This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
User:Jaelin Lunato/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
== Structure == | == Structure == | ||
=== Cellular Domains === | === Cellular Domains === | ||
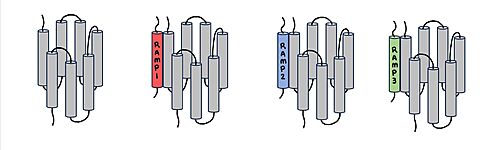
| - | [[Image:RAMP_diagram.jpg|500px|right|thumb|'''Figure 1.''' Three different RAMPs to compose AMY1R, AMY2R, and AMY3R when associated with the calcitonin receptor (shown in grey). RAMP1 is in red, RAMP2 is in blue, and RAMP3 is in green.]] AMYR has three domains: extracellular, transmembrane, and intracellular. | + | [[Image:RAMP_diagram.jpg|500px|right|thumb|'''Figure 1.''' Three different RAMPs to compose AMY1R, AMY2R, and AMY3R when associated with the calcitonin receptor (shown in grey). RAMP1 is in red, RAMP2 is in blue, and RAMP3 is in green.]] AMYR has three domains: extracellular, transmembrane, and intracellular. The CTR and the RAMP have both <scene name='10/1037495/Extracellular_domain/7'>extracellular domains</scene> and <scene name='10/1037495/Transmembrane/6'>transmembrane domains</scene>. The calcitonin receptor is a 7-pass helix chain to which RAMP binds to become the amylin receptor <ref name="Hay">PMID:26071095</ref>. The ligand, amylin, binds within the transmembrane domain. The [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/G_protein G protein] is located <scene name='10/1037495/Intracellular_domain/2'>inside the cell</scene>. The location of each component of the amylin receptor is essential in determining structure and function. For example, it is important for the G protein to be located inside the cell in order to initiate a signal cascade for cell signaling <ref name="Cao">PMID:35324283</ref>. |
=== CTR and RAMP Heterodimer === | === CTR and RAMP Heterodimer === | ||
| Line 57: | Line 57: | ||
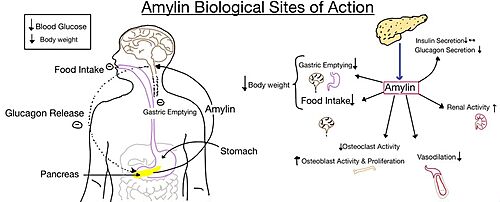
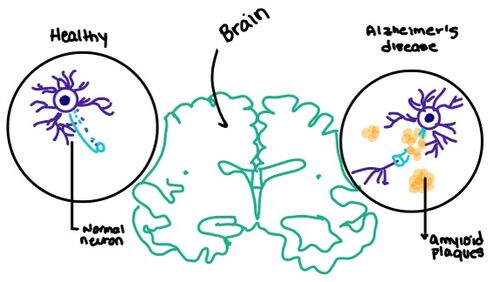
| - | [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Alzheimer%27s_disease Alzheimer's] is a neurodegenerative disease that is commonly associated with the slow progression of amyloid plaque build-up within the gray matter of the aging brain. [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Amyloid_plaques Amyloid Plaques], also known as neuritic plaques or senile plaques, are extracellular deposits of the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Amyloid_beta amyloid beta protein] that vary in both size and shape with the ability to clump together <ref name="Press">Press, M., Jung, T., Konig, J., Grune, T., & Hohn, A. (2019). Protein aggregates and proteostasis in aging: Amylin and β-cell function. ''Mechanisms of Ageing and Development. 3,'' 46-54. [http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.mad.2018.03.010 DOI:10.1016/j.mad.2018.03.010]</ref>. When abnormal levels of amylin containing plaques clump together, it creates deposits within the brain region to disrupt proper cell function (Figure 7.). Understanding this disruption is important due the structural overlap seen with amylin and calcitonin binding sites. It can be hypothesized that the conformational similarities between the receptor bringing regions is a key proponent in amyloid plaque build-up and neurodegenerative issues. | + | [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Alzheimer%27s_disease Alzheimer's] is a neurodegenerative disease that is commonly associated with the slow progression of amyloid plaque build-up within the gray matter of the aging brain. [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Amyloid_plaques Amyloid Plaques], also known as neuritic plaques or senile plaques, are extracellular deposits of the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Amyloid_beta amyloid beta protein] that vary in both size and shape with the ability to clump together <ref name="Press">Press, M., Jung, T., Konig, J., Grune, T., & Hohn, A. (2019). Protein aggregates and proteostasis in aging: Amylin and β-cell function. ''Mechanisms of Ageing and Development. 3,'' 46-54. [http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.mad.2018.03.010 DOI:10.1016/j.mad.2018.03.010]</ref>. When abnormal levels of amylin containing plaques clump together, it creates deposits within the brain region to disrupt proper cell function (Figure 7.) <ref name="Grizzanti">PMID:30282360</ref>. Understanding this disruption is important due the structural overlap seen with amylin and calcitonin binding sites. It can be hypothesized that the conformational similarities between the receptor bringing regions is a key proponent in amyloid plaque build-up and neurodegenerative issues. |
| Line 67: | Line 67: | ||
<ref name="7TYF"/> | <ref name="7TYF"/> | ||
<ref name="Hay"> | <ref name="Hay"> | ||
| + | <ref name="Cao"> | ||
<ref name="Thapa"> | <ref name="Thapa"> | ||
<ref name="Press"> | <ref name="Press"> | ||
| + | <ref name="Grizzanti"> | ||
== Student Contributors == | == Student Contributors == | ||
Revision as of 22:04, 24 April 2024
Amylin Receptor (AMYR)
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Cao J, Belousoff MJ, Liang YL, Johnson RM, Josephs TM, Fletcher MM, Christopoulos A, Hay DL, Danev R, Wootten D, Sexton PM. A structural basis for amylin receptor phenotype. Science. 2022 Mar 25;375(6587):eabm9609. PMID:35324283 doi:10.1126/science.abm9609
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 Hay DL, Chen S, Lutz TA, Parkes DG, Roth JD. Amylin: Pharmacology, Physiology, and Clinical Potential. Pharmacol Rev. 2015 Jul;67(3):564-600. PMID:26071095 doi:10.1124/pr.115.010629
- ↑ Cao J, Belousoff MJ, Liang YL, Johnson RM, Josephs TM, Fletcher MM, Christopoulos A, Hay DL, Danev R, Wootten D, Sexton PM. A structural basis for amylin receptor phenotype. Science. 2022 Mar 25;375(6587):eabm9609. PMID:35324283 doi:10.1126/science.abm9609
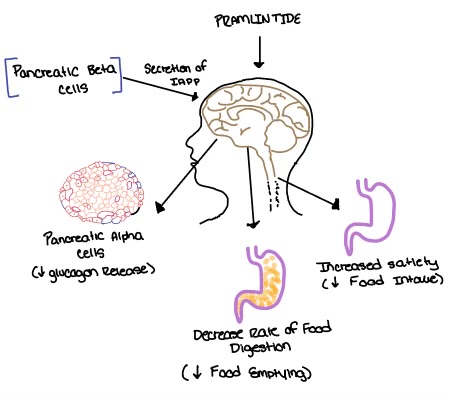
- ↑ Thapa, G., Kumari, A., Dasgupta, D., Bandyopadhy, S., Sarkar, N., Roy, K., Karunakaran, G., Kazmi, I., Karmakar, S., & Chakraborty, M. (2023). Chapter 5- Insight into the mechanism of action of anti-diabetic drugs. How Synthetic Drugs Work. 95-122. DOI:10.1016/B978-0-323-99855-0.00005-1
- ↑ Press, M., Jung, T., Konig, J., Grune, T., & Hohn, A. (2019). Protein aggregates and proteostasis in aging: Amylin and β-cell function. Mechanisms of Ageing and Development. 3, 46-54. DOI:10.1016/j.mad.2018.03.010
- ↑ Grizzanti J, Corrigan R, Casadesus G. Neuroprotective Effects of Amylin Analogues on Alzheimer's Disease Pathogenesis and Cognition. J Alzheimers Dis. 2018;66(1):11-23. PMID:30282360 doi:10.3233/JAD-180433