We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 1794
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
== Introduction == | == Introduction == | ||
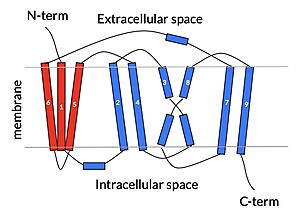
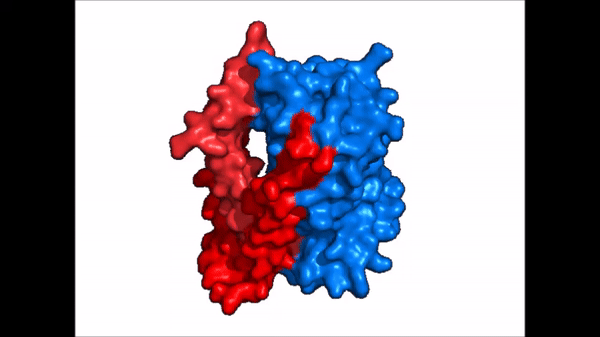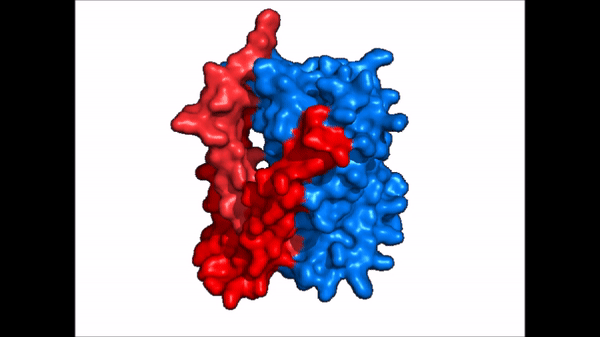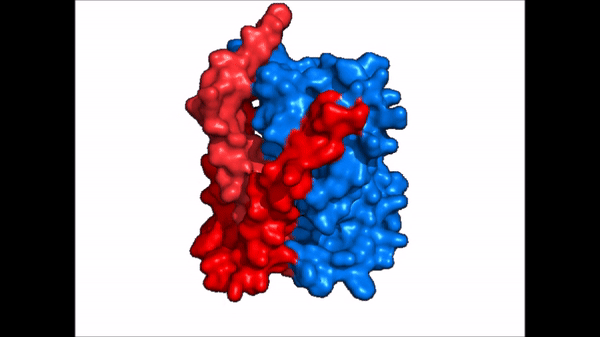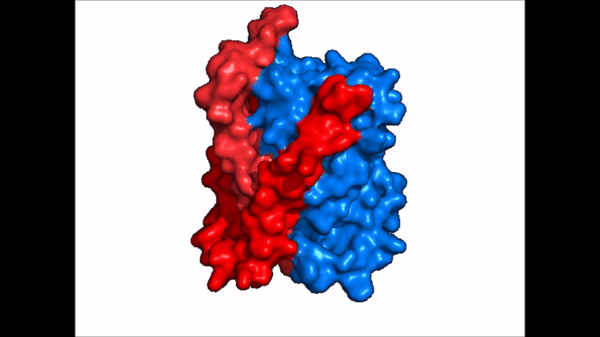
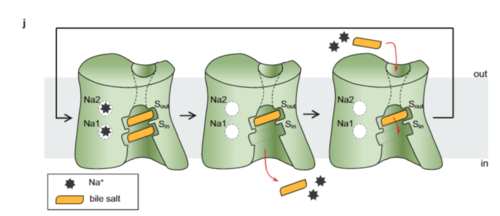
| - | Sodium Taurocholate Co-Transporting Polypeptide, or NTCP, is a [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Membrane_transport_protein membrane transporter protein] that is found in the plasma membrane of liver cells, or [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hepatocyte hepatocytes]. NTCP's primary function is the transportation of taurocholates, or '''bile salts''', into the liver and out of the liver to the small intestine <Ref> Stieger B. The role of the sodium-taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide (NTCP) and of the bile salt export pump (BSEP) in physiology and pathophysiology of bile formation. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2011;(201):205-59. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-14541-4_5. PMID: 21103971. [https://dx.doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-14541-4_5 DOI: DOI: 10.1007/978-3-642-14541-4_5]. </Ref> Bile salts play various roles in metabolism and digestion, but their main function is the emulsification of lipid droplets into smaller fragments so that lipases are able to break down the droplets into their monomers, or triglycerides. NTCP is part of the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Solute_carrier_family solute carrier superfamily], more specifically SLC10. NTCP is the founding member of the SLC10 family, first discovered in rat hepatocytes in 1978 <ref name = "SLC10"> | + | Sodium Taurocholate Co-Transporting Polypeptide, or NTCP, is a [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Membrane_transport_protein membrane transporter protein] that is found in the plasma membrane of liver cells, or [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hepatocyte hepatocytes]. NTCP's primary function is the transportation of taurocholates, or '''bile salts''', into the liver and out of the liver to the small intestine <Ref> Stieger B. The role of the sodium-taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide (NTCP) and of the bile salt export pump (BSEP) in physiology and pathophysiology of bile formation. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2011;(201):205-59. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-14541-4_5. PMID: 21103971. [https://dx.doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-14541-4_5 DOI: DOI: 10.1007/978-3-642-14541-4_5]. </Ref> Bile salts play various roles in metabolism and digestion, but their main function is the emulsification of lipid droplets into smaller fragments so that lipases are able to break down the droplets into their monomers, or triglycerides. NTCP is part of the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Solute_carrier_family solute carrier superfamily], more specifically SLC10. NTCP is the founding member of the SLC10 family, first discovered in rat hepatocytes in 1978 <ref name = "SLC10"> Geyer, J., Wilke, T. & Petzinger, E. The solute carrier family SLC10: more than a family of bile acid transporters regarding function and phylogenetic relationships. Naunyn Schmied Arch Pharmacol 372, 413–431 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-006-0043-8 </ref> NTCP has a key role in [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Enterohepatic_circulation Enterohepatic circulation], and it's unique ability to transport other solutes lends it therapeutic potential for lowering cholesterol and [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Liver_disease liver disease]. |
NTCP also serves as a binding site for [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hepatitis_B hepatitis B virus] and [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hepatitis_D hepatitis d virus] <ref name = "Park"> Park, JH., Iwamoto, M., Yun, JH. et al. Structural insights into the HBV receptor and bile acid transporter NTCP. Nature 606, 1027–1031 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-022-04857-0. </ref> Future studies into HBV binding mechanism can help understand infection pathways and the development of viral inhibitors. | NTCP also serves as a binding site for [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hepatitis_B hepatitis B virus] and [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hepatitis_D hepatitis d virus] <ref name = "Park"> Park, JH., Iwamoto, M., Yun, JH. et al. Structural insights into the HBV receptor and bile acid transporter NTCP. Nature 606, 1027–1031 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-022-04857-0. </ref> Future studies into HBV binding mechanism can help understand infection pathways and the development of viral inhibitors. | ||
Revision as of 16:02, 30 March 2023
| This Sandbox is Reserved from February 27 through August 31, 2023 for use in the course CH462 Biochemistry II taught by R. Jeremy Johnson at the Butler University, Indianapolis, USA. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1765 through Sandbox Reserved 1795. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
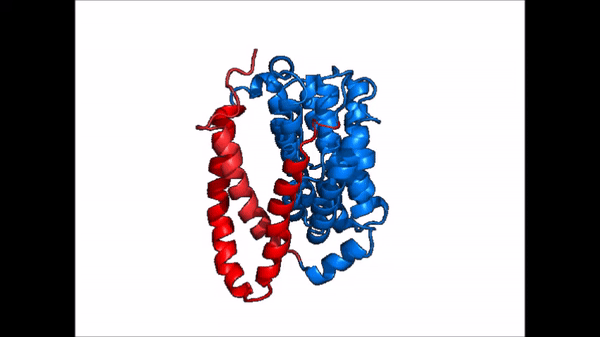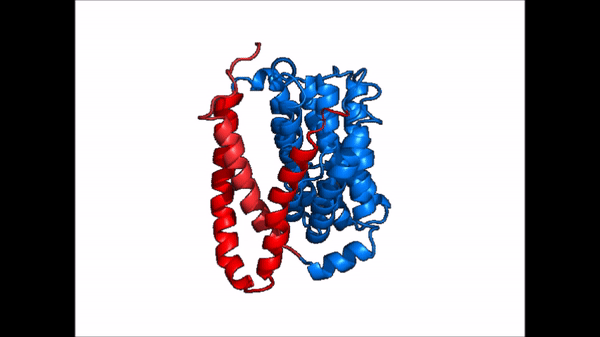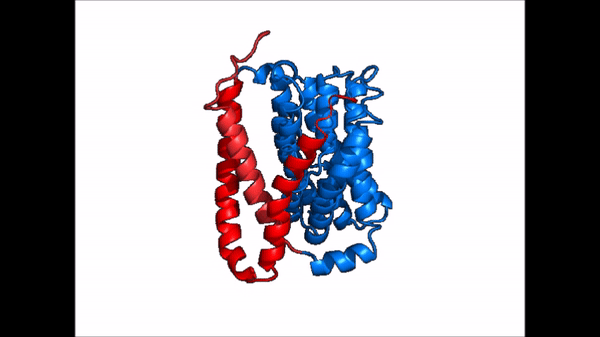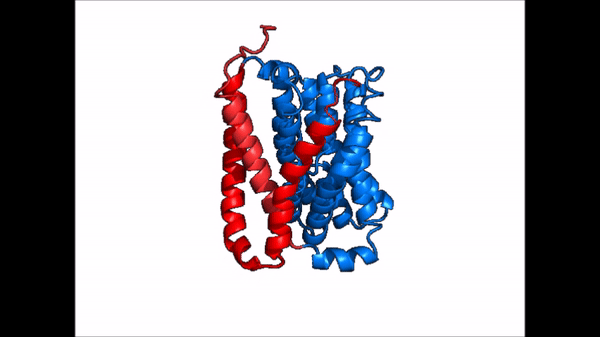
Sodium Taurocholate Co-Transporting Polypeptide
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Stieger B. The role of the sodium-taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide (NTCP) and of the bile salt export pump (BSEP) in physiology and pathophysiology of bile formation. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2011;(201):205-59. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-14541-4_5. PMID: 21103971. DOI: DOI: 10.1007/978-3-642-14541-4_5.
- ↑ Geyer, J., Wilke, T. & Petzinger, E. The solute carrier family SLC10: more than a family of bile acid transporters regarding function and phylogenetic relationships. Naunyn Schmied Arch Pharmacol 372, 413–431 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-006-0043-8
- ↑ Park, JH., Iwamoto, M., Yun, JH. et al. Structural insights into the HBV receptor and bile acid transporter NTCP. Nature 606, 1027–1031 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-022-04857-0.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Goutam, K., Ielasi, F.S., Pardon, E. et al. Structural basis of sodium-dependent bile salt uptake into the liver. Nature 606, 1015–1020 (2022). DOI: 10.1038/s41586-022-04723-z.
Student Contributers
- Isabelle White
- Lena Barko