User:Brynn Baker/Sandbox1
From Proteopedia
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
== Amylin == | == Amylin == | ||
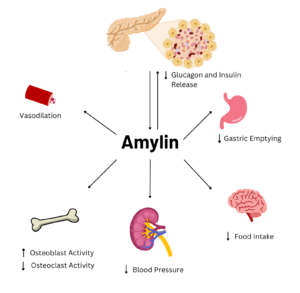
| - | Amylin is a neuroendocrine hormone that is synthesized with insulin in the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Beta_cell beta cells] of pancreatic islets. It can cross the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Blood%E2%80%93brain_barrier blood-brain barrier] and regulates glucose homeostasis via inhibiting gastric emptying, inhibiting the release of glucagon, and inducing meal-ending satiety <ref name=" | + | Amylin is a neuroendocrine hormone that is synthesized with insulin in the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Beta_cell beta cells] of pancreatic islets. It can cross the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Blood%E2%80%93brain_barrier blood-brain barrier] and regulates glucose homeostasis via inhibiting gastric emptying, inhibiting the release of glucagon, and inducing meal-ending satiety<ref name="Hay">PMID:26071095</ref>. In doing so, it prevents spikes in blood glucose and overeating, making it a suitable target for [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Type_2_diabetes Type 2 Diabetes] treatments and therapies. Seeing as Type 2 Diabetes is a major risk factor for [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Alzheimer%27s_disease Alzheimer's Disease], as Type 2 Diabetes cases continue to increase, there will likely be a spike in Alzheimer’s Disease as well <ref name="Grizzanti">PMID:30282360</ref>. Therefore, it is vital that amylin, its receptor, and analogs, such as pramlintide, are understood to aid in rational drug design. |
[[Image:AmylinFlowchart.png|300 px|left|thumb|Figure 2. Effects of Amylin in Humans]] | [[Image:AmylinFlowchart.png|300 px|left|thumb|Figure 2. Effects of Amylin in Humans]] | ||
Revision as of 00:32, 10 April 2024
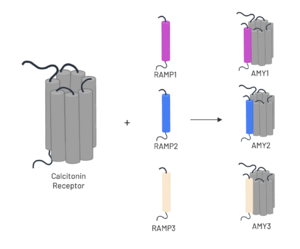
Homo sapiens Amylin3 Receptor, AMYR3
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Hay DL, Chen S, Lutz TA, Parkes DG, Roth JD. Amylin: Pharmacology, Physiology, and Clinical Potential. Pharmacol Rev. 2015 Jul;67(3):564-600. PMID:26071095 doi:10.1124/pr.115.010629
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Grizzanti J, Corrigan R, Casadesus G. Neuroprotective Effects of Amylin Analogues on Alzheimer's Disease Pathogenesis and Cognition. J Alzheimers Dis. 2018;66(1):11-23. PMID:30282360 doi:10.3233/JAD-180433
- ↑ Bower RL, Hay DL. Amylin structure-function relationships and receptor pharmacology: implications for amylin mimetic drug development. Br J Pharmacol. 2016 Jun;173(12):1883-98. PMID:27061187 doi:10.1111/bph.13496
- ↑ Cao J, Belousoff MJ, Liang YL, Johnson RM, Josephs TM, Fletcher MM, Christopoulos A, Hay DL, Danev R, Wootten D, Sexton PM. A structural basis for amylin receptor phenotype. Science. 2022 Mar 25;375(6587):eabm9609. PMID:35324283 doi:10.1126/science.abm9609
Bower, R.; Hay, D. Amylin structure-function relationships and receptor pharmacology: implications for amylin mimetic drug development. British Journal of Pharmacology. 2016, 173, 1883-1898. [1].
Cao, J.; Belousoff, J.; Liang, Y.; Johnson, R.; Josephs, T.; Fletcher, M.; Christopoulus, A.; Hay, D.; Danev, R.; Wootten, D.; Sexton, P. A structural basis for amylin receptor phenotype. Science. 2022, 375. [2].
Grizzanti, J.; Corrigan, R.; Casadesus, G. Neuroprotective Effects of Amylin Analogues on Alzheimer’s Disease Pathogenesis and Cognition. Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease. 2019, 66, 11-23. [3].
Hay, D.; Chen, S.; Lutz, T.; Parkes, D.; Roth, J. Amylin: Pharmacology, Physiology, and Clinical Potential. Pharmacological Reviews. 2015, 67, 564-600. [4].
Student Contributors
- Brynn Baker
- Emily Berkman
- Sepp Hall