This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
Sandbox Reserved 1781
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
== Structure == | == Structure == | ||
===Overview=== | ===Overview=== | ||
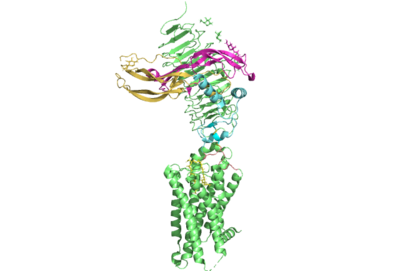
| - | The thyrotropin receptor has an extracellular domain (ECD) that is composed of a <scene name='95/952709/Lrrd_real/2'>leucine rich repeat domain (LRRD)</scene> as well as a hinge region. This <scene name='95/952709/Hinge_region_real/2'>hinge region</scene> links the ECD to the seven transmembrane helices <scene name='95/952709/7tm_helices/4'>(7TM domain)</scene>, which span from the extracellular domain to the intracellular domain <ref name= "Keinau et al."> | + | The thyrotropin receptor has an extracellular domain (ECD) that is composed of a <scene name='95/952709/Lrrd_real/2'>leucine rich repeat domain (LRRD)</scene> as well as a hinge region. This <scene name='95/952709/Hinge_region_real/2'>hinge region</scene> links the ECD to the seven transmembrane helices <scene name='95/952709/7tm_helices/4'>(7TM domain)</scene>, which span from the extracellular domain to the intracellular domain <ref name= "Keinau et al.">Kleinau, G., Worth, C. L., Kreuchwig, A., Biebermann, H., Marcinkowski, P., Scheerer, P., & Krause, G. (2017). Structural–functional features of the thyrotropin receptor: A class A G-protein-coupled receptor at work. Frontiers in Endocrinology, 8. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2017.00086</ref>. When thyrotropin or an autoantibody binds, it causes a conformational change in the receptor through the transmembrane helices. This causes the thyrotropin receptor to interact differently with its respective <scene name='95/952709/G_protein/2'>G-protein</scene> when in the active and inactive states. |
| + | ===Hinge Region=== | ||
| + | Several parts of TSHR are very important for the functioning of TSH signaling. The <scene name='95/952709/Hinge_region_real/2'>hinge region</scene> is a scaffold for the attachment of the ECD to the 7TMD. Also, this region, has been found to have impact on the binding potency of TSH as well as intracellular cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) levels, which are partially mediated by the activation of the GPCR. Several features of this region have been found to be crucial to the potent activation of of the TSHR by TSH.<ref name="Mizutori et al.">Yumiko Mizutori, Chun-Rong Chen, Sandra M. McLachlan, Basil Rapoport, The Thyrotropin Receptor Hinge Region Is Not Simply a Scaffold for the Leucine-Rich Domain but Contributes to Ligand Binding and Signal Transduction, Molecular Endocrinology, Volume 22, Issue 5, 1 May 2008, Pages 1171–1182, https://doi.org/10.1210/me.2007-0407</ref>. This being said, the region is not required for the activation of the receptor. In many of the aforementioned misregulations of thyroid hormone release, auto-antibodies are responsible. These auto-antibodies bind to the receptor through alternative interactions which cause conformational changes to the 7TMD without any need for a conformational change or extensive interactions with the hinge region. This is supported by the fact that select autoantibodies are able to bind to the activate the receptor without any contacts. | ||
===7 Transmembrane Helices=== | ===7 Transmembrane Helices=== | ||
The thyrotropin receptor is anchored to the membrane through seven transmembrane helices which is characteristic of | The thyrotropin receptor is anchored to the membrane through seven transmembrane helices which is characteristic of | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
== Relevance == | == Relevance == | ||
<scene name='95/952709/Interactions_with_thyrotropin/1'>Glu 98 and Asp 91</scene> | <scene name='95/952709/Interactions_with_thyrotropin/1'>Glu 98 and Asp 91</scene> | ||
Revision as of 19:00, 29 March 2023
| This Sandbox is Reserved from February 27 through August 31, 2023 for use in the course CH462 Biochemistry II taught by R. Jeremy Johnson at the Butler University, Indianapolis, USA. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1765 through Sandbox Reserved 1795. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
Your Heading Here (maybe something like 'Structure')
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Hanson, R. M., Prilusky, J., Renjian, Z., Nakane, T. and Sussman, J. L. (2013), JSmol and the Next-Generation Web-Based Representation of 3D Molecular Structure as Applied to Proteopedia. Isr. J. Chem., 53:207-216. doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/ijch.201300024
- ↑ Herraez A. Biomolecules in the computer: Jmol to the rescue. Biochem Mol Biol Educ. 2006 Jul;34(4):255-61. doi: 10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644. PMID:21638687 doi:10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644
- ↑ Yen PM. Physiological and molecular basis of thyroid hormone action. Physiol Rev. 2001 Jul;81(3):1097-142. doi: 10.1152/physrev.2001.81.3.1097. PMID: 11427693.
- ↑ Duan J, Xu P, Luan X, Ji Y, He X, Song N, Yuan Q, Jin Y, Cheng X, Jiang H, Zheng J, Zhang S, Jiang Y, Xu HE. Hormone- and antibody-mediated activation of the thyrotropin receptor. Nature. 2022 Aug 8. pii: 10.1038/s41586-022-05173-3. doi:, 10.1038/s41586-022-05173-3. PMID:35940204 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41586-022-05173-3
- ↑ Kohn LD, Shimura H, Shimura Y, Hidaka A, Giuliani C, Napolitano G, Ohmori M, Laglia G, Saji M. The thyrotropin receptor. Vitam Horm. 1995;50:287-384. doi: 10.1016/s0083-6729(08)60658-5. PMID: 7709602.
- ↑ Kleinau, G., Worth, C. L., Kreuchwig, A., Biebermann, H., Marcinkowski, P., Scheerer, P., & Krause, G. (2017). Structural–functional features of the thyrotropin receptor: A class A G-protein-coupled receptor at work. Frontiers in Endocrinology, 8. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2017.00086
- ↑ Yumiko Mizutori, Chun-Rong Chen, Sandra M. McLachlan, Basil Rapoport, The Thyrotropin Receptor Hinge Region Is Not Simply a Scaffold for the Leucine-Rich Domain but Contributes to Ligand Binding and Signal Transduction, Molecular Endocrinology, Volume 22, Issue 5, 1 May 2008, Pages 1171–1182, https://doi.org/10.1210/me.2007-0407