This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
Sandbox Reserved 1785
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
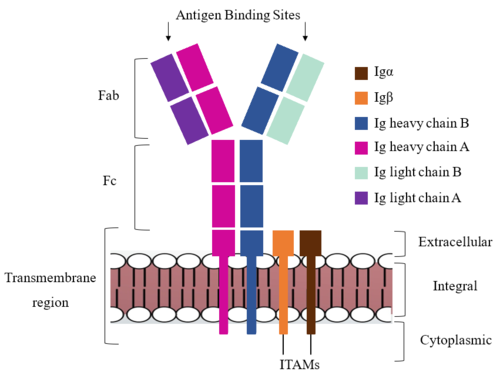
Because a conformational change occurs throughout the entirety of the IgM-BCR complex, the Fc region must be able to tolerate the contortion of the molecule as the antigen binds. In constant region two, which is located at the start of the Fc region, heavy chains A and B make a <scene name='95/952713/Disulfides/4'>disulfide bridge</scene> to stabilize the IgM-BCR and drive downstream signaling. | Because a conformational change occurs throughout the entirety of the IgM-BCR complex, the Fc region must be able to tolerate the contortion of the molecule as the antigen binds. In constant region two, which is located at the start of the Fc region, heavy chains A and B make a <scene name='95/952713/Disulfides/4'>disulfide bridge</scene> to stabilize the IgM-BCR and drive downstream signaling. | ||
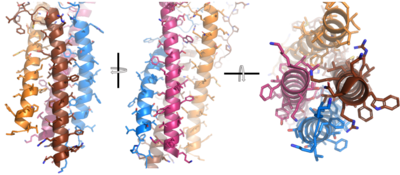
| - | To maximize the Fc region’s signal transduction efficiency and Van der Waals contacts, constant region two of heavy chain A makes an asymmetrical association with constant region three of heavy chain B to create a <scene name='95/952713/Trans_heavy/5'>heavy chain interface</scene>. More specifically, Arg243 and Arg251 residues from heavy chain A donate three hydrogen bonds to Leu433, Thr431, and Asp376 residues on heavy chain B. Furthermore, Leu313 of heavy chain A accepts a hydrogen bond from Thr429 on heavy chain B. | + | To maximize the Fc region’s signal transduction efficiency and Van der Waals contacts, constant region two of heavy chain A makes an asymmetrical association with constant region three of heavy chain B to create a <scene name='95/952713/Trans_heavy/5'>heavy chain interface</scene>. More specifically, Arg243 and Arg251 residues from heavy chain A donate three hydrogen bonds to Leu433, Thr431, and Asp376 residues on heavy chain B. Furthermore, Leu313 of heavy chain A accepts a hydrogen bond from Thr429 on heavy chain B (cite). |
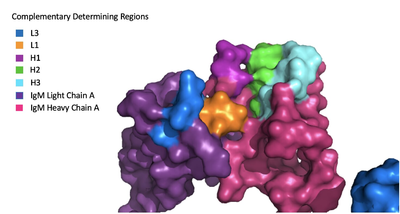
===Fab Region=== | ===Fab Region=== | ||
| Line 49: | Line 49: | ||
=='''Signal Transduction'''== | =='''Signal Transduction'''== | ||
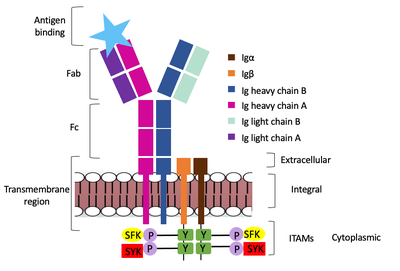
| - | The diagram in Figure 4 depicts the initial process of B cell activation by the antigen binding to the antibody at the Fab region. The underlying mechanism for signal transduction is unknown but it is speculated to operate under what is known as the conserved assembly mechanism ( | + | The diagram in Figure 4 depicts the initial process of B cell activation by the antigen binding to the antibody at the Fab region. The underlying mechanism for signal transduction is unknown but it is speculated to operate under what is known as the conserved assembly mechanism (cite). This means that upon antigen binding, BCRs on the surface of the cell begin to cluster to cause the phosphorylation of the immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motifs located in Igα and Igβ. In its “off” state, the constant region four of heavy chain B overlaps the extracellular components of Igα and Igβ. As the antigen binds, it induces a conformational change to release the overlap and allow for clustering about the BCR. Now, in its “on” state the phosphorylation of the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Immunoreceptor_tyrosine-based_activation_motif ITAM region] (observed here as the conserved tyrosine residues are phosphorylated) within the intracellular tails of Igα and Igβ drives downstream kinase activity to continue to process of [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tyrosine-protein_kinase_SYK signal cascading] |
[[Image:Signal_transduction-2.png|400 px|left|thumb|'''Figure 4. IgM Antibody Signal Transduction following Antigen Binding.''']] | [[Image:Signal_transduction-2.png|400 px|left|thumb|'''Figure 4. IgM Antibody Signal Transduction following Antigen Binding.''']] | ||
Revision as of 14:38, 7 April 2023
Human B-cell Antigen Receptor: IgM BCR
| |||||||||||
References
Student Contributors
Detonyeá Dickson, Allison Goss, Jackson Payton