This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
User:Jaelin Lunato/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
== Structure == | == Structure == | ||
=== Cellular Domains === | === Cellular Domains === | ||
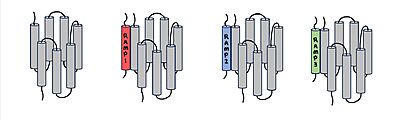
| - | [[Image:RAMP_diagram.jpg| | + | [[Image:RAMP_diagram.jpg|400px|right|thumb|'''Figure 1.''' Three different RAMPs to compose AMY1R, AMY2R, and AMY3R when associated with the calcitonin receptor (shown in grey). RAMP1 is in red, RAMP2 is in blue, and RAMP3 is in green.]] AMYR has three domains: extracellular, transmembrane, and intracellular. The CTR and the RAMP have both <scene name='10/1037495/Extracellular_domain/7'>extracellular domains</scene> and <scene name='10/1037495/Transmembrane/6'>transmembrane domains</scene>. The calcitonin receptor is a 7-pass helix chain to which RAMP binds to become the amylin receptor <ref name="Hay">PMID:26071095</ref>. The ligand, amylin, binds within the transmembrane domain. The [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/G_protein G protein] is located <scene name='10/1037495/Intracellular_domain/2'>inside the cell</scene>. The location of each component of the amylin receptor is essential in determining structure and function. For example, it is important for the G protein to be located inside the cell in order to initiate a signal cascade for cell signaling <ref name="Cao">PMID:35324283</ref>. |
=== CTR and RAMP Heterodimer === | === CTR and RAMP Heterodimer === | ||
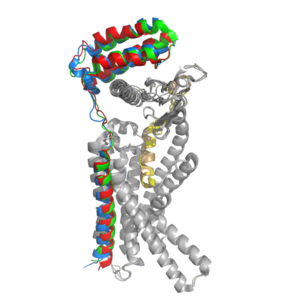
[[Image:Overlay of RAMPs.png|300 px|right|thumb|'''Figure 2.''' Superimposition of RAMP1, RAMP2, and RAMP3. RAMP1 is red, RAMP2 is blue, and RAMP3 is green. The amylin ligand is dark yellow, and the calcitonin ligand is pale yellow.]] AMYR is a heterodimer of a calcitonin receptor and a receptor activity-modifying protein. There are three different RAMPs, RAMP1, RAMP2, and RAMP3, that compose AMY1R, AMY2R, and AMY3R when associated with the CTR (Figure 1). The three different RAMPs are structurally similar to each other, so all three RAMPs are able to bind to the CTR without any modification of the CTR (Figure 2) <ref name="Hay">PMID:26071095</ref>. | [[Image:Overlay of RAMPs.png|300 px|right|thumb|'''Figure 2.''' Superimposition of RAMP1, RAMP2, and RAMP3. RAMP1 is red, RAMP2 is blue, and RAMP3 is green. The amylin ligand is dark yellow, and the calcitonin ligand is pale yellow.]] AMYR is a heterodimer of a calcitonin receptor and a receptor activity-modifying protein. There are three different RAMPs, RAMP1, RAMP2, and RAMP3, that compose AMY1R, AMY2R, and AMY3R when associated with the CTR (Figure 1). The three different RAMPs are structurally similar to each other, so all three RAMPs are able to bind to the CTR without any modification of the CTR (Figure 2) <ref name="Hay">PMID:26071095</ref>. | ||
| - | In the absence of a RAMP, the calcitonin receptor has greater affinity for calcitonin than amylin, but because the <scene name='10/1037495/Overlay_of_ligands/1'>two ligands are structurally similar</scene>, both calcitonin and amylin can bind to the CTR without any modification of the receptor <ref name="Hay">PMID:26071095</ref>. The two ligands have many conserved residues (highlighted in blue), and this shows that the two ligands share many chemical properties which explains why they are structurally similar. In addition to having many conserved residues, both ligands also have an amidated C-terminus (Figure 3). When the CTR is bound to a RAMP, the complex becomes the AMYR and has greater affinity for the <scene name='10/1037495/Ligand_in_membrane/2'>amylin ligand</scene> relative to the calcitonin ligand. Therefore, the RAMP is essential to AMYR because it causes AMYR to have greater affinity for the amylin ligand rather than the calcitonin ligand. [[Image:Sequence alignment ligands.png| | + | In the absence of a RAMP, the calcitonin receptor has greater affinity for calcitonin than amylin, but because the <scene name='10/1037495/Overlay_of_ligands/1'>two ligands are structurally similar</scene>, both calcitonin and amylin can bind to the CTR without any modification of the receptor <ref name="Hay">PMID:26071095</ref>. The two ligands have many conserved residues (highlighted in blue), and this shows that the two ligands share many chemical properties which explains why they are structurally similar. In addition to having many conserved residues, both ligands also have an amidated C-terminus (Figure 3). When the CTR is bound to a RAMP, the complex becomes the AMYR and has greater affinity for the <scene name='10/1037495/Ligand_in_membrane/2'>amylin ligand</scene> relative to the calcitonin ligand. Therefore, the RAMP is essential to AMYR because it causes AMYR to have greater affinity for the amylin ligand rather than the calcitonin ligand. [[Image:Sequence alignment ligands.png|400px|left|thumb|'''Figure 3.''' Sequence alignment of rat amylin and salmon calcitonin. Conserved residues are highlighted in blue.]] |
== Ligands == | == Ligands == | ||
| Line 46: | Line 46: | ||
==== Pramlintide ==== | ==== Pramlintide ==== | ||
| - | [[Image:Pram sequ.png| | + | [[Image:Pram sequ.png|400px|left|thumb|'''Figure 5.''' Sequence alignment of rat amylin and pramlintide.]] |
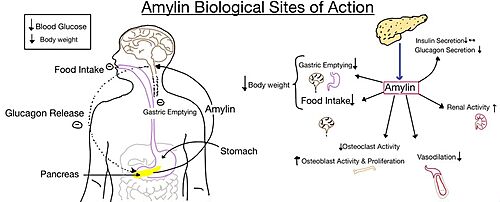
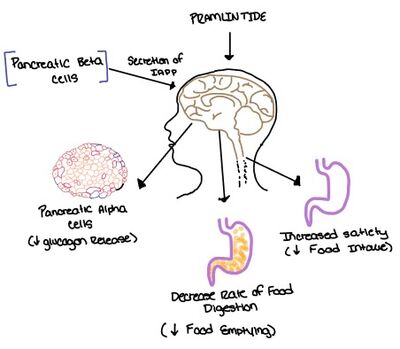
Pramlintide, a peptide analog of human amylin, is FDA-approved for the treatment of insulin-requiring diabetes (Figure 5) <ref name="Hay">PMID:26071095</ref>. Pramlintide is injected into the bloodstream by the beta cells of the pancreas along with insulin after a meal, aiding in the regulation of blood glucose by slowing [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Stomach gastric emptying], promoting [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Satiety satiety] via [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hypothalamus hypothalamic] receptors, and inhibiting secretion of glucagon which opposes the effects of insulin and amylin (Figure 6) <ref name="Thapa">Thapa, G., Kumari, A., Dasgupta, D., Bandyopadhy, S., Sarkar, N., Roy, K., Karunakaran, G., Kazmi, I., Karmakar, S., & Chakraborty, M. (2023). Chapter 5- Insight into the mechanism of action of anti-diabetic drugs. ''How Synthetic Drugs Work.'' 95-122. [http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-323-99855-0.00005-1 DOI:10.1016/B978-0-323-99855-0.00005-1]</ref>. | Pramlintide, a peptide analog of human amylin, is FDA-approved for the treatment of insulin-requiring diabetes (Figure 5) <ref name="Hay">PMID:26071095</ref>. Pramlintide is injected into the bloodstream by the beta cells of the pancreas along with insulin after a meal, aiding in the regulation of blood glucose by slowing [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Stomach gastric emptying], promoting [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Satiety satiety] via [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hypothalamus hypothalamic] receptors, and inhibiting secretion of glucagon which opposes the effects of insulin and amylin (Figure 6) <ref name="Thapa">Thapa, G., Kumari, A., Dasgupta, D., Bandyopadhy, S., Sarkar, N., Roy, K., Karunakaran, G., Kazmi, I., Karmakar, S., & Chakraborty, M. (2023). Chapter 5- Insight into the mechanism of action of anti-diabetic drugs. ''How Synthetic Drugs Work.'' 95-122. [http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-323-99855-0.00005-1 DOI:10.1016/B978-0-323-99855-0.00005-1]</ref>. | ||
Revision as of 22:09, 24 April 2024
Amylin Receptor (AMYR)
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Cao J, Belousoff MJ, Liang YL, Johnson RM, Josephs TM, Fletcher MM, Christopoulos A, Hay DL, Danev R, Wootten D, Sexton PM. A structural basis for amylin receptor phenotype. Science. 2022 Mar 25;375(6587):eabm9609. PMID:35324283 doi:10.1126/science.abm9609
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 Hay DL, Chen S, Lutz TA, Parkes DG, Roth JD. Amylin: Pharmacology, Physiology, and Clinical Potential. Pharmacol Rev. 2015 Jul;67(3):564-600. PMID:26071095 doi:10.1124/pr.115.010629
- ↑ Cao J, Belousoff MJ, Liang YL, Johnson RM, Josephs TM, Fletcher MM, Christopoulos A, Hay DL, Danev R, Wootten D, Sexton PM. A structural basis for amylin receptor phenotype. Science. 2022 Mar 25;375(6587):eabm9609. PMID:35324283 doi:10.1126/science.abm9609
- ↑ Mathiesen DS, Lund A, Vilsbøll T, Knop FK, Bagger JI. Amylin and Calcitonin: Potential Therapeutic Strategies to Reduce Body Weight and Liver Fat. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021 Jan 8;11:617400. PMID:33488526 doi:10.3389/fendo.2020.617400
- ↑ Thapa, G., Kumari, A., Dasgupta, D., Bandyopadhy, S., Sarkar, N., Roy, K., Karunakaran, G., Kazmi, I., Karmakar, S., & Chakraborty, M. (2023). Chapter 5- Insight into the mechanism of action of anti-diabetic drugs. How Synthetic Drugs Work. 95-122. DOI:10.1016/B978-0-323-99855-0.00005-1
- ↑ Press, M., Jung, T., Konig, J., Grune, T., & Hohn, A. (2019). Protein aggregates and proteostasis in aging: Amylin and β-cell function. Mechanisms of Ageing and Development. 3, 46-54. DOI:10.1016/j.mad.2018.03.010
- ↑ Grizzanti J, Corrigan R, Casadesus G. Neuroprotective Effects of Amylin Analogues on Alzheimer's Disease Pathogenesis and Cognition. J Alzheimers Dis. 2018;66(1):11-23. PMID:30282360 doi:10.3233/JAD-180433