Journal:MicroPubl Biol:000867
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)

| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
<hr/> | <hr/> | ||
<b>Molecular Tour</b><br> | <b>Molecular Tour</b><br> | ||
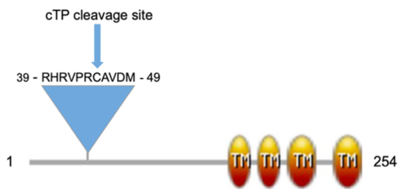
| - | Cotton plays a significant role in the United States economy and research on cotton is essential as the price of cotton and the financial gain to the cotton grower is dependent on the fiber yield and quality. Recently, the genomes of five allotetraploid cotton species (''Gossypium hirsutum'', ''Gossypium barbadense'', ''Gossypium mustelinum'', ''Gossypium tomentosum'', ''Gossypium darwinii'') were sequenced<ref name="Chen">PMID:32313247</ref>, and analysis of gene annotations revealed many genes of unknown function in common across the species. One of these genes of unknown function, the ''Gossypium hirsutum'' gene Gohir.A03G073700 and associated protein (UniProt: A0A1U8HKT6) here referred to as GhCPP1-A0A1U8HKT6, was studied using bioinformatic tools and is proposed to be a chaperone-like protein of POR1 (CPP1). | + | Cotton plays a significant role in the United States economy and research on cotton is essential as the price of cotton and the financial gain to the cotton grower is dependent on the fiber yield and quality. Recently, the genomes of five allotetraploid cotton species (''Gossypium hirsutum'', ''Gossypium barbadense'', ''Gossypium mustelinum'', ''Gossypium tomentosum'', ''Gossypium darwinii'') were sequenced<ref name="Chen">PMID:32313247</ref>, and analysis of gene annotations revealed many genes of unknown function in common across the species. One of these genes of unknown function, the ''Gossypium hirsutum'' gene Gohir.A03G073700 and associated protein (UniProt: A0A1U8HKT6) here referred to as GhCPP1-A0A1U8HKT6, was studied using bioinformatic tools and is proposed to be a chaperone-like protein of POR1 (CPP1). <scene name='97/977777/Test/8'>TextToBeDisplayed</scene> |
Most plants require light for the biosynthesis of the green pigment chlorophyll, which is central to the process of photosynthesis. One of the later steps of the chlorophyll biosynthetic pathway is facilitated by protochlorophyllide oxidoreductase (POR), a light-dependent enzyme<ref name="Lee">PMID:24151298</ref>. To complete chlorophyll biosynthesis, the POR enzyme must be post-translationally imported into the chloroplast. The chaperone-like protein of POR1 (CPP1) in Arabidopsis has been shown to regulate POR transport and function during this process although its specific role in the process is still unclear<ref name="Lee">PMID:24151298</ref>. Due to the structural similarity between the J-like domain in CPP1 and the J domain in the DnaJ/HSP70 protein family, it has been suggested that CPP1 has a function similar to the “holdase” chaperone function of the J domain that helps organize interactions with Hsp70 chaperone partners<ref name="Kelley">PMID:9644977</ref>. A functionally conserved His-Pro-Asp (HPD) motif within J-domains facilitates this interaction and, although very similar in structure to the J domain, the HPD motif is absent in J-like domain proteins such as CPP1, indicating these domains may perform a similar molecular function but may have diverged interaction partners. | Most plants require light for the biosynthesis of the green pigment chlorophyll, which is central to the process of photosynthesis. One of the later steps of the chlorophyll biosynthetic pathway is facilitated by protochlorophyllide oxidoreductase (POR), a light-dependent enzyme<ref name="Lee">PMID:24151298</ref>. To complete chlorophyll biosynthesis, the POR enzyme must be post-translationally imported into the chloroplast. The chaperone-like protein of POR1 (CPP1) in Arabidopsis has been shown to regulate POR transport and function during this process although its specific role in the process is still unclear<ref name="Lee">PMID:24151298</ref>. Due to the structural similarity between the J-like domain in CPP1 and the J domain in the DnaJ/HSP70 protein family, it has been suggested that CPP1 has a function similar to the “holdase” chaperone function of the J domain that helps organize interactions with Hsp70 chaperone partners<ref name="Kelley">PMID:9644977</ref>. A functionally conserved His-Pro-Asp (HPD) motif within J-domains facilitates this interaction and, although very similar in structure to the J domain, the HPD motif is absent in J-like domain proteins such as CPP1, indicating these domains may perform a similar molecular function but may have diverged interaction partners. | ||
Revision as of 12:20, 26 July 2023
| |||||||||||
This page complements a publication in scientific journals and is one of the Proteopedia's Interactive 3D Complement pages. For aditional details please see I3DC.