N-terminal domain
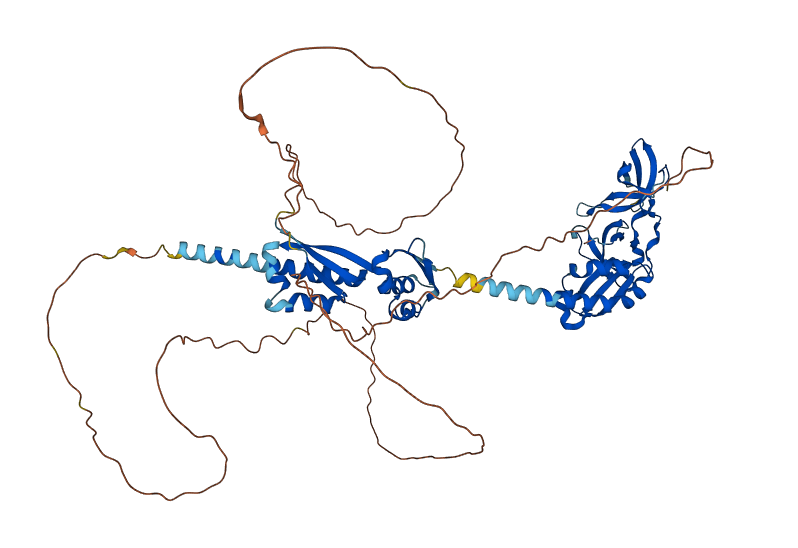
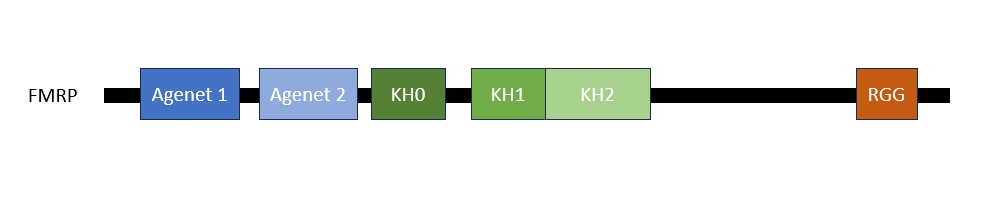
The N-terminal domain (NTD) of the FMRP includes the first 215 aminoacids of the protein, containing two in tandem Agenet domains and one KH domain. The NTD is important for the functions of the protein as a RBP and its participation in the ribonucleoprotein (RNP) complex.
The NTD was shown to adopt independent folding, and its tertiary structure was found to be compatible with two tandem . Both of the Agenet domains resemble those of Argonaute, a protein involved with interference RNA, and as they resemble structuraly Tudor domains, it is possible to assume functional similarities between them.
The , characterize the Agenet domain and its structure, and there is a , highlighted in magenta, between the beta sheets of the Agenet 1 and Agenet 2 connecting and stabilizing them.
It's been shown that, when the FMRP is in the nucleus, the Agenet domain allow the FMRP to interact with the chromatin and regulate DNA damage response, as it has been demonstrated that the Agenet domains bind to methylated lysine, in support to the histone binding function of the FMRP, due to its aromatic cage in the structure; specifically, the Agenet motif 2 binds to trimethylated lysine. The highlited in red are part of the Agenet 1 and the ones highlited in blue are part of the Agenet 2 domain related to the recognition of methylated lysine as they all have aromatic cages with the potential for this binding.
The K-homology domain (KH domain) folding is similar to other RBPs domains, which play an important role in RNA binding and protein-protein interactions.
Here, it is the highlighted in red. Many RNA-binding proteins contain the KH motif, a conserved RNA-binding domain, but different from the KH1 and KH2 motifs, which contain a G-X-X-G canonical motif, that will be explained in further details in the next topic, instead this one has an . It is most likely involved in RNA binding and regulation, as seen in other proteins that also contain KH motifs. To give a more thorough response addressing the precise role played by the KH theme in FMRP, additional details would be needed.
Overall, the FMRP NTD plays an important role as an RNA-binding protein, and its involvement in RNP complexes and its specific domains and motifs allow it to bind to specific RNAs and regulate their translation. [3]
The 3D structure of the N-terminal domain was obtained by X-ray diffraction with a 3.19 Å resolution and expressed in E. coli.
Central portion
The central portion of the protein contains the in tandem . The type of KH domains in eukaryots is type 1 fold, present in eukaryotes, in which a , and they both have a canonical (glycine followed by any two aminoacids and another glycine) conserved domain, highlighted in magenta, connecting the central helices of the domain and a variable loop. There is a gap in the KH motif, which can hold four nucleic acid bases; it happens when an alpha-helix 1, alpha-helix 2, a G-X-X-G on the left, and a variable loop are present in the domain, in the case of the FMRP another beta-sheet. This helps the FMRP in its RBP function, as they are motifs that are related to RNA or ssDNA binding. [4]
RGG motif
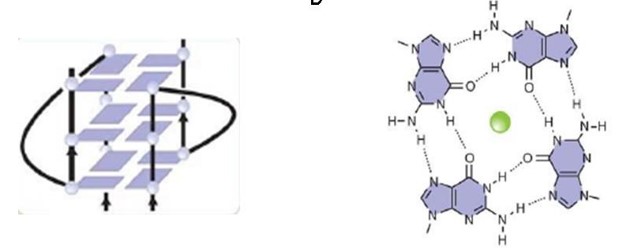
An important motif of the FMRP is the , which the protein uses to bind to guanine G-quadruplexes, a structure that consists of nucleic acid folding in which four guanines arrange in a planar conformation stabilized by Hoogsteen-type hydrogen bonds, named tetrad. FMRP RGG motifs seem to prefer binding to specific structures, not linear motifs.
Different domains and motifs mediate the RNA binding mechanism, and the exon 15-encoded (arginine - glycine - glycine) motif is one of them, it is located in the C-terminal region of the protein and is well conserved in vertebrates.
The secondary RNA structure being represented is one of the sc1 RNA and it's forming a three planar as shown, and the binding with the sc1 RNA and the FMRP occurs through β turns in the FMRP and as it makes some arginine residues bind by hydroge binding to the guanines, and in the middle of the planar conformations there are K+ cations binding to specific sites within the RNA structure, and contribute to the stability and folding of the G-quadruplex. The presence of K+ cations is crucial for the binding of the RGG motif of FMRP to the RNA, as it favors G-quadruplex folding and enhances the binding affinity, in the image below the green ball represent an ion in the middle of the planar conformation. Several tetrads can stack in a single G-quadruplex structure and be stabilized further by potassium cations, in the case of FMRP targets, whereas they are destabilized by lithium cations.
The regulation of particular mRNAs and the binding of FMRP with ribosomes and proteins depend on this interaction between the RGG motif and G-quadruplex RNA.
Therefore, understanding the interaction RGG-RNA is important for the comprehension of FMRP and FXS. The structure being represented on the right represents the FMRP RGG motif and the G-quadruplex secondary structure in the RNA.
The protein structure was obtained by X-ray diffraction with a resolution of 3 Å. [5]
Associated diseases
Trinucleotides repeats (CGG) are located in CpG islands in the 5' untranslated region (UTR) of the gene related to the expression of the gene. Individuals carrying up to 44 repeats of trinucleotides are of common aleles. Individuals that have between 44 and 55 repeats are known to carry the premutation, usually associated with FXTAS and PFO1. However, when the repeat expansion is above 55 the individual is carrying the full mutation, which leads to the silencing of the gene, due to methylation, therefore there is absence or reduced levels of the FMRP, causing abnormal synaptic development and symptons associated with the FXS.
References
- ↑ SUARDI, G. A. M.; HADDAD, L. A. Chapter Three - FMRP ribonucleoprotein complexes and RNA homeostasis.[1]
- ↑ Hu, Y., Chen, Z., Fu, Y., He, Q., Jiang, L., Zheng, J., Gao, Y., Mei, P., Chen, Z. and Ren, X. (2015). The amino-terminal structure of human fragile X mental retardation protein obtained using precipitant-immobilized imprinted polymers. Nature Communications, [online] 6(1), p.6634. [2]
- ↑ MYRICK, L. K. et al. Human FMRP contains an integral tandem Agenet (Tudor) and KH motif in the amino terminal domain. Human Molecular Genetics, v. 24, n. 6, p. 1733–1740, 20 nov. 2014.[3]
- ↑ Valverde, R., Edwards, L. and Regan, L. (2008). Structure and function of KH domains. FEBS Journal, 275(11), pp.2712–2726. [4]
- ↑ VASILYEV, N. et al. Crystal structure reveals specific recognition of a G-quadruplex RNA by a β-turn in the RGG motif of FMRP. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, v. 112, n. 39, p. E5391–E5400, 15 set. 2015.[5]