Introduction
Myosin consists of a superfamily of actin motor protein, being composed of at least 20 structurally and functionally distinct classes. Specifically in humans, there are 39 myosin genes, encoding 12 of these classes. Myosins use ATP hydrolysis to move molecular cargoes along the actin filaments inside the cell. To this day, all characterized myosins move toward the plus-end of the filaments, except for myosin VI, which moves in the opposite direction.
Myosin VI is the only myosin that moves towards the minus-end of the actin filament and this unique property was the target of different studies throughout the years, and it is studied until nowadays, showing the versatility and importance of this protein.
This is a figure of Myosin VI structure in gradient rainbow representation, where blue is N-terminal (5’) and red the C-terminal (3’).
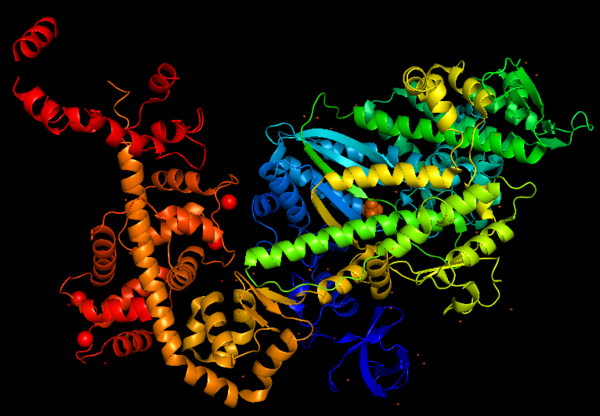
The basic structure of myosin VI, and most myosin molecule heavy chains, consists of three regions:
- The catalytic motor head domain (N-terminal motor): responsible for binding to actin and hydrolysis of ATP. It is a highly conserved structure;
- The neck region: contains the IQ domain/motif that bind light chains (calcium sensor calmodulin);
- The tail domain (C-terminal): binds cargoes and anchors the protein to specific membrane compartments.
Predicted amino acid sequences and cDNA comparison of myosin VI in different species shows strong evolutionary conservation, mainly in the head/motor domain and in the distal tail region. This is probably due to the unique and different functions of this protein. This scene represents the , where pink gradient shows the more conserved region, white is average, blue gradient is the variable region and grey or yellow is insufficient data.
Function
Myosins (including Myosin VI) are involved in a wide variety of functions, such as cell migration and adhesion, cytokinesis, phagocytosis, maintenance of cell shape, signal transduction and intracellular transport and localization of organelles and macromolecules. Due to these diverse roles, each year more studies emerge with the objective to understand more of the structure, mechanisms and functions of myosins.
ATPase cycle of myosin VI
Structure features
The crystal structure of the entry '2BKI' was determined by x-ray diffraction with the resolution of 2,90 Å and is composed by 3 chains: and two chains of .
Secondary structures
The figure below portrays Myosin VI structure in terms of alpha helix (in red) and β-sheet (in yellow). The central β-sheet is the major component of the transducer and it can adopt differently twisted conformations depending on the nucleotide- and actin-binding states of the motor, such as post-rigor (ATP) or pre-powerstroke (ADP.Pi). This distortion also differs from classes of myosin.

Unique features
The unique function and distinct characteristic of myosin VI is due to its structure, having several unusual features, listed below.
The motor domain contains two inserts that are unique in the myosin superfamily:
Insert 1: .
- Location: This insert belongs to the U50kDa subdomain and it is located near the nucleotide-binding pocket and the Switch I.
- Function: This insert provides unique kinetic characteristics: it modulates nucleotide binding and Switch I flexibility, therefore, it slows ADP release and ATP-induced dissociation of the motor from actin (at saturating ATP concentrations).
- Mechanism: As also seen in all other myosins, the conformation of Switch I relative to the U50kDa subdomain is not altered by the presence of insert 1. However, the small loop ( - in grey) that follows this insert, is repositioned, standing out in the nucleotide-binding pocket (decreasing nucleotide accessibility by steric impediment) and strongly interacting with Switch I by the residues: (in red). Also, (in green) of insert 1 interacts with Switch I. (highlighted in blue) is specifically important because its position selectively interferes with ATP binding, while having little or no effect on ADP binding. Mutation of leucine 310 to glycine removes all influence of insert-1 on ATP binding.
Insert 2:
- Location: This insert is between the converter and the IQ motif
- Function: Redirectionare the lever arm and contains a new CaM-binding motif.
- Mechanism: The proximal part of insert 2 ( - in red) wraps around the converter, while the distal part ( - in green) forms a CaM-binding motif. The insert 2 and its associated CaM molecule (with 4Ca2+), make specific interactions with the converter, many involving a variable loop ( - in magenta). The result of interactions is that IQ helix emerges ~120° from the position that it emerges in all other myosins, redirecting the IQ helix and the CaM towards the minus end of the actin filament.
3D structure
All 3D structure, models and scenes were based on 2BKI - Myosin VI nucleotide-free (MDinsert2-IQ) crystal structure, published in https://doi.org/10.1038/nature03592 - Ménétrey, J., Bahloul, A., Wells, A. L., Yengo, C. M., Morris, C. A., Sweeney, H. L., & Houdusse, A. (2005). The structure of the myosin VI motor reveals the mechanism of directionality reversal. Nature, 435(7043), 779–785.
References


