We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 1777
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
==Overview== | ==Overview== | ||
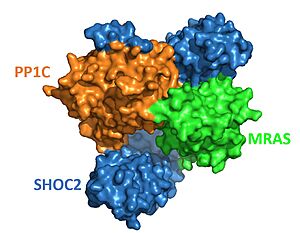
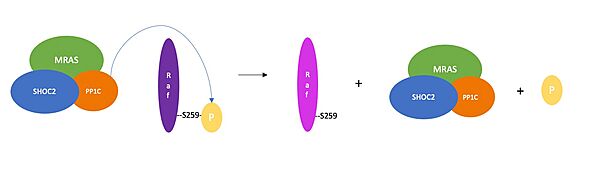
| - | The | + | The complex combines three separate proteins, SHOC2, PP1C, and MRAS, to form the active protein (SMP complex), as seen in Figure 2<Ref name='Hauseman'>Hauseman, Z.J., Fodor, M., Dhembi, A. et al. Structure of the MRAS–SHOC2–PP1C phosphatase complex. Nature 609, 416–423 (2022). doi: 10.1038/s41586-022-05086-1. [https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-022-05086-1. DOI:10.1038/s41586-022-05086-1]. </Ref>. In complex, each of these proteins are responsible for a different role. MRAS is the "on and off" switch; when MRAS is activated from binding GTP, '''fill in here'''. PP1C by itself is a catalytic enzyme that ''' fill in here'''. In complex, PP1C is tasked with being the catalytic domain and removing a phosphate from RAF. The last piece of the complex is SHOC2, which is responsible for holding and stabilizing MRAS and PP1C <Ref name= 'Hahn'> Kwon, J. J., & Hahn, W. C. A Leucine-Rich Repeat Protein Provides a SHOC2 the RAS Circuit: a Structure-Function Perspective. Molecular and cellular biology, 41(4), e00627-20 (2021). doi:10.1128/MCB.00627-20. [http://doi.org/10.1128/MCB.00627-20. DOI: 10.1128/MCB.00627-20]. </Ref>. The SMP complex was determined via cryo-electron microscopy as well as x-ray diffraction. The overall architecture has PP1C and MRAS bound within the concave surface of SHOC2, leaving the catalytic site of PP1C and the GTP binding cleft in MRAS exposed. |
==SHOC2== | ==SHOC2== | ||
[[Image:SHOC2-PP1C-MRAS Surface.JPG|300px|right|thumb|<font size="2"><div style="text-align: center;">'''Figure 2'''. Surface representation of SHOC2-PP1C-MRAS ([https://www.rcsb.org/structure/7UPI PDB 7upi]). SHOC2 (blue), PP1C (orange) and MRAS (green). </div></font>]] | [[Image:SHOC2-PP1C-MRAS Surface.JPG|300px|right|thumb|<font size="2"><div style="text-align: center;">'''Figure 2'''. Surface representation of SHOC2-PP1C-MRAS ([https://www.rcsb.org/structure/7UPI PDB 7upi]). SHOC2 (blue), PP1C (orange) and MRAS (green). </div></font>]] | ||
| - | SHOC2 is a scaffolding protein which acts as a cradle to bind PP1C and MRAS <ref name="Hauseman" />, serving as an aggregation point to enable reciprocal interactions between these three signaling proteins. <scene name='95/952705/Shoc2_structure/2'>SHOC2</scene> is a leucine rich repeat ([https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Leucine-rich_repeat LRR]) protein consisting of 20 consecutive <scene name='95/952706/Shoc2_structure/9'>LRR motifs</scene>. LRR motifs form an extended β-sheet on the inner concave surface of SHOC2 with α-helices facing outward to facilitate binding of the protein complex. These LRR motifs result in a largely hydrophobic core within the concave region.< | + | SHOC2 is a scaffolding protein which acts as a cradle to bind PP1C and MRAS <ref name="Hauseman" />, serving as an aggregation point to enable reciprocal interactions between these three signaling proteins. <scene name='95/952705/Shoc2_structure/2'>SHOC2</scene> is a leucine rich repeat ([https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Leucine-rich_repeat LRR]) protein consisting of 20 consecutive <scene name='95/952706/Shoc2_structure/9'>LRR motifs</scene>. LRR motifs form an extended β-sheet on the inner concave surface of SHOC2 with α-helices facing outward to facilitate binding of the protein complex. These LRR motifs result in a largely hydrophobic core within the concave region. <ref name="Hahn" />. |
| - | + | ||
==PP1C== | ==PP1C== | ||
<scene name='95/952705/Pp1c_structure/1'>PP1C</scene> is the catalytic domain of the phosphatase enzyme [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene/5499 PP1], which removes reversible phosphorylations from signaling proteins. PP1C is a serine/threonine phosphatase involved in signaling pathways that control cell growth, division, and metabolism '''(REF)''' '''and explain more, see notes'''. | <scene name='95/952705/Pp1c_structure/1'>PP1C</scene> is the catalytic domain of the phosphatase enzyme [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene/5499 PP1], which removes reversible phosphorylations from signaling proteins. PP1C is a serine/threonine phosphatase involved in signaling pathways that control cell growth, division, and metabolism '''(REF)''' '''and explain more, see notes'''. | ||
Revision as of 03:56, 17 April 2023
| This Sandbox is Reserved from February 27 through August 31, 2023 for use in the course CH462 Biochemistry II taught by R. Jeremy Johnson at the Butler University, Indianapolis, USA. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1765 through Sandbox Reserved 1795. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Bernal Astrain G, Nikolova M, Smith MJ. Functional diversity in the RAS subfamily of small GTPases. Biochem Soc Trans. 2022 Apr 29;50(2):921-933. doi: 10.1042/BST20211166. DOI:10.1042/BST20211166
- ↑ Molina JR, Adjei AA. The Ras/Raf/MAPK pathway. J Thorac Oncol. 2006 Jan;1(1):7-9. DOI:10.1016/S1556-0864(15)31506-9.
- ↑ Li, L., Zhao, G. D., Shi, Z. et. al.The Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK signaling pathway (Figure 1) and its role in the occurrence and development of HCC. Oncology letters, 12(5), 3045–3050. DOI:10.3892/ol.2016.5110.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Hauseman, Z.J., Fodor, M., Dhembi, A. et al. Structure of the MRAS–SHOC2–PP1C phosphatase complex. Nature 609, 416–423 (2022). doi: 10.1038/s41586-022-05086-1. DOI:10.1038/s41586-022-05086-1.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Kwon, J. J., & Hahn, W. C. A Leucine-Rich Repeat Protein Provides a SHOC2 the RAS Circuit: a Structure-Function Perspective. Molecular and cellular biology, 41(4), e00627-20 (2021). doi:10.1128/MCB.00627-20. DOI: 10.1128/MCB.00627-20.
- ↑ Zhou, Y., Prakash, P., Liang, H., et al. Lipid-Sorting Specificity Encoded in K-Ras Membrane Anchor Regulates Signal Output. Cell, 168(1-2), 239–251.e16 doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2016.11.059. DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2016.11.059.
- ↑ Young, L., Rodriguez-Viciana, P. MRAS: A Close but Understudied Member of the RAS Family. Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Medicine (2018). doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a033621. DOI: 0.1101/cshperspect.a033621.
- ↑ Daniel A. Bonsor, Patrick Alexander, Kelly Snead, Nicole Hartig, Matthew Drew, Simon Messing, Lorenzo I. Finci, Dwight V. Nissley, Frank McCormick, Dominic Esposito, Pablo Rodrigiguez-Viciana, Andrew G. Stephen, Dhirendra K. Simanshu. Structure of the SHOC2–MRAS–PP1C complex provides insights into RAF activation and Noonan syndrome. bioRxiv. 2022.05.10.491335. doi: 10.1101/2022.05.10.491335. DOI:10.1101/2022.05.10.491335.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 9.3 9.4 Kwon, J.J., Hajian, B., Bian, Y. et al. Structure–function analysis of the SHOC2–MRAS–PP1C holophosphatase complex. Nature 609, 408–415 (2022).doi: 10.1038/s41586-022-04928-2. DOI:10.1038/s41586-022-04928-2
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 10.2 Kwon, J., Jajian, B., Bian, Y. et al. Comprehensive structure-function evaluation of the SHOC2 holophosphatase reveals disease mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities. In: Proceedings of the American Association for Cancer Research Annual Meeting 2022. DOI: 10.1158/1538-7445.AM2022-LB029.
- ↑ Liau NPD, Johnson MC, Izadi S, Gerosa L, Hammel M, Bruning JM, Wendorff TJ, Phung W, Hymowitz SG, Sudhamsu J. Structural basis for SHOC2 modulation of RAS signalling. Nature. 2022 Jun 29. pii: 10.1038/s41586-022-04838-3. doi:, 10.1038/s41586-022-04838-3. PMID:35768504 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41586-022-04838-3
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 Lavoie, H., Therrien, M. Structural keys unlock RAS–MAPK cellular signaling pathway. Nature 609, 248-249 (2022). doi: 10.1038/d41586-022-02189-7. DOI:10.1038/d41586-022-02189-7.
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 van der Burgt, I. Noonan syndrome. Orphanet J Rare Dis 2, 4 (2007). doi: 10.1186/1750-1172-2-4 DOI: 10.1186/1750-1172-2-4.