Sandbox Reserved 1780
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
===M22 Agonist=== | ===M22 Agonist=== | ||
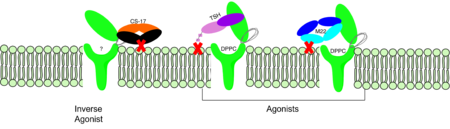
| - | <scene name='95/952708/M22_edited/ | + | <scene name='95/952708/M22_edited/3'>M22</scene> is a [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Monoclonal_antibody monoclonal antibody] that was isolated from a patient with [https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/endocrine-diseases/graves-disease Graves' Disease]. In Graves' disease, TSHR autoantibodies like M22 mimic TSH function and cause thyroid overactivity. <ref name="Miguel"> doi:10.1677/JME-08-0152</ref>. The M22 [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Autoantibody autoantibody] activates TSHR by causing a membrane clash with the ECD and cell membrane, keeping the TSHR in the active state by preventing the TSHR from rotating to the inactive state (Figure 2). This autoantibody mimics TSH action and binding to TSHR resulting in a potent activator for TSHR. <ref name="Faust"> DOI:10.1038/s41586-022-05159-1</ref> Although M22 binds in a similar manner to TSH, there is a key difference in binding between the two that can reveal the function of the hinge region (GREEN LINK). M22 does not make interactions with the hinge region when bound to TSHR, whereas TSH bound to TSHR does.<ref name="Faust"> DOI:10.1038/s41586-022-05159-1</ref> This finding shows that the hinge region is not necessary for the activation of TSHR, and leads to the discovery of other methods of activation. [[Image:Agonist pic.png|450 px|right|thumb|Figure 2: Agonist and antagonist drugs for activating or inactivating the TSHR protein.]] |
===CS-17 Inverse Agonist=== | ===CS-17 Inverse Agonist=== | ||
Revision as of 19:53, 3 April 2023
| This Sandbox is Reserved from February 27 through August 31, 2023 for use in the course CH462 Biochemistry II taught by R. Jeremy Johnson at the Butler University, Indianapolis, USA. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1765 through Sandbox Reserved 1795. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Faust B, Billesbolle CB, Suomivuori CM, Singh I, Zhang K, Hoppe N, Pinto AFM, Diedrich JK, Muftuoglu Y, Szkudlinski MW, Saghatelian A, Dror RO, Cheng Y, Manglik A. Autoantibody mimicry of hormone action at the thyrotropin receptor. Nature. 2022 Aug 8. pii: 10.1038/s41586-022-05159-1. doi:, 10.1038/s41586-022-05159-1. PMID:35940205 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41586-022-05159-1
- ↑ Nunez Miguel R, Sanders J, Chirgadze DY, Furmaniak J, Rees Smith B. Thyroid stimulating autoantibody M22 mimics TSH binding to the TSH receptor leucine rich domain: a comparative structural study of protein-protein interactions. J Mol Endocrinol. 2009 May;42(5):381-95. Epub 2009 Feb 16. PMID:19221175 doi:10.1677/JME-08-0152
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 doi: https://dx.doi.org/10.1210/en.2006-1754
- ↑ Duan J, Xu P, Luan X, Ji Y, He X, Song N, Yuan Q, Jin Y, Cheng X, Jiang H, Zheng J, Zhang S, Jiang Y, Xu HE. Hormone- and antibody-mediated activation of the thyrotropin receptor. Nature. 2022 Aug 8. pii: 10.1038/s41586-022-05173-3. doi:, 10.1038/s41586-022-05173-3. PMID:35940204 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41586-022-05173-3