User:Jaelin Lunato/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
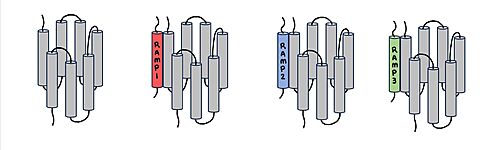
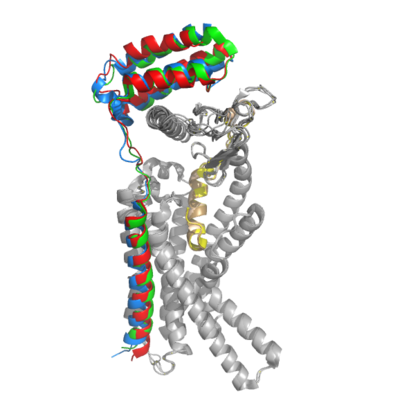
[[Image:Overlay of RAMPs.png|400 px|right|thumb|'''Figure 2.''' Superimposition of RAMP1, RAMP2, and RAMP3. RAMP1 is red, RAMP2 is blue, and RAMP3 is green. The amylin ligand is dark yellow, and the calcitonin ligand is pale yellow.]] AMYR is a heterodimer of a calcitonin receptor (CTR) and a receptor activity-modifying protein (RAMP). There are three different RAMPs, RAMP1, RAMP2, and RAMP3, that compose AMY1R, AMY2R, and AMY3R when associated with the CTR (Figure 1). The three different RAMPs are structurally similar to each other, so all three RAMPs are able to bind to the CTR without any modification of the CTR (Figure 2). | [[Image:Overlay of RAMPs.png|400 px|right|thumb|'''Figure 2.''' Superimposition of RAMP1, RAMP2, and RAMP3. RAMP1 is red, RAMP2 is blue, and RAMP3 is green. The amylin ligand is dark yellow, and the calcitonin ligand is pale yellow.]] AMYR is a heterodimer of a calcitonin receptor (CTR) and a receptor activity-modifying protein (RAMP). There are three different RAMPs, RAMP1, RAMP2, and RAMP3, that compose AMY1R, AMY2R, and AMY3R when associated with the CTR (Figure 1). The three different RAMPs are structurally similar to each other, so all three RAMPs are able to bind to the CTR without any modification of the CTR (Figure 2). | ||
| - | The two major ligands of the calcitonin receptor are [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Calcitonin calcitonin] and [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Amylin amylin]. In the absence of a RAMP, the calcitonin receptor has greater affinity for calcitonin than amylin, but because the <scene name='10/ | + | The two major ligands of the calcitonin receptor are [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Calcitonin calcitonin] and [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Amylin amylin]. In the absence of a RAMP, the calcitonin receptor has greater affinity for calcitonin than amylin, but because the <scene name='10/1037495/Overlay_of_ligands/1'>two ligands are structurally similar</scene>, both calcitonin and amylin can bind to the CTR without any modification of the receptor (Figure 3). When the CTR is bound to a RAMP, the complex becomes the AMYR and has greater affinity for the <scene name='10/1037495/Ligand_in_membrane/2'>amylin ligand</scene> relative to the calcitonin ligand.(REFERENCE NEEDED HERE******)[[Image:Sequence alignment ligands.png|500px|left|thumb|'''Figure 3.''' Sequence alignment of rat amylin and salmon calcitonin. Conserved residues are highlighted in blue.]] |
| - | There are two required post-translational modifications of amylin in order for the ligand to have any bioactivity: (1) <scene name='10/1037495/C-term_amide/ | + | There are two required post-translational modifications of amylin in order for the ligand to have any bioactivity: (1) <scene name='10/1037495/C-term_amide/2'>amidation of the C-terminus</scene> and (2) a <scene name='10/1037495/Amylin_disulfide_bond2/4'>disulfide bond</scene> between C2 and C7. |
=== Binding Site Residues === | === Binding Site Residues === | ||
| Line 44: | Line 44: | ||
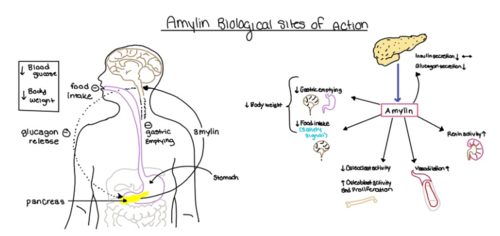
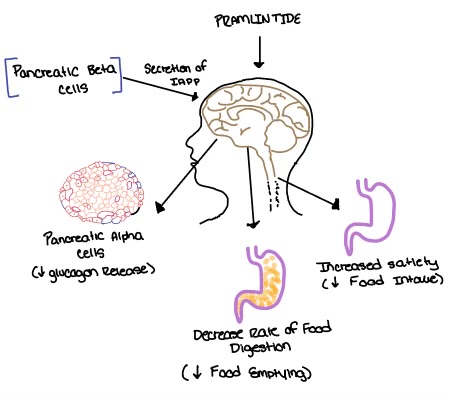
Pramlintide, a peptide analog of human amylin, is FDA-approved for the treatment of insulin-requiring diabetes (Figure 5). Pramlintide is injected into the bloodstream by the beta cells of the pancreas along with insulin after a meal, aiding in the regulation of blood glucose by slowing [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Stomach gastric emptying], promoting [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Satiety satiety] via [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hypothalamus hypothalamic] receptors, and inhibiting secretion of glucagon which opposes the effects of insulin and amylin (Figure 6). | Pramlintide, a peptide analog of human amylin, is FDA-approved for the treatment of insulin-requiring diabetes (Figure 5). Pramlintide is injected into the bloodstream by the beta cells of the pancreas along with insulin after a meal, aiding in the regulation of blood glucose by slowing [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Stomach gastric emptying], promoting [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Satiety satiety] via [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hypothalamus hypothalamic] receptors, and inhibiting secretion of glucagon which opposes the effects of insulin and amylin (Figure 6). | ||
| - | [[Image:Pramlintide.jpeg|500 px|right|thumb|'''Figure 6.''' Pramlintide's effect on the human body. Pramlintide is a peptide agonist of human amylin and is | + | [[Image:Pramlintide.jpeg|500 px|right|thumb|'''Figure 6.''' Pramlintide's effect on the human body. Pramlintide is a peptide agonist of human amylin and is a FDA approved treatment for diabetes.]] |
| Line 51: | Line 51: | ||
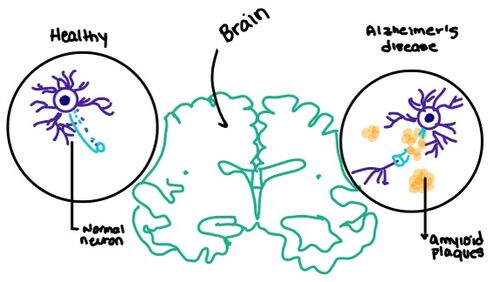
[[Image:Amylin brain.jpeg|500 px|right|thumb|'''Figure 7.''' Amylin's effect on the brain through the buildup of amyloid plaques.]] | [[Image:Amylin brain.jpeg|500 px|right|thumb|'''Figure 7.''' Amylin's effect on the brain through the buildup of amyloid plaques.]] | ||
| - | + | ||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
Revision as of 13:23, 23 April 2024
Amylin Receptor (AMYR)
| |||||||||||