We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Gluconeogenesis
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
[by [[Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase]]] <scene name='39/392339/Cv1/8'>phosphoenolpyruvate</scene> (PEP) => ... => <scene name='39/392339/Cv/3'>Glucose</scene> | [by [[Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase]]] <scene name='39/392339/Cv1/8'>phosphoenolpyruvate</scene> (PEP) => ... => <scene name='39/392339/Cv/3'>Glucose</scene> | ||
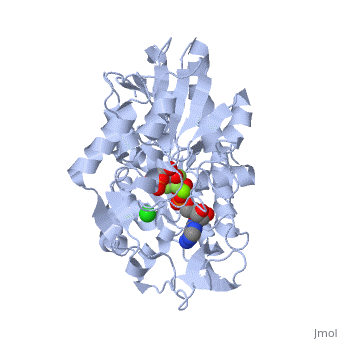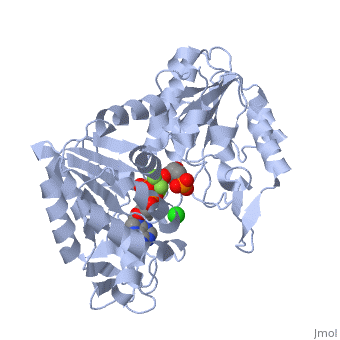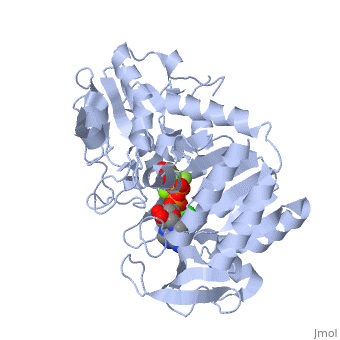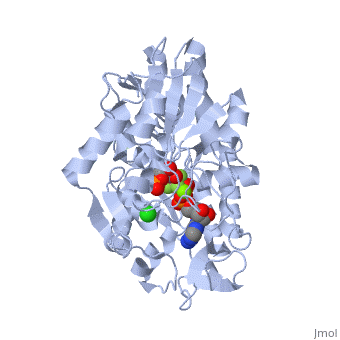
| - | + | The location of the enzyme that links these two parts of gluconeogenesis by converting oxaloacetate to PEP – [[PEP carboxykinase]] (PEPCK) – is variable by species: it can be found entirely within the mitochondria, entirely within the cytosol, or dispersed evenly between the two, as it is in humans. ''E. coli'' GTP-driven PEPCK <scene name='54/540171/Cv/9'>active site</scene> is located in a pocket at the enzyme surface<ref>PMID:11851336</ref>. Water molecules are shown as red spheres. | |
'''Fatty acids''' | '''Fatty acids''' | ||
Revision as of 15:16, 27 November 2022
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Dunten P, Belunis C, Crowther R, Hollfelder K, Kammlott U, Levin W, Michel H, Ramsey GB, Swain A, Weber D, Wertheimer SJ. Crystal structure of human cytosolic phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase reveals a new GTP-binding site. J Mol Biol. 2002 Feb 15;316(2):257-64. PMID:11851336 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1006/jmbi.2001.5364