We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Glycogenesis
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
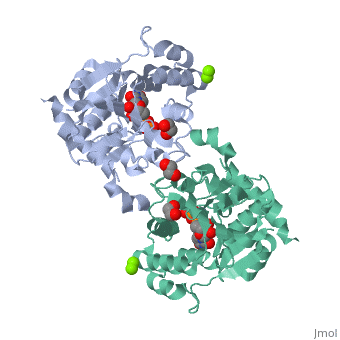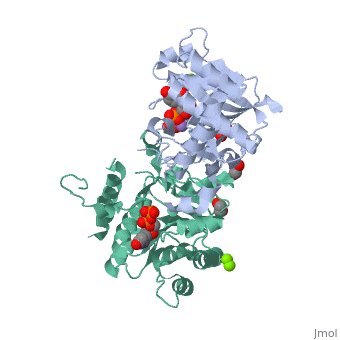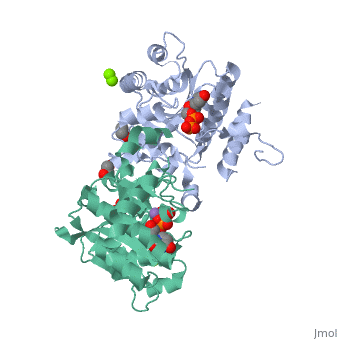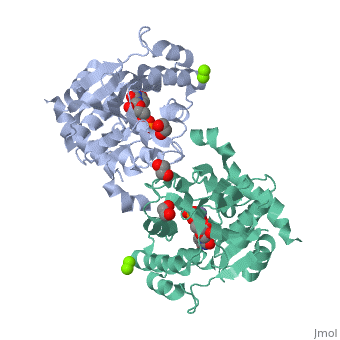
| - | <StructureSection load=' | + | <StructureSection load='3rmv' size='350' side='right' scene='' caption='Human glycogenin-1 complex with UDP, ethanediol, Mg+2 (green) and Mn+2 (purple) ions (PDB code [[3rmv]])'> |
Glycogenesis is the process of glycogen synthesis, in which glucose molecules are added to chains of glycogen for storage. This process is activated during rest periods following the [[Cori cycle]], in the liver, and also activated by [[insulin]] in response to high glucose levels. | Glycogenesis is the process of glycogen synthesis, in which glucose molecules are added to chains of glycogen for storage. This process is activated during rest periods following the [[Cori cycle]], in the liver, and also activated by [[insulin]] in response to high glucose levels. | ||
Revision as of 12:07, 18 December 2022
| |||||||||||