domain? It is a methyl-lysine and methyl arginine binding domain present in proteins.