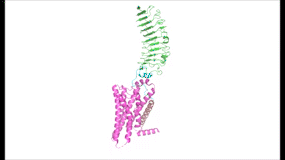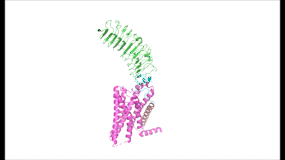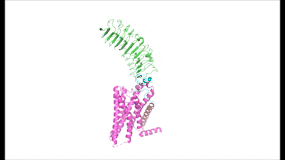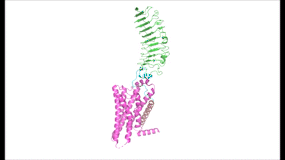Thyroid Stimulating Hormone Receptor (TSHR) Structure and Function
Introduction
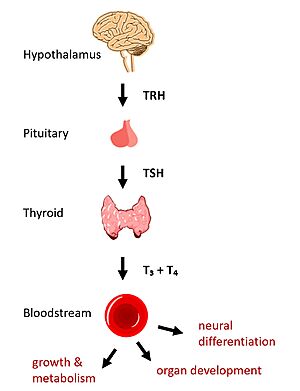
Figure 1: TSH binds TSHR on the surface of thyroid cells in the HPT signaling axis pathway, which regulates metabolism and growth.
In humans, the hypothalamic-pituitary-thyroid (HPT) signaling axis regulates functions including metabolism, growth, organ development, and neural differentiation [1]. In this pathway, the thyroid stimulating hormone receptor (TSHR) activates transcription of thyroid hormones thyroxine (T3) and triiodothyronine (T4) in response to ligand binding by thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) [2]. After a brief introduction to the biological significance of TSHR, this page explores the structure of TSHR and its significance to TSH binding and receptor activation.
Biological Significance of TSHR
The HPT signaling axis involves the brain, thyroid gland, and bloodstream circulation. In the first step of the pathway, thyrotropin releasing hormone (TRH) is secreted by the hypothalamus, which in turn stimulates the anterior pituitary gland to produce TSH [1]. TSH binds to TSHR on the surface of thyroid cells and triggers the production of T3 and T4 through G-protein coupled receptor (GPCR) signaling [2]. T3 and T4 circulate in the bloodstream and enter cells via thyroid hormone transporters to regulate metabolic functions including neural differentiation, metabolism, and growth and development (Fig. 1). Additionally, T3 and T4 act in a negative feedback loop to inhibit further TSH production [1].
Dysregulation of TSHR can lead to disease. In Grave's disease, antibody analogs of TSH cause overactivation of TSHR, leading to clinical symptoms of hyperthyroidism [2]. In contrast, congenital mutations which inactivate TSHR can lead to hypothyroidism, which results in growth retardation and neurologic impairment if left untreated [1].
Molecular Structure and Function of TSHR
Role of TSHR Domains
To understand how the structure of TSHR contributes to its function, it is helpful to become familiar with the of TSHR (7XW5). First is the , which is concave in shape. It is also called the because it is made primarily of beta sheets which are rich in leucine [3]. The ECD contains which play a key role in TSH binding. Second is the , which is composed of seven transmembrane alpha helices which are connected by extracellular loops (ECL). The TMD undergoes a conformation change upon ligand binding that activates the intracellular signal cascade [4]. The third region of the TSHR is the , which plays a key role in the movement and stability of the TSHR. The details of the hinge mechanism are discussed in the proceeding section.
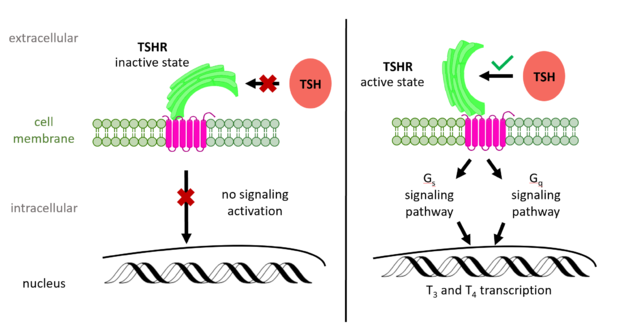
Figure 2: (Left) In the downright, inactive state, TSH cannot bind and no signaling activation occurs. (Right) In the upright, active state, binding of TSH leads to GPCR signaling activation and production of T3 and T4 hormones.
Importance of Hinge Region to Signaling Activation
The TSHR hinges between two states: . When the extracellular domain is hinged down, the receptor is inactive and no signaling activation occurs. When the extracellular domain raises into the upright position, the hinge region deforms and interacts with the extracellular loops to cause a conformation change in the TMD and corresponding G-protein activation [5]. While transition between the active and inactive states occurs spontaneously, favoring of one state over the other is influenced by hinge interactions and ligand binding [6]. When stabilized in the upright conformation, the activated GPCR signaling pathway results in transcription of thyroid hormones T3 and T4 (Fig. 2) [2].
Modulation of TSHR signaling would not be possible without the hinge region, which accommodates up-and-down rotation of the extracellular domain as a rigid body about an imaginary 55 degree axis [6]. During this transition, the hinge region undergoes and is displaced approximately 5 Angstroms upward as it uncoils [6]. The hinge region pulls on the linked transmembrane helices as it stretches, shifting approximately 4 Angstroms inward and leading to G-protein signaling activation [6], [5].
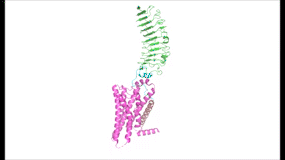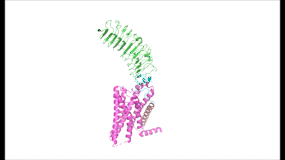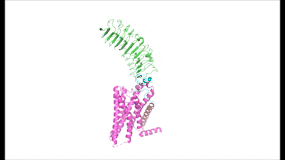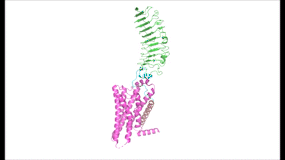
|
| Fig. 3 Animation of TSHR hinging between the active (upright, 7T9I) and inactive (downward, 7T9M) conformations. The ECD rotates 55 degrees as a rigid body.
|
Stabilizing Interactions in the Hinge
TSHR hinge motion is influenced by molecular interactions in the . To understand these interactions, the hinge region can be subdivided into several parts:
- The , which lies at the intersection of the extracellular and transmembrane domains;
- , which sticks up and serves as a binding platform for the TSH ligand
- The region, which connects helix 1 with the p10 region
- The region, a conserved 10-amino acid sequence which connects to transmembrane helix 7 and undergoes most of the deformation [6] [4].
Of the TSHR hinge subregions, the p10 peptide is noteworthy because it serves as an internal agonist of TSHR activation [5]. Specifically, an between K660 in TM helix 7 and E409 in the p10 region stabilizes TSHR in the active conformation. If this interaction is disrupted with an E409A mutation, diminished receptor activation and TSH potency is observed [6]. Other mutations in the p10 are poorly tolerated in both TSHR and other glycoprotein hormone receptors [6].
Beyond the p10 region, the active conformation of TSHR is also stabilized by a between Y279 in the hinge helix and I486 in ECL region 1 [6]. If this interaction is disrupted with an I496F mutation, the result is constitutive receptor activation and decreased sensitivity to the TSH ligand. This receptor overactivation is attributed to over-stabilization of the hydrophobic interaction by the bulkier phenylalanine [6]. In this way, TSHR function is directly affected by stabilizing interactions in the hinge.
Rather than stabilization, two disulfide bonds in the hinge region are responsible for constraining the movement of the hinge [3]. The connects the hinge helix to the linker region, and the connects the hinge helix to the p10 region [4]. By directly linking parts of the hinge, the disulfide bonds serve to keep the ECD and TMD in close proximity while allowing the domains to move relative to one another [3].
Ligand Binding
Binding of Thyroid Stimulating Hormone to TSHR
The thyroid stimulating hormone by complementary shape[4]. The ECD is curved and compliments the curvature of TSH similar to how a baseball fits into a glove. Several key ionic interactions between the TSH and TSHR also occur in the . The seatbelt region is located in the beta subunit of the TSH. is Glu118 from TSH and Lys58 from the ECD. is between Asp111 from the TSH and Lys209 from the ECD. These interactions form salt bridges between the ECD and the TSH which allows for specificity of binding for TSH to TSHR [4][6].
Other key interactions that determine the specificity of binding are between TSH and helix 1. Helix 1 contains several polar residues that interact with surrounding nonpolar residues like Leu62 and Phe17. Positively charged Arg54 was also seen to interact with Helix 1. These interactions increase the activation potency and help activate the rotation of the hinge region [4][6].
Ligand Regulation of Signaling Activation
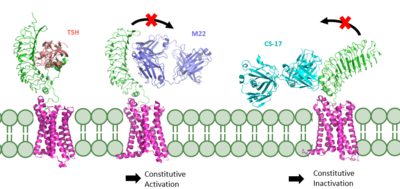
Figure 2 TSHR in active and inactive binding states.
Left is TSH bound to TSHR (
7T9I).
Middle is M22 bound to TSHR (
7T9N).
Right is CS-17 bound to TSHR (
7T9M).
The interactions between the TSH ligand and the TSHR receptor have significant consequences for disease states as antibodies can stabilize TSHR in the fully active or inactive state[6]. In the image shown to the right are three different states of TSHR. In contrast to the native TSH conformation, the autoimmune antibody, M22, bound to TSHR (middle) locks the receptor in the upright state and prevents transition to the down state because of steric clash with the membrane. This conformation causes constitutive activation and elevated levels of thyroid hormones found in a person with Grave's disease[6]. In contrast to TSH and M22 binding, antibody CS-17 binds to the TSHR and locks it in the down, inactive conformation. This prevents the signaling cascade to translation and causes constitutive inactivation [6].
These different ways to active and inactive TSHR could represent potential therapies for someone with Grave's disease or other thyroid-related diseases with overactive TSH binding. Whereas current therapies target T3/T4 synthesis or destroy the gland using artificial hormones, these diseases could instead be targeted with something like CS-17 which would compete with M22 and TSH to lessen overactivation[6].
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Brent GA. Mechanisms of thyroid hormone action. J Clin Invest. 2012;122(9):3035-3043. DOI: 10.1172/JCI60047
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 Chu YD, Yeh CT. The Molecular Function and Clinical Role of Thyroid Stimulating Hormone Receptor in Cancer Cells. Cells. 2020;9(7):1730. DOI:10.3390/cells9071730
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Kleinau G, Worth CL, Kreuchwig A, et al. Structural–Functional Features of the Thyrotropin Receptor: A Class A G-Protein-Coupled Receptor at Work. Frontiers in Endocrinology. 2017;8. Accessed April 2, 2023. DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2017.00086
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 4.5 Duan J, Xu P, Luan X, Ji Y, He X, Song N, Yuan Q, Jin Y, Cheng X, Jiang H, Zheng J, Zhang S, Jiang Y, Xu HE. Hormone- and antibody-mediated activation of the thyrotropin receptor. Nature. 2022 Aug 8. pii: 10.1038/s41586-022-05173-3. doi:, 10.1038/s41586-022-05173-3. PMID:35940204 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41586-022-05173-3
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 Bruser A, Schulz A, Rothemund S, et al. The Activation Mechanism of Glycoprotein Hormone Receptors with Implications in the Cause and Therapy of Endocrine Diseases. J Biol Chem. 2016;291(2):508-520. DOI:10.1074/jbc.M115.701102
- ↑ 6.00 6.01 6.02 6.03 6.04 6.05 6.06 6.07 6.08 6.09 6.10 6.11 6.12 6.13 6.14 Faust B, Billesbolle CB, Suomivuori CM, Singh I, Zhang K, Hoppe N, Pinto AFM, Diedrich JK, Muftuoglu Y, Szkudlinski MW, Saghatelian A, Dror RO, Cheng Y, Manglik A. Autoantibody mimicry of hormone action at the thyrotropin receptor. Nature. 2022 Aug 8. pii: 10.1038/s41586-022-05159-1. doi:, 10.1038/s41586-022-05159-1. PMID:35940205 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41586-022-05159-1