We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 1790
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 39: | Line 39: | ||
=Signaling Pathway= | =Signaling Pathway= | ||
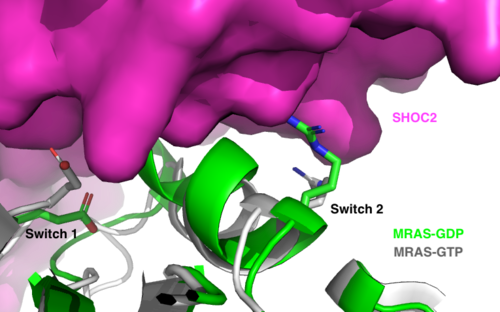
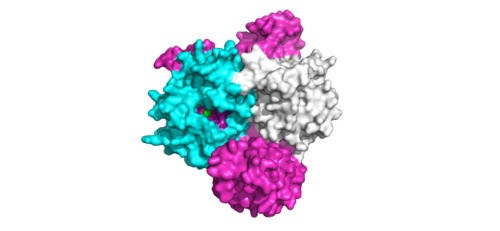
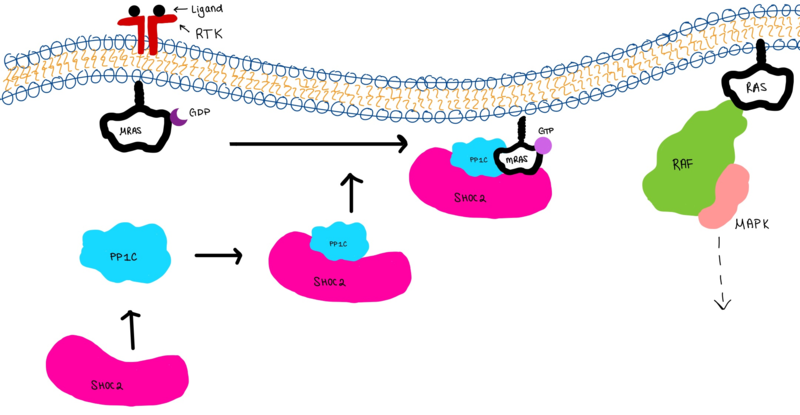
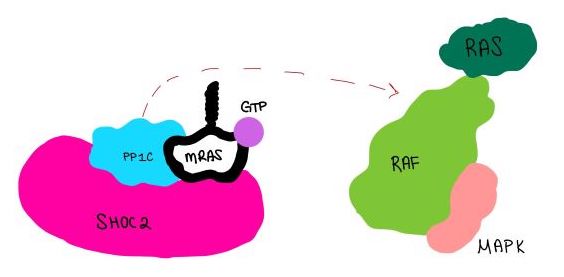
| - | The SMP signaling pathway begins with the formation of the SMP complex. Initially, a ligand must bind to a receptor tyrosine kinase. This signals SHOC2 to bind to PP1C forming a binary complex that then binds to the membrane bound MRAS. There is some discrepancy about when the different proteins of the SMP complex come together <ref name="Liau">PMID:35768504</ref>. Some experiments indicate that the three proteins bind at the same time but the order is largely unknown. Once the SMP complex forms, its intracellular target is a key inactivation phosphorylation (Ser259) on MAPK Raf1. The serine is directly dephosphorylated by PP1C, while SHOC2 and MRAS increase PP1C’s specificity for S259 on Raf <ref name="Liau" />. When analyzing the surface structure of SHOC1-PP1C-MRAS, there was a hydrophobic groove on the SHOC2 terminus and another hydrophobic groove near the active site on PP1C <ref name="Liau" />. This region is crucial in making PP1C specific to Raf, because the NTpS region that is right next to the phosphoserine on Raf is able to bind to the hydrophobic patch on both SHOC2 and PP1C <ref name="Liau" />. | + | The SMP signaling pathway begins with the formation of the SMP complex. Initially, a ligand must bind to a receptor tyrosine kinase. This signals SHOC2 to bind to PP1C forming a binary complex that then binds to the membrane bound MRAS. There is some discrepancy about when the different proteins of the SMP complex come together <ref name="Liau">PMID:35768504</ref>, however we chose to depict the order ass shown in Figure 3 for a more clear visualization. Some experiments indicate that the three proteins bind at the same time but the order is largely unknown. Once the SMP complex forms, its intracellular target is a key inactivation phosphorylation (Ser259) on MAPK Raf1. The serine is directly dephosphorylated by PP1C, while SHOC2 and MRAS increase PP1C’s specificity for S259 on Raf <ref name="Liau" />. When analyzing the surface structure of SHOC1-PP1C-MRAS, there was a hydrophobic groove on the SHOC2 terminus and another hydrophobic groove near the active site on PP1C <ref name="Liau" />. This region is crucial in making PP1C specific to Raf, because the NTpS region that is right next to the phosphoserine on Raf is able to bind to the hydrophobic patch on both SHOC2 and PP1C <ref name="Liau" />. |
Mutations affecting SMP complex formation and stability can increase or decrease MAPK signaling, where increased stability of the complex increases MAPK signaling while decreased stability decreases signaling <ref name="Liau" />. There are a set of mutations that can happen on the SMP complex as a whole that can cause [https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/noonan-syndrome/symptoms-causes/syc-20354422. Noonan syndrome], a rasopathy disorder <ref name="Liau" />. On SHOC2, if the following mutations S2G, C260Y, and P510L caused differences in the complex formation with PP1C <ref name="Liau" />. On PP1C, the mutation P50R resulted in stronger ionic interactions with residues on SHOC2, resulting in a more stabilized complex <ref name="Liau" />. On MRAS, mutations such as G23V and T681I, can increase the proportion of MRAS that is GTP bound, which results in increased affinity in the SMP complex overall <ref name="Liau" />. If these mutations happen all at once, or just one or two at a time, it can still significantly alter the functionality of the SMP complex <ref name="Liau" />. This can lead to diseases like Noonan syndrome, which is where there are developmental and growth issues, and can even lead to cancers <ref name="Liau" />. | Mutations affecting SMP complex formation and stability can increase or decrease MAPK signaling, where increased stability of the complex increases MAPK signaling while decreased stability decreases signaling <ref name="Liau" />. There are a set of mutations that can happen on the SMP complex as a whole that can cause [https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/noonan-syndrome/symptoms-causes/syc-20354422. Noonan syndrome], a rasopathy disorder <ref name="Liau" />. On SHOC2, if the following mutations S2G, C260Y, and P510L caused differences in the complex formation with PP1C <ref name="Liau" />. On PP1C, the mutation P50R resulted in stronger ionic interactions with residues on SHOC2, resulting in a more stabilized complex <ref name="Liau" />. On MRAS, mutations such as G23V and T681I, can increase the proportion of MRAS that is GTP bound, which results in increased affinity in the SMP complex overall <ref name="Liau" />. If these mutations happen all at once, or just one or two at a time, it can still significantly alter the functionality of the SMP complex <ref name="Liau" />. This can lead to diseases like Noonan syndrome, which is where there are developmental and growth issues, and can even lead to cancers <ref name="Liau" />. | ||
===Future Studies=== | ===Future Studies=== | ||
| - | With this understood knowledge about how the SMP is able to contribute to an increase or decrease of MAPK pathways, there can be further research done to develop treatments for various cancers and rasopathies <ref name="Liau" />. Research can be done to develop inhibitors that can alter the affinity of the SMP complex in order to regulate MAPK signaling pathways <ref name="Liau" />. This can help treat diseases that are caused by unregulated cell proliferation <ref name="Liau" />. | + | With this understood knowledge about how the SMP is able to contribute to an increase or decrease of MAPK pathways, there can be further research done to develop treatments for various cancers and rasopathies <ref name="Liau" />. Research can be done to develop inhibitors that can alter the affinity of the SMP complex in order to regulate MAPK signaling pathways <ref name="Liau" />. This can help treat diseases that are caused by unregulated cell proliferation <ref name="Liau" />. Another possible point of inhibition is the growth factor that signals SHOC2-PP1C and Raf to the cell membrane. <ref name="Liau" /> . |
[[Image:Complex.png|800 px|thumb|center|'''Figure 3:'''Signaling cascade is shown with SHOC2 (magenta), PP1C (blue), and MRAS (white). SHOC2 binds to PP1C then to MRAS at the cell membrane. The SMP complex is now oriented near the membrane bound RAF complex (green). ]] | [[Image:Complex.png|800 px|thumb|center|'''Figure 3:'''Signaling cascade is shown with SHOC2 (magenta), PP1C (blue), and MRAS (white). SHOC2 binds to PP1C then to MRAS at the cell membrane. The SMP complex is now oriented near the membrane bound RAF complex (green). ]] | ||
[[Image:Dephosphorylation.jpg|600 px|thumb|center|'''Figure 4:'''PP1C dephosphorylates RAF protein at serine 259 ]] | [[Image:Dephosphorylation.jpg|600 px|thumb|center|'''Figure 4:'''PP1C dephosphorylates RAF protein at serine 259 ]] | ||
| - | + | ||
| + | |||
| - | ==RASopathies== | ||
| - | RASopathy is a broad term used to describe developmental syndromes that stem from [https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/medicine-and-dentistry/germline-mutation. germline mutations] of proteins along the RAS/MAPK pathway such as SHOC2, PP1C, and MRAS. These mutations can be either gain or loss of function. Rasopathies can also lead to cancer <ref name=”Rauen”>Rauen KA. The RASopathies. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet. 2013;14:355-69. [http://dx.doi.org/10.1146/annurev-genom-091212-153523 doi: 10.1146/annurev-genom-091212-153523.]</ref>. | ||
| - | |||
| - | ==Cancer== | ||
| - | |||
| - | Because the RAS/MAPK pathway activated by SMP regulates cell proliferation and survival, overactivity can cause tumor formation and cancer. For example, the complex has been found to play a role in the perpetuation of melanoma, leukemia, and lung cancer <ref name="Kwon" />. | ||
| - | |||
| - | =Future Studies= | ||
| - | |||
| - | Further study of the SMP complex includes clarification of the steps of the pathway. Firstly, the order of binding to form the SMP complex is unclear. Furthermore, the interaction between SMP and the Raf complex is largely unknown. Study into this step is especially important to understand how SMP activates downstream signaling. | ||
| - | The current knowledge of SMP can be used to study possible treatments for rasopathies and cancer. For example, the development of inhibitors that target SMP binding could prevent the effects caused by mutations that overactivate SMP. Another possible point of inhibition is the growth factor that signals SHOC2-PP1C and Raf to the cell membrane. <ref name="Liau" /> . | ||
Revision as of 22:39, 20 April 2023
| |||||||||||