|
Introduction
(SMP) is a ternary holophosphotase complex formed by the individual proteins: SHOC2, PP1C, and MRAS. The SMP complex is involved in signaling the initiation of MAPK pathways, which is responsible for cellular growth and development, cell proliferation, and apoptosis [1]. Formation of this complex begins with an extracellular signal binding to a membrane embedded receptor tyrosine kinase receptor(RTK) [1]. This causes membrane-bound MRAS to exchange GDP for GTP. Initiating the SMP complex formation at the plasma membrane consists of the SHOC2 and PP1C binding first. When the MRAS exchanges GDP to GTP, it then assembles with the combined SHOC2 and PP1C. Based on MRAS targeting, PP1C catalyzes the dephosphorylation of the N-terminal phosphoserine (NTpS) on the RAF complex leading to the amplification of MAPK signaling [1]. In a normal cell, this would regulate cell proliferation but dysfunction in the ternary complex has shown signs to lead to tumor formation due to unregulated cell growth [1].
 Figure 1: Mechanism for Shoc2-MRAS-PP1C  Figure 2: PP1C phosphorylates Serine 259. Overall Structure
SHOC2
is a scaffold protein composed of 20 leucine-rich repeat (LRR) domains that form a solenoid structure [1]. The leucine rich region forms a concave hydrophobic core which is necessary for binding with PP1C and MRAS. SHOC2 is the crucial mediator for SHOC2-PP1C-MRAS complex formation [1]. The leucine rich domain is very important in creating selectivity for the PP1C protein, as that protein is used for so many other complex pathways [1]. The LRR domains are stabilized by an N-terminal flanking 𝝰-helix and a C-terminal helix-turn-helix [2]. Alongside the conserved leucine residues in the LRR domain, there is a group of conserved asparagine residues that creates a stabilizing “asparagine ladder” that is necessary for the LRR fold, giving the SHOC2 its concave structure [2].
PP1C
MRAS
Key Ligand Interactions
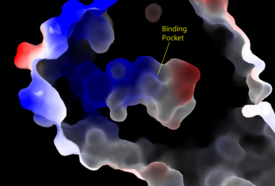 Figure 3: Electrostatic illustration of the amphipathic binding pocket of the LPA 1 receptor. This binding pocket was revealed by cutting away the exterior or the protein. This binding pocket, located in the interior of the protein, has both polar and nonpolar regions. The blue and red coloration highlight the positively and negatively charged regions, respectively, and the white color shows the nonpolar region of the binding pocket. SHOC2 and PP1C
SHOC2 and MRAS
PP1C and MRAS
Signaling Pathway
Disease Relevance
Cancer
RASopathies
Future Studies
3D structures of lysophosphatidic acid receptor
4z34, 4z35, 4z36 - hLPA1 + antagonist - human
2lq4 – hLPA1 second extracellular loop – NMR
4p0c – hLPA2/NHERF2
5xsz – LPA6A (mutant) – zebra fish
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 Hauseman ZJ, Fodor M, Dhembi A, Viscomi J, Egli D, Bleu M, Katz S, Park E, Jang DM, Porter KA, Meili F, Guo H, Kerr G, Molle S, Velez-Vega C, Beyer KS, Galli GG, Maira SM, Stams T, Clark K, Eck MJ, Tordella L, Thoma CR, King DA. Structure of the MRAS-SHOC2-PP1C phosphatase complex. Nature. 2022 Jul 13. pii: 10.1038/s41586-022-05086-1. doi:, 10.1038/s41586-022-05086-1. PMID:35830882 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41586-022-05086-1
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Kwon JJ, Hajian B, Bian Y, Young LC, Amor AJ, Fuller JR, Fraley CV, Sykes AM, So J, Pan J, Baker L, Lee SJ, Wheeler DB, Mayhew DL, Persky NS, Yang X, Root DE, Barsotti AM, Stamford AW, Perry CK, Burgin A, McCormick F, Lemke CT, Hahn WC, Aguirre AJ. Structure-function analysis of the SHOC2-MRAS-PP1C holophosphatase complex. Nature. 2022 Jul 13. pii: 10.1038/s41586-022-04928-2. doi:, 10.1038/s41586-022-04928-2. PMID:35831509 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41586-022-04928-2
Proteopedia Resources
Category:Lysophosphatidic acid binding
Category:Lysophosphatidic acid
Butler University Proteopedia Pages
See also:
|



