This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
Sandbox Reserved 1777
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
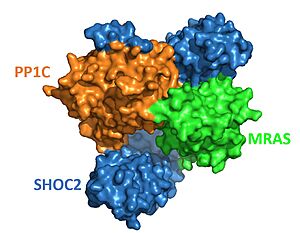
<StructureSection load='7pui' size='350' side='right' caption='SHOC2-PP1C-MRAS (PDB entry [[7pui]])' scene='95/952704/Smpcolored/1'> | <StructureSection load='7pui' size='350' side='right' caption='SHOC2-PP1C-MRAS (PDB entry [[7pui]])' scene='95/952704/Smpcolored/1'> | ||
=Introduction= | =Introduction= | ||
| - | SHOC2-PP1C-MRAS is a human enzyme that is involved in regulating cell proliferation and division<Ref name='Astrain'>Bernal Astrain G, Nikolova M, Smith MJ. Functional diversity in the RAS subfamily of small GTPases. Biochem Soc Trans. 2022 Apr 29;50(2):921-933. doi: 10.1042/BST20211166. [https://doi.org/10.1042/BST20211166. DOI:10.1042/BST20211166] </Ref> | + | SHOC2-PP1C-MRAS is a human enzyme that is involved in regulating cell proliferation and division <Ref name='Astrain'>Bernal Astrain G, Nikolova M, Smith MJ. Functional diversity in the RAS subfamily of small GTPases. Biochem Soc Trans. 2022 Apr 29;50(2):921-933. doi: 10.1042/BST20211166. [https://doi.org/10.1042/BST20211166. DOI:10.1042/BST20211166] </Ref> The enzyme is involved in the vast RAS-MAPK pathway, which is initially activated by an extracellular growth factor binding to a membrane bound RAS [https://www.mechanobio.info/what-is-mechanosignaling/what-are-small-gtpases/what-are-ras-gtpases/. GTPase.] such as HRAS, NRAS, or KRAS. RAS-GTPases are a family of proteins that work by functioning as molecular switches[https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fonc.2019.01088/full#:~:text=In%20human%20cells%2C%20three%20closely,proliferation%20and%20survival%20among%20others]. This occurs from the protein alternating between binding GTP to be active and GDP to be inactive <ref name="Astrain" />. After activation via an extracellular growth factor, the RAS-GTPase enzyme binds GTP, which activates [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6311149/#:~:text=Full%20activation%20of%20Raf%20requires,plasma%20membrane%20(Roy%20et%20al. RAF]<Ref name='Molina'>Molina JR, Adjei AA. The Ras/Raf/MAPK pathway. J Thorac Oncol. 2006 Jan;1(1):7-9. [https://doi.org/10.1016/S1556-0864(15)31506-9. DOI:10.1016/S1556-0864(15)31506-9]. </Ref> by phosphorylating the serine 259 residue. RAF triggers a series of downstream signaling pathways including MEK and ERK. The Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK pathway is a critical signaling cascade for activating transcription factors and regulating gene expression<Ref name='Li'>Li, L., Zhao, G. D., Shi, Z. et. al.The Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK signaling pathway and its role in the occurrence and development of HCC. Oncology letters, 12(5), 3045–3050. [https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2016.5110. DOI:10.3892/ol.2016.5110]. </Ref>. |
=Structure= | =Structure= | ||
Revision as of 18:07, 3 April 2023
| This Sandbox is Reserved from February 27 through August 31, 2023 for use in the course CH462 Biochemistry II taught by R. Jeremy Johnson at the Butler University, Indianapolis, USA. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1765 through Sandbox Reserved 1795. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Bernal Astrain G, Nikolova M, Smith MJ. Functional diversity in the RAS subfamily of small GTPases. Biochem Soc Trans. 2022 Apr 29;50(2):921-933. doi: 10.1042/BST20211166. DOI:10.1042/BST20211166
- ↑ Molina JR, Adjei AA. The Ras/Raf/MAPK pathway. J Thorac Oncol. 2006 Jan;1(1):7-9. DOI:10.1016/S1556-0864(15)31506-9.
- ↑ Li, L., Zhao, G. D., Shi, Z. et. al.The Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK signaling pathway and its role in the occurrence and development of HCC. Oncology letters, 12(5), 3045–3050. DOI:10.3892/ol.2016.5110.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Hauseman, Z.J., Fodor, M., Dhembi, A. et al. Structure of the MRAS–SHOC2–PP1C phosphatase complex. Nature 609, 416–423 (2022). doi: 10.1038/s41586-022-05086-1. DOI:10.1038/s41586-022-05086-1.
- ↑ Daniel A. Bonsor, Patrick Alexander, Kelly Snead, Nicole Hartig, Matthew Drew, Simon Messing, Lorenzo I. Finci, Dwight V. Nissley, Frank McCormick, Dominic Esposito, Pablo Rodrigiguez-Viciana, Andrew G. Stephen, Dhirendra K. Simanshu. Structure of the SHOC2–MRAS–PP1C complex provides insights into RAF activation and Noonan syndrome. bioRxiv. 2022.05.10.491335. doi: 10.1101/2022.05.10.491335. DOI:10.1101/2022.05.10.491335.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Kwon, J.J., Hajian, B., Bian, Y. et al. Structure–function analysis of the SHOC2–MRAS–PP1C holophosphatase complex. Nature 609, 408–415 (2022).doi: 10.1038/s41586-022-04928-2. DOI:10.1038/s41586-022-04928-2
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 Kwon, J., Jajian, B., Bian, Y. et al. Comprehensive structure-function evaluation of the SHOC2 holophosphatase reveals disease mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities. In: Proceedings of the American Association for Cancer Research Annual Meeting 2022. DOI: 10.1158/1538-7445.AM2022-LB029.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Lavoie, H., Therrien, M. Structural keys unlock RAS–MAPK cellular signalling pathway. Nature 609, 248-249 (2022). doi: 10.1038/d41586-022-02189-7. DOI:10.1038/d41586-022-02189-7.
- ↑ Liau NPD, Johnson MC, Izadi S, Gerosa L, Hammel M, Bruning JM, Wendorff TJ, Phung W, Hymowitz SG, Sudhamsu J. Structural basis for SHOC2 modulation of RAS signalling. Nature. 2022 Jun 29. pii: 10.1038/s41586-022-04838-3. doi:, 10.1038/s41586-022-04838-3. PMID:35768504 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41586-022-04838-3