User:Marcos Vinícius Caetano/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
== Introduction == | == Introduction == | ||
| + | Myosin consists of a superfamily of '''actin motor protein''', being composed of at least 20 structurally and functionally distinct classes. Specifically in humans, there are 39 myosin genes, encoding 12 of these classes. Myosins use ATP hydrolysis to move molecular cargoes along the actin filaments inside the cell. To this day, all characterized myosins move toward the plus-end of the filaments, except for '''myosin VI''', which moves in the opposite direction. | ||
| + | '''Myosin VI''' is the only myosin that moves towards the '''minus-end of the actin filament''' and this unique property was the target of different studies throughout the years, and it is studied until nowadays, showing the versatility and importance of this protein. | ||
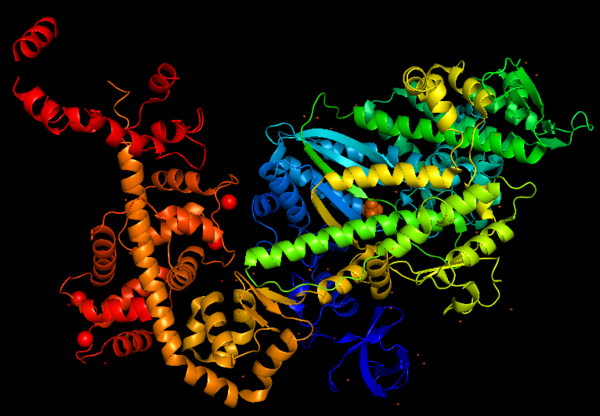
This is a figure of Myosin VI structure in gradient rainbow representation, where <span style="color:blue">'''blue'''</span> is N-terminal (5’) and <span style="color:red">'''red'''</span> the C-terminal (3’). | This is a figure of Myosin VI structure in gradient rainbow representation, where <span style="color:blue">'''blue'''</span> is N-terminal (5’) and <span style="color:red">'''red'''</span> the C-terminal (3’). | ||
[[Image:MyoVI.png|600px]] | [[Image:MyoVI.png|600px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Function == | ||
| + | Myosins (including Myosin VI) are involved in a wide variety of functions, such as cell migration and adhesion, cytokinesis, phagocytosis, maintenance of cell shape, signal transduction and intracellular transport and localization of organelles and macromolecules. Due to these diverse roles, each year more studies emerge with the objective to understand more of the structure, mechanisms and functions of myosins. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Structure == | ||
| + | The basic structure of myosin VI, and most myosin molecule heavy chains, consists of three regions: | ||
| + | The catalytic motor head domain (NH2-terminal motor): responsible for binding to actin and hydrolysis of ATP. It is a highly conserved structure; | ||
| + | The neck region: contains the IQ domain/motif that bind light chains (calcium sensor calmodulin); | ||
| + | The tail domain (COOH-terminal): binds cargoes and anchors the protein to specific membrane compartments. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
This figure portrays Myosin VI structure in terms of alpha helix (in <span style="color:red">'''red'''</span>) and β-sheet (in <span style="color:yellow">'''yellow'''</span>). The distortion of the central β-sheet differs depending on the states of the motor, such as post-rigor (ATP) or pre-powerstroke (ADP.Pi), and from other classes of myosin. | This figure portrays Myosin VI structure in terms of alpha helix (in <span style="color:red">'''red'''</span>) and β-sheet (in <span style="color:yellow">'''yellow'''</span>). The distortion of the central β-sheet differs depending on the states of the motor, such as post-rigor (ATP) or pre-powerstroke (ADP.Pi), and from other classes of myosin. | ||
| Line 11: | Line 24: | ||
[[Image:MyoVI alpha and beta v2.png|600px]] | [[Image:MyoVI alpha and beta v2.png|600px]] | ||
| - | == Function == | ||
Predicted amino acid sequences and cDNA comparison of Myosin VI in different species shows strong evolutionary conservation, mainly in the head/motor domain and in the distal tail region. This is probably due to the unique and different functions of this protein. This scene represents the <scene name='97/973101/Conservation/1'>Myosin VI evolutionary conservation</scene>, where <span style="color:pink">'''pink gradient'''</span> shows the more conserved region, <span style="color:grey">'''white'''</span> is average, <span style="color:blue">'''blue gradient'''</span> is the variable region and <span style="color:grey">'''grey'''</span> or <span style="color:yellow">'''yellow'''</span> is insufficient data. | Predicted amino acid sequences and cDNA comparison of Myosin VI in different species shows strong evolutionary conservation, mainly in the head/motor domain and in the distal tail region. This is probably due to the unique and different functions of this protein. This scene represents the <scene name='97/973101/Conservation/1'>Myosin VI evolutionary conservation</scene>, where <span style="color:pink">'''pink gradient'''</span> shows the more conserved region, <span style="color:grey">'''white'''</span> is average, <span style="color:blue">'''blue gradient'''</span> is the variable region and <span style="color:grey">'''grey'''</span> or <span style="color:yellow">'''yellow'''</span> is insufficient data. | ||
Revision as of 22:43, 25 June 2023
Myosin VI nucleotide-free (MDinsert2-IQ) crystal structure
| |||||||||||