Sandbox Reserved 1777
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
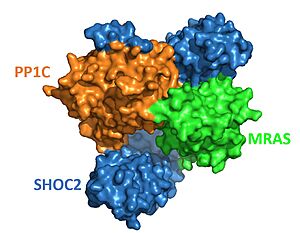
[[Image:SHOC2-PP1C-MRAS Surface.JPG|300px|right|thumb|<font size="3.5"><div style="text-align: center;">Surface representation of SHOC2-PP1C-MRAS from PDB 7pui. Blue is SHOC2, orange is PP1C and green is MRAS. </div></font>]] | [[Image:SHOC2-PP1C-MRAS Surface.JPG|300px|right|thumb|<font size="3.5"><div style="text-align: center;">Surface representation of SHOC2-PP1C-MRAS from PDB 7pui. Blue is SHOC2, orange is PP1C and green is MRAS. </div></font>]] | ||
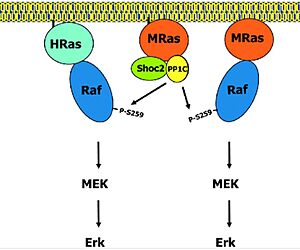
| - | The enzyme requires 3 domains (SHOC-2(blue), PP1C(coral), and MRAS (green)) to form the active enzyme (SMP Complex), also known as a holoenzyme<Ref name='Hauseman'>Hauseman, Z.J., Fodor, M., Dhembi, A. et al. Structure of the MRAS–SHOC2–PP1C phosphatase complex. Nature 609, 416–423 (2022). doi: 10.1038/s41586-022-05086-1. [https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-022-05086-1. DOI:10.1038/s41586-022-05086-1]. </Ref>. SHOC-2 is a | + | The enzyme requires 3 domains (SHOC-2(blue), PP1C(coral), and MRAS (green)) to form the active enzyme (SMP Complex), also known as a holoenzyme<Ref name='Hauseman'>Hauseman, Z.J., Fodor, M., Dhembi, A. et al. Structure of the MRAS–SHOC2–PP1C phosphatase complex. Nature 609, 416–423 (2022). doi: 10.1038/s41586-022-05086-1. [https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-022-05086-1. DOI:10.1038/s41586-022-05086-1]. </Ref>. SHOC-2 is a scaffolding protein that holds the other subunits in the correct orientation, allowing for the holoenzyme to be functional. PP1C is a catalytic domain of a phosphatase enzyme [https://proteopedia.org/wiki/index.php/Protein_phosphatase. PP1], which cleaves a phosphate. MRAS is a GTPase protein and is located near (typically just below) the cell membrane. When MRAS binds GTP, it becomes active and triggers the assembly of the active holoenzyme<ref name="Hauseman" />. The SMP complex was determined via cryo-electron microscopy as well as x-ray diffraction. These studies found that PP1C and MRAS occupy the concave surface of SHOC2, leaving the catalytic site of PP1C and the substrate binding cleft in MRAS exposed. |
==SHOC2== | ==SHOC2== | ||
Revision as of 22:46, 2 April 2023
| This Sandbox is Reserved from February 27 through August 31, 2023 for use in the course CH462 Biochemistry II taught by R. Jeremy Johnson at the Butler University, Indianapolis, USA. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1765 through Sandbox Reserved 1795. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Bernal Astrain G, Nikolova M, Smith MJ. Functional diversity in the RAS subfamily of small GTPases. Biochem Soc Trans. 2022 Apr 29;50(2):921-933. doi: 10.1042/BST20211166. DOI:10.1042/BST20211166.
- ↑ Molina JR, Adjei AA. The Ras/Raf/MAPK pathway. J Thorac Oncol. 2006 Jan;1(1):7-9. DOI:10.1016/S1556-0864(15)31506-9.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Hauseman, Z.J., Fodor, M., Dhembi, A. et al. Structure of the MRAS–SHOC2–PP1C phosphatase complex. Nature 609, 416–423 (2022). doi: 10.1038/s41586-022-05086-1. DOI:10.1038/s41586-022-05086-1.
- ↑ Daniel A. Bonsor, Patrick Alexander, Kelly Snead, Nicole Hartig, Matthew Drew, Simon Messing, Lorenzo I. Finci, Dwight V. Nissley, Frank McCormick, Dominic Esposito, Pablo Rodrigiguez-Viciana, Andrew G. Stephen, Dhirendra K. Simanshu. Structure of the SHOC2–MRAS–PP1C complex provides insights into RAF activation and Noonan syndrome. bioRxiv. 2022.05.10.491335. doi: 10.1101/2022.05.10.491335. DOI:10.1101/2022.05.10.491335.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Kwon, J.J., Hajian, B., Bian, Y. et al. Structure–function analysis of the SHOC2–MRAS–PP1C holophosphatase complex. Nature 609, 408–415 (2022).doi: 10.1038/s41586-022-04928-2. DOI:10.1038/s41586-022-04928-2.
- ↑ Liau NPD, Johnson MC, Izadi S, Gerosa L, Hammel M, Bruning JM, Wendorff TJ, Phung W, Hymowitz SG, Sudhamsu J. Structural basis for SHOC2 modulation of RAS signalling. Nature. 2022 Jun 29. pii: 10.1038/s41586-022-04838-3. doi:, 10.1038/s41586-022-04838-3. PMID:35768504 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41586-022-04838-3