This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
User:Brynn Baker/Sandbox1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 59: | Line 59: | ||
The first human amylin analogue, <scene name='10/1037520/Pramlintide_overall/2'>pramlintide</scene>, was developed in 1995, and marked a significant advancement in the treatment of Type 2 Diabetes<ref name="Bower">PMID:27061187</ref>. As of 2024, it is the only FDA-approved drug for the treatment of Type 2 Diabetes using the AMYR as a target. Recent studies in rodent Alzheimer’s Disease models suggest that pramlintide reduces amyloid-beta plaques, making it a potential therapeutic target for Alzheimer’s Disease<ref name="Grizzanti">PMID:30282360</ref>. | The first human amylin analogue, <scene name='10/1037520/Pramlintide_overall/2'>pramlintide</scene>, was developed in 1995, and marked a significant advancement in the treatment of Type 2 Diabetes<ref name="Bower">PMID:27061187</ref>. As of 2024, it is the only FDA-approved drug for the treatment of Type 2 Diabetes using the AMYR as a target. Recent studies in rodent Alzheimer’s Disease models suggest that pramlintide reduces amyloid-beta plaques, making it a potential therapeutic target for Alzheimer’s Disease<ref name="Grizzanti">PMID:30282360</ref>. | ||
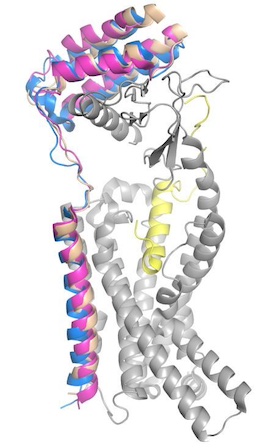
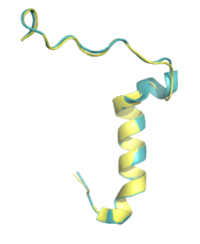
| - | There is limited knowledge about how human amylin binds to the human AMYR, so many studies utilize rat amylin as the peptide for the human AMYR. Rat amylin and pramlintide showcase very similar structures and maintain a high sequence similarity. For instance, the N-term lysine residue is conserved between <scene name='10/1037520/K1/ | + | There is limited knowledge about how human amylin binds to the human AMYR, so many studies utilize rat amylin as the peptide for the human AMYR. Rat amylin and pramlintide showcase very similar structures and maintain a high sequence similarity. For instance, the N-term lysine residue is conserved between <scene name='10/1037520/K1/2'>rat amylin</scene> and <scene name='10/1037516/Pramlintide_k1/1'>pramlintide</scene>, as well as human amylin<ref name="Cao">PMID:35324283</ref>, suggesting that the lysine is integral for binding to AMYR. One of these residue changes is <scene name='10/1038871/Rat_pram_18/1'>R18 in rat amylin to H18 in pramlintide</scene>. Another mutation is <scene name='10/1037520/Rat_pram_19/3'>S19 in rat amylin to K19 in pramlintide</scene>. S19 is highly conserved in most observed variants of amylin, as the <scene name='10/1037520/S19/1'>sidechain of S19 hydrogen bonds to the backbone of P100 of CT</scene><ref name="Cao">PMID:35324283</ref> <ref name="Bower">PMID:27061187</ref>. Other mutations include <scene name='10/1038871/Rat_l23/1'>L23</scene> in rat amylin to <scene name='10/1038871/Pramlintide_f23/1'>F23</scene> in pramlintide and <scene name='10/1038871/Rat_v26/1'>V26</scene> in rat amylin to <scene name='10/1037516/Pramlintide_i26/1'>I26</scene> in pramlintide. While these residues differ, the overall properties of the various residues remain consistent, so many of the same interactions with AMYR are likely still able to form. |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
Rat amylin and pramlintide have 3 proline residues, which are absent in human amylin. Human amylin and pramlintide only differ at these 3 residues, with all three being changed to proline in pramlintide. The <scene name='10/1037520/Pramlintide_mutations_labeled/2'>Ala25Pro, Ser28Pro, and Ser29Pro</scene> mutations break the helical nature present in human amylin, which likely prevents the aggregation of amyloid beta plaques in Alzheimer’s Disease. | Rat amylin and pramlintide have 3 proline residues, which are absent in human amylin. Human amylin and pramlintide only differ at these 3 residues, with all three being changed to proline in pramlintide. The <scene name='10/1037520/Pramlintide_mutations_labeled/2'>Ala25Pro, Ser28Pro, and Ser29Pro</scene> mutations break the helical nature present in human amylin, which likely prevents the aggregation of amyloid beta plaques in Alzheimer’s Disease. | ||
Revision as of 01:05, 25 April 2024
Homo sapiens Amylin3 Receptor, AMYR3
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Hay DL, Chen S, Lutz TA, Parkes DG, Roth JD. Amylin: Pharmacology, Physiology, and Clinical Potential. Pharmacol Rev. 2015 Jul;67(3):564-600. PMID:26071095 doi:10.1124/pr.115.010629
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Grizzanti J, Corrigan R, Casadesus G. Neuroprotective Effects of Amylin Analogues on Alzheimer's Disease Pathogenesis and Cognition. J Alzheimers Dis. 2018;66(1):11-23. PMID:30282360 doi:10.3233/JAD-180433
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 3.6 3.7 3.8 3.9 Cao J, Belousoff MJ, Liang YL, Johnson RM, Josephs TM, Fletcher MM, Christopoulos A, Hay DL, Danev R, Wootten D, Sexton PM. A structural basis for amylin receptor phenotype. Science. 2022 Mar 25;375(6587):eabm9609. PMID:35324283 doi:10.1126/science.abm9609
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Bower RL, Hay DL. Amylin structure-function relationships and receptor pharmacology: implications for amylin mimetic drug development. Br J Pharmacol. 2016 Jun;173(12):1883-98. PMID:27061187 doi:10.1111/bph.13496
Student Contributors
- Brynn Baker
- Emily Berkman
- Sepp Hall