This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
Sandbox Reserved 1790
From Proteopedia
| Line 37: | Line 37: | ||
== Signaling Pathway == | == Signaling Pathway == | ||
| - | + | [[Image:Dephosphorylation.png|380 px|thumb|center|'''Figure 1:'''Comparison of Delta-opioid receptor to human free-fatty acid receptor (hGPR40) both of which are G-protein coupled receptors. The binding pocket of the delta-opioid receptor is solvent exposed allowing ligands to enter directly from the extracellular space while the binding pocket of hGPR40 is covered by the extracellular loop 2 (ECL2) preventing entry from the extracellular space (ECL2 represented in cyan). The Delta-opioid displays the canonical binding site typical of most GPCRs while ligands of hGPR40 bind to a noncanonical pocket represented in pink.]] | |
Revision as of 17:06, 17 March 2023
This page, as it appeared on June 14, 2016, was featured in this article in the journal Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Education.
Contents |
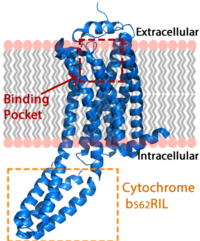
SHOC2-PP1C-MRAS
Introduction
Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Receptor
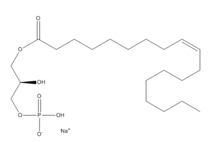
Lysophosphatidic Acid
Overall Structure
SHOC2
PP1C
MRAS
Key Ligand Interactions
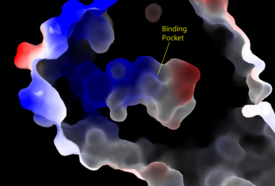
SHOC2 and PP1C
SHOC2 and MRAS
PP1C and MRAS
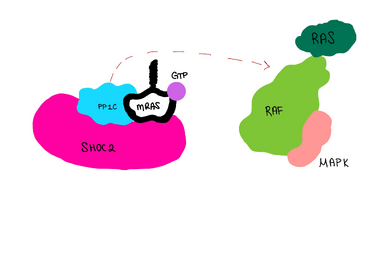
Signaling Pathway
Disease Relevance
Cancer
RASopathies
Future Studies
3D structures of lysophosphatidic acid receptor
4z34, 4z35, 4z36 - hLPA1 + antagonist - human
2lq4 – hLPA1 second extracellular loop – NMR
4p0c – hLPA2/NHERF2
5xsz – LPA6A (mutant) – zebra fish
References
Proteopedia Resources
Category:Lysophosphatidic acid binding
Category:Lysophosphatidic acid
Butler University Proteopedia Pages
See also:
</StructureSection>
Student Contributors
Madeline Gilbert Inaya Patel Rushda Hussein