We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 1790
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
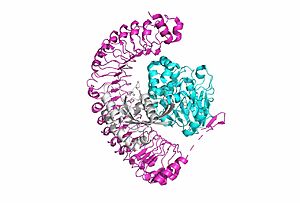
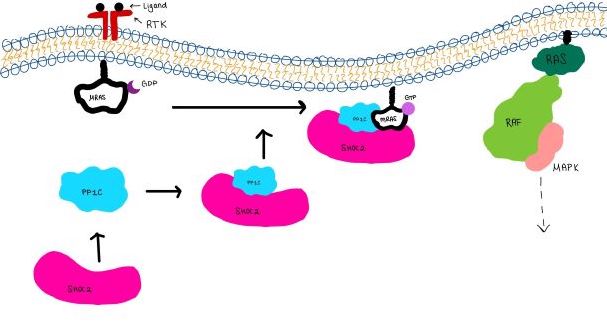
<scene name='95/952717/Shoc2/1'>SHOC2</scene> is a scaffold protein that is composed of 20 leucine-rich repeat domains that form a solenoid structure. The leucine rich region forms a concave hydrophobic core which is necessary for binding with PP1C and MRAS. | <scene name='95/952717/Shoc2/1'>SHOC2</scene> is a scaffold protein that is composed of 20 leucine-rich repeat domains that form a solenoid structure. The leucine rich region forms a concave hydrophobic core which is necessary for binding with PP1C and MRAS. | ||
==PP1C== | ==PP1C== | ||
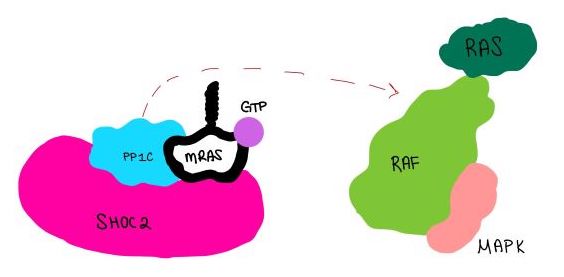
| - | <scene name='95/952717/Pp1c/1'>PP1C</scene> is a catalytic protein. After forming a ternary complex, the <scene name='95/952717/Pp1c_hydrophobic_patch/1'>hydrophobic active site</scene> on the protein interacts with Raf to act as a phosphatase and dephosphorylate Ser 259. | + | <scene name='95/952717/Pp1c/1'>PP1C</scene> is a catalytic protein. After forming a ternary complex, the <scene name='95/952717/Pp1c_hydrophobic_patch/1'>hydrophobic active site</scene> on the protein interacts with Raf to act as a phosphatase and dephosphorylate Ser 259<ref name="Hauseman" />. |
==MRAS== | ==MRAS== | ||
| - | <scene name='95/952717/Mras/2'>MRAS</scene> is a membrane bound structure that aids the complex in localizing near other structures such as the RAS-RAF-MAPK complex in order to initiate downstream signaling. In its inactive state, MRAS is bound to GDP. When signaled by [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK442024/. growth factors], the GDP is exchanged for GTP. The now <scene name='95/952718/Zoom_in_gtp/1'>GTP bound MRAS</scene> undergoes a conformational change of the <scene name='95/952716/Ras-switch-zoomed/1'>switch I and switch II regions</scene>. This conformational change activates the protein allowing it to bind more easily with the SHOC2-PP1C complex. In comparison to other RAS proteins, MRAS has a greater affinity for the SHOC2-PP1C complex. | + | <scene name='95/952717/Mras/2'>MRAS</scene> is a membrane bound structure that aids the complex in localizing near other structures such as the RAS-RAF-MAPK complex in order to initiate downstream signaling. In its inactive state, MRAS is bound to GDP. When signaled by [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK442024/. growth factors], the GDP is exchanged for GTP. The now <scene name='95/952718/Zoom_in_gtp/1'>GTP bound MRAS</scene> undergoes a conformational change of the <scene name='95/952716/Ras-switch-zoomed/1'>switch I and switch II regions</scene>. This conformational change activates the protein allowing it to bind more easily with the SHOC2-PP1C complex. In comparison to other RAS proteins, MRAS has a greater affinity for the SHOC2-PP1C complex<ref name="Lavoie" />. |
| Line 39: | Line 39: | ||
==RASopathies== | ==RASopathies== | ||
| - | RASopathy is a broad term used to describe developmental syndromes that stem from [https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/medicine-and-dentistry/germline-mutation. germline mutations] of proteins along the RAS/MAPK pathway such as SHOC2, PP1C, and MRAS. These mutations can be either gain or loss of function. Rasopathies can also lead to cancer. | + | RASopathy is a broad term used to describe developmental syndromes that stem from [https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/medicine-and-dentistry/germline-mutation. germline mutations] of proteins along the RAS/MAPK pathway such as SHOC2, PP1C, and MRAS. These mutations can be either gain or loss of function. Rasopathies can also lead to cancer<ref name="Rauen" />. |
==Cancer== | ==Cancer== | ||
| Line 58: | Line 58: | ||
<ref name=”Lavoie”>PMID:35970881</ref>. | <ref name=”Lavoie”>PMID:35970881</ref>. | ||
<ref name=”Liau”>PMID:35768504</ref>. | <ref name=”Liau”>PMID:35768504</ref>. | ||
| - | <ref name=”Rauen”>PMID: | + | <ref name=”Rauen”>PMID:23875798</ref>. |
<references/> | <references/> | ||
Revision as of 15:10, 7 April 2023
| |||||||||||