User:Brynn Baker/Sandbox1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
== Introduction == | == Introduction == | ||
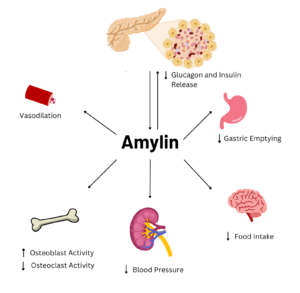
| - | In 1900, amylin deposits were first discovered in [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pancreatic_islets pancreatic islet cells] in diabetic patients. Later in 1943, it was determined that these amylin deposits were [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Amyloid amyloid] in nature. By the 1980s, the 37 amino acid sequence of amylin was identified. By 1995, the first analogue of amylin, [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pramlintide pramlintide], was synthesized. In the late 1990s, it was discovered, through [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cryogenic_electron_microscopy cryogenic electron microscopy], that the amylin receptor was made of the calcitonin receptor core. The calcitonin heterodimerizes with a [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Receptor_activity-modifying_protein receptor-activating modifying protein | + | In 1900, amylin deposits were first discovered in [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pancreatic_islets pancreatic islet cells] in diabetic patients. Later in 1943, it was determined that these amylin deposits were [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Amyloid amyloid] in nature. By the 1980s, the 37 amino acid sequence of amylin was identified. By 1995, the first analogue of amylin, [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pramlintide pramlintide], was synthesized. In the late 1990s, it was discovered, through [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cryogenic_electron_microscopy cryogenic electron microscopy], that the amylin receptor was made of the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Calcitonin_receptor calcitonin receptor (CT)] core. The calcitonin heterodimerizes with a [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Receptor_activity-modifying_protein receptor-activating modifying protein (RAMP)] to form different amylin receptors. Overall, the human amylin receptor is a [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/G_protein-coupled_receptor G-coupled protein receptor]. |
== Amylin == | == Amylin == | ||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
=== Structure === | === Structure === | ||
== Amylin Receptor == | == Amylin Receptor == | ||
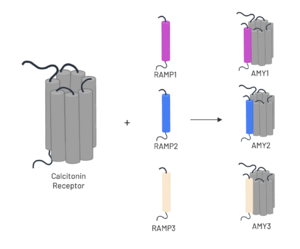
| - | The amylin receptor (AMYR) is the result of the heterodimerization of the | + | The amylin receptor (AMYR) is the result of the heterodimerization of the <scene name='10/1037516/Ct/1'>calcitonin receptor</scene> and a RAMP, such as <scene name='10/1037516/Ramp3/1'>RAMP3</scene>. The patterns of peptide interaction between CT and AMYR are very similar overall, but amylin has a higher affinity for AMYR1 and AMYR3 than AMYR2<ref name="Cao">PMID:35324283</ref>. |
[[Image:AMYR.png|300 px|left|thumb|Figure 3. Heterodimerization of CT and RAMPs]] | [[Image:AMYR.png|300 px|left|thumb|Figure 3. Heterodimerization of CT and RAMPs]] | ||
== Calcitonin Receptor and G-alpha Interactions == | == Calcitonin Receptor and G-alpha Interactions == | ||
| - | The calcitonin receptor forms several highly conserved interactions with the Gɑ subunit. The main chain of N396 on CT hydrogen bonds with the sidechain of E392 on Gɑ, as do the main chain of I248 and sidechain of Q384, respectively<ref name="Cao">PMID:35324283</ref>. | + | The calcitonin receptor forms several highly conserved interactions with the Gɑ subunit. The <scene name='10/1037516/Calc_and_galpha_nande/2'>main chain of N396 on CT hydrogen bonds with the sidechain of E392 on Gɑ</scene>, as do the <scene name='10/1037516/Calc_and_galpha_qandi/2>main chain of I248 and sidechain of Q384</scene>, respectively<ref name="Cao">PMID:35324283</ref>. |
== RAMPs == | == RAMPs == | ||
Revision as of 20:19, 21 April 2024
Homo sapiens Amylin3 Receptor, AMYR3
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Hay DL, Chen S, Lutz TA, Parkes DG, Roth JD. Amylin: Pharmacology, Physiology, and Clinical Potential. Pharmacol Rev. 2015 Jul;67(3):564-600. PMID:26071095 doi:10.1124/pr.115.010629
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Grizzanti J, Corrigan R, Casadesus G. Neuroprotective Effects of Amylin Analogues on Alzheimer's Disease Pathogenesis and Cognition. J Alzheimers Dis. 2018;66(1):11-23. PMID:30282360 doi:10.3233/JAD-180433
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 3.6 3.7 3.8 3.9 Cao J, Belousoff MJ, Liang YL, Johnson RM, Josephs TM, Fletcher MM, Christopoulos A, Hay DL, Danev R, Wootten D, Sexton PM. A structural basis for amylin receptor phenotype. Science. 2022 Mar 25;375(6587):eabm9609. PMID:35324283 doi:10.1126/science.abm9609
- ↑ Bower RL, Hay DL. Amylin structure-function relationships and receptor pharmacology: implications for amylin mimetic drug development. Br J Pharmacol. 2016 Jun;173(12):1883-98. PMID:27061187 doi:10.1111/bph.13496
Student Contributors
- Brynn Baker
- Emily Berkman
- Sepp Hall