We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Ben Whiteside
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
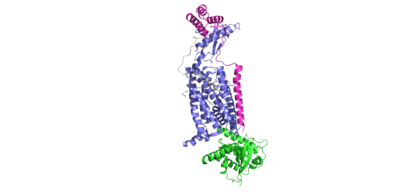
=== Transmembrane Domain === | === Transmembrane Domain === | ||
| - | + | Within the transmembrane domain of the CTR, hydrophobic R groups span the phospholipid bilayer, anchoring the protein into the cell membrane upon amylin binding to the receptor. | |
=== N Terminal Disulfide === | === N Terminal Disulfide === | ||
=== Receptor Activity Modifying Proteins === | === Receptor Activity Modifying Proteins === | ||
| - | <scene name='10/1038828/Ramp_ctr_interface/ | + | <scene name='10/1038828/Ramp_ctr_interface/8'>RAMP CTR Interface </scene> is a key interaction that stabilizes the protein complex and positions the receptor to favorably bind to amylin. The RAMP-CTR interface extends into the plasma membrane, providing additional non-covalent bonding between the protein complex and the cell membrane. |
==== Extracellular Domain - RAMP interactions ==== | ==== Extracellular Domain - RAMP interactions ==== | ||
| - | <scene name='10/1038828/Ctr_ramp_ecd_stablization/ | + | <scene name='10/1038828/Ctr_ramp_ecd_stablization/6'>RAMP CTR Extracellular Domain Interaction</scene> |
=== Bypass Motif === | === Bypass Motif === | ||
=== G-alpha Interactions with CTR TMD === | === G-alpha Interactions with CTR TMD === | ||
| - | <scene name='10/1038828/Ctr_g_alpha/ | + | <scene name='10/1038828/Ctr_g_alpha/10'>G alpha interactions with the Calcitonin Receptor 1 </scene> |
| + | <scene name='10/1038828/Ctr_g_alpha/11'>G alpha interactions with the Calcitonin Receptor 2 </scene> | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
Revision as of 13:24, 16 April 2024
AMYR
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Hanson, R. M., Prilusky, J., Renjian, Z., Nakane, T. and Sussman, J. L. (2013), JSmol and the Next-Generation Web-Based Representation of 3D Molecular Structure as Applied to Proteopedia. Isr. J. Chem., 53:207-216. doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/ijch.201300024
- ↑ Herraez A. Biomolecules in the computer: Jmol to the rescue. Biochem Mol Biol Educ. 2006 Jul;34(4):255-61. doi: 10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644. PMID:21638687 doi:10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644
- ↑ Ransey E, Paredes E, Dey SK, Das SR, Heroux A, Macbeth MR. Crystal structure of the Entamoeba histolytica RNA lariat debranching enzyme EhDbr1 reveals a catalytic Zn(2+) /Mn(2+) heterobinucleation. FEBS Lett. 2017 Jul;591(13):2003-2010. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.12677. Epub 2017, Jun 14. PMID:28504306 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/1873-3468.12677
- ↑ Cao J, Belousoff MJ, Liang YL, Johnson RM, Josephs TM, Fletcher MM, Christopoulos A, Hay DL, Danev R, Wootten D, Sexton PM. A structural basis for amylin receptor phenotype. Science. 2022 Mar 25;375(6587):eabm9609. PMID:35324283 doi:10.1126/science.abm9609
Student Contributors
Ben Whiteside, Mathias Vander Eide, Andrew Helmerich,