We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 1771
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
==Structure== | ==Structure== | ||
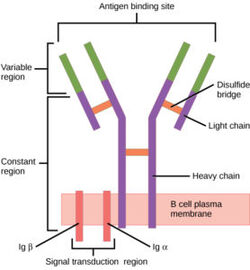
| - | B cell receptors have distinct functional domains each playing a unique role in response to a foreign antigen. These include the extracellular domain, the transmembrane domain, and the intracellular domain (the structure of this domain is still unclear). To accomplish B cell signaling, the BCR must bind an antigen and transmit the signal through the receptor domains. Exploring the different sections of a BCR, the antigen binding site (located in the extracellular region) is specific to antigens, but the process is highly conserved across different BCRs. More specifically, the IgM BCR has a unique interaction concerning its Fc chains and a/b subunits. These interactions contribute to the overall structure of the protein. This section will explore these structural regions starting with the extracellular domain, describing the antigen binding domain, outlining unique interactions between Fc chains and a/b subunits, and describing the intermolecular interactions that keep subunits together. Ultimately, the interactions of the transmembrane domain that anchor the complex to the membrane are examined. | + | B cell receptors have distinct functional domains each playing a unique role in response to a foreign antigen. These include the extracellular domain, the transmembrane domain, and the intracellular domain (the structure of this domain is still unclear).<Ref name="Su Q"> Su Q, Chen M, Shi Y, Zhang X, Huang G, Huang B, Liu D, Liu Z, Shi Y. Cryo-EM structure of the human IgM B cell receptor. Science. 2022 Aug 19;377(6608):875-880. [doi: 10.1126/science.abo3923. Epub 2022 Aug 18. PMID: 35981043.]</Ref> To accomplish B cell signaling, the BCR must bind an antigen and transmit the signal through the receptor domains. Exploring the different sections of a BCR, the antigen binding site (located in the extracellular region) is specific to antigens, but the process is highly conserved across different BCRs.<Ref name="Su Q"> Su Q, Chen M, Shi Y, Zhang X, Huang G, Huang B, Liu D, Liu Z, Shi Y. Cryo-EM structure of the human IgM B cell receptor. Science. 2022 Aug 19;377(6608):875-880. [doi: 10.1126/science.abo3923. Epub 2022 Aug 18. PMID: 35981043.]</Ref> More specifically, the IgM BCR has a unique interaction concerning its Fc chains and a/b subunits.<Ref name="Su Q"> Su Q, Chen M, Shi Y, Zhang X, Huang G, Huang B, Liu D, Liu Z, Shi Y. Cryo-EM structure of the human IgM B cell receptor. Science. 2022 Aug 19;377(6608):875-880. [doi: 10.1126/science.abo3923. Epub 2022 Aug 18. PMID: 35981043.]</Ref> These interactions contribute to the overall structure of the protein. This section will explore these structural regions starting with the extracellular domain, describing the antigen binding domain, outlining unique interactions between Fc chains and a/b subunits, and describing the intermolecular interactions that keep subunits together. Ultimately, the interactions of the transmembrane domain that anchor the complex to the membrane are examined. |
===Antigen Binding Site=== | ===Antigen Binding Site=== | ||
Revision as of 03:54, 14 April 2023
| This Sandbox is Reserved from February 27 through August 31, 2023 for use in the course CH462 Biochemistry II taught by R. Jeremy Johnson at the Butler University, Indianapolis, USA. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1765 through Sandbox Reserved 1795. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
IgM B-cell Receptor
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Robinson R. Distinct B cell receptor functions are determined by phosphorylation. PLoS Biol. 2006 Jul;4(7):e231. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0040231. Epub 2006 May 30. PMID: 20076604; PMCID: PMC1470464.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 Su Q, Chen M, Shi Y, Zhang X, Huang G, Huang B, Liu D, Liu Z, Shi Y. Cryo-EM structure of the human IgM B cell receptor. Science. 2022 Aug 19;377(6608):875-880. [doi: 10.1126/science.abo3923. Epub 2022 Aug 18. PMID: 35981043.]
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 Janeway CA Jr, Travers P, Walport M, et al. Immunobiology: The Immune System in Health and Disease. 5th edition. New York: Garland Science; 2001.
- ↑ Ma X, Zhu Y, Dong D, Chen Y, Wang S, Yang D, Ma Z, Zhang A, Zhang F, Guo C, Huang Z. Cryo-EM structures of two human B cell receptor isotypes. Science. 2022 Aug 19;377(6608):880-885. [doi: 10.1126/science.abo3828. Epub 2022 Aug 18. PMID: 35981028]
- ↑ Zhixun Shen, Sichen Liu, Xinxin Li, Zhengpeng Wan, Youxiang Mao, Chunlai Chen, Wanli Liu (2019) Conformational change within the extracellular domain of B cell receptor in B cell activation upon antigen binding eLife 8:e42271. Doi: https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.42271
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Tolar P, Pierce SK. Unveiling the B cell receptor structure. Science. 2022 Aug 19;377(6608):819-820. [doi: 10.1126/science.add8065. Epub 2022 Aug 18. PMID: 35981020.]
- ↑ Althwaiqeb, S. Histology, B Cell Lymphocyte; StatPearls Publishing, 2023.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 Yanaba K, Bouaziz JD, Matsushita T, Magro CM, St Clair EW, Tedder TF. B-lymphocyte contributions to human autoimmune disease. Immunol Rev. 2008 Jun;223:284-99. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2008.00646.x. PMID: 18613843.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 Chandrashekara S. The treatment strategies of autoimmune disease may need a different approach from conventional protocol: a review. Indian J Pharmacol. 2012 Nov-Dec;44(6):665-71. doi: 10.4103/0253-7613.103235. PMID: 23248391; PMCID: PMC3523489.
- ↑ Shu SA, Wang J, Tao MH, Leung PS. Gene Therapy for Autoimmune Disease. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2015 Oct;49(2):163-76. doi: 10.1007/s12016-014-8451-x. PMID: 25277817.
Student Contributors
- Joel Wadas
- Olivia Gooch
- Delaney Lupoi