This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
Sandbox Reserved 1790
From Proteopedia
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | {{ | + | {{BAMBED |
| - | == | + | |DATE=June 14, 2016 |
| - | + | |OLDID=2607465 | |
| - | + | |BAMBEDDOI=10.1002/bmb.21026 | |
| - | + | }} | |
| + | |||
| + | ==Lysophosphatidic Acid Receptor 1== | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | == Introduction == | ||
| + | '''Lysophosphatidic Acid Receptor''' | ||
| + | *[[Lipid signaling]] | ||
| + | *[[Transmembrane (cell surface) receptors]] | ||
| + | |||
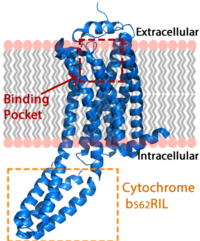
| + | [[Image:LPA_in_membrane4.fw.png|200px|center|thumb|'''Figure 1:''' LPA receptor (blue) bound to the cell membrane. The binding pocket is highlighted in red. The added bRIL protein is highlighted in orange.]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Lysophosphatidic Acid == | ||
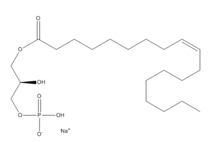
| + | [[Image:LPA.png|220px|left|thumb|'''Figure 2:''' Chemical Structure of LPA (monoacyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphate)]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | == Structure == | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | === Structural Stabilization === | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | === Key Ligand Interactions === | ||
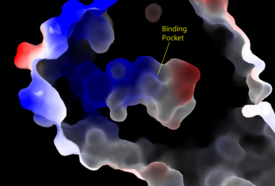
| + | [[Image:Amphbindingfinal.png|275 px|right|thumb|'''Figure 3''': Electrostatic illustration of the amphipathic binding pocket of the LPA<sub>1</sub> receptor. This binding pocket was revealed by cutting away the exterior or the protein. This binding pocket, located in the interior of the protein, has both polar and nonpolar regions. The blue and red coloration highlight the positively and negatively charged regions, respectively, and the white color shows the nonpolar region of the binding pocket.]] | ||
| + | |||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
| - | == | + | == Receptor Comparison == |
| - | == | + | === Sphingosine 1-Phosphate Receptor === |
| - | == Structural highlights == | ||
| - | This is a sample scene created with SAT to <scene name="/12/3456/Sample/1">color</scene> by Group, and another to make <scene name="/12/3456/Sample/2">a transparent representation</scene> of the protein. You can make your own scenes on SAT starting from scratch or loading and editing one of these sample scenes. | ||
| - | </ | + | |
| + | === Endocannabinoid Receptor 1 === | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | == Disease Relevance == | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | === Cancer === | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ===Pain=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | === Fibrosis === | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ==3D structures of lysophosphatidic acid receptor== | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[4z34]], [[4z35]], [[4z36]] - hLPA1 + antagonist - human<br /> | ||
| + | [[2lq4]] – hLPA1 second extracellular loop – NMR<br /> | ||
| + | [[4p0c]] – hLPA2/NHERF2<br /> | ||
| + | [[5xsz]] – LPA6A (mutant) – zebra fish<br /> | ||
| + | |||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
| + | ==Proteopedia Resources== | ||
| + | [http://proteopedia.org/wiki/index.php/Category:Lysophosphatidic_acid_binding Category:Lysophosphatidic acid binding] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [http://proteopedia.org/wiki/index.php/Category:Lysophosphatidic_acid Category:Lysophosphatidic acid] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [http://proteopedia.org/wiki/index.php/User:R._Jeremy_Johnson/CH462:Biochemistry_II_Butler_University Butler University Proteopedia Pages] | ||
| + | |||
| + | See also: | ||
| + | *[[Receptor]] | ||
| + | *[[Transmembrane (cell surface) receptors]] | ||
| + | *[[G protein-coupled receptors]] | ||
| + | </StructureSection> | ||
| + | ==Student Contributors== | ||
| + | Heather Hansen | ||
| + | |||
| + | Stephanie Kuhlman | ||
| + | |||
| + | Chandler Mitchell | ||
| + | |||
| + | Clayton Taylor | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:Featured in BAMBED]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Topic Page]] | ||
Revision as of 16:32, 17 March 2023
This page, as it appeared on June 14, 2016, was featured in this article in the journal Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Education.
Contents |
Lysophosphatidic Acid Receptor 1
Introduction
Lysophosphatidic Acid Receptor
Lysophosphatidic Acid
Structure
Structural Stabilization
Key Ligand Interactions
Function
Receptor Comparison
Sphingosine 1-Phosphate Receptor
Endocannabinoid Receptor 1
Disease Relevance
Cancer
Pain
Fibrosis
3D structures of lysophosphatidic acid receptor
4z34, 4z35, 4z36 - hLPA1 + antagonist - human
2lq4 – hLPA1 second extracellular loop – NMR
4p0c – hLPA2/NHERF2
5xsz – LPA6A (mutant) – zebra fish
References
Proteopedia Resources
Category:Lysophosphatidic acid binding
Category:Lysophosphatidic acid
Butler University Proteopedia Pages
See also:
</StructureSection>
Student Contributors
Heather Hansen
Stephanie Kuhlman
Chandler Mitchell
Clayton Taylor