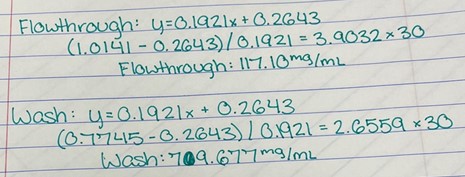We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox326
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
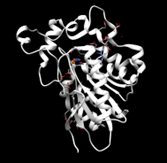
<StructureSection load='2qru' size='340' side='right' caption='The protein 2QRU is believed to be a hydrolase, functioning best in a near neutral pH environment which could potentially be in muscle cells or in neuronal cells.' scene=''> | <StructureSection load='2qru' size='340' side='right' caption='The protein 2QRU is believed to be a hydrolase, functioning best in a near neutral pH environment which could potentially be in muscle cells or in neuronal cells.' scene=''> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
== '''Introduction''' == | == '''Introduction''' == | ||
| Line 64: | Line 66: | ||
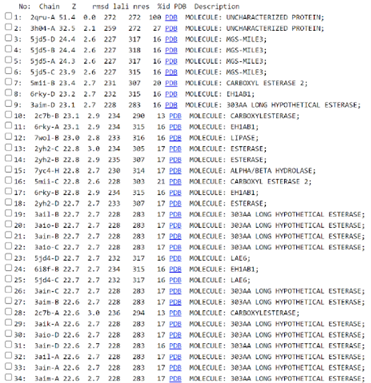
Figure 1: List of hits of 2QRU from SPRITE (10 of 200 entries shown here). The first column tells what hit each row shows and the second column has the source PDB ID that the program uses to identify each protein in the database. The third column gives a description of the protein and the final column shows the RMSD value of that protein when compared to the search protein of 2QRU. | Figure 1: List of hits of 2QRU from SPRITE (10 of 200 entries shown here). The first column tells what hit each row shows and the second column has the source PDB ID that the program uses to identify each protein in the database. The third column gives a description of the protein and the final column shows the RMSD value of that protein when compared to the search protein of 2QRU. | ||
| + | |||
[[Image:SPRITE_pic_2.png]] | [[Image:SPRITE_pic_2.png]] | ||
Figure 2: Alignment of 2QRU with 6 different motifs (A 33 GLY, A 102 SER, A 219 ASP, A 247 HIS; A 102 SER, A 130 GLY, A 219 ASP, A 247 HIS; A 102 SER, A 104 GLY, A 219 ASP, A 247 HIS; A 34 GLY, A 102 SER, A 219 ASP, A 247 HIS; A 102 SER, A 219 ASP, A 247 HIS; A 104 GLY, A 219 ASP, A 247 HIS) from 3 different views in SPRITE. Alignment was generated from the “Full Details” and the “Superposed motifs” function was utilized such that all proteins are visible. | Figure 2: Alignment of 2QRU with 6 different motifs (A 33 GLY, A 102 SER, A 219 ASP, A 247 HIS; A 102 SER, A 130 GLY, A 219 ASP, A 247 HIS; A 102 SER, A 104 GLY, A 219 ASP, A 247 HIS; A 34 GLY, A 102 SER, A 219 ASP, A 247 HIS; A 102 SER, A 219 ASP, A 247 HIS; A 104 GLY, A 219 ASP, A 247 HIS) from 3 different views in SPRITE. Alignment was generated from the “Full Details” and the “Superposed motifs” function was utilized such that all proteins are visible. | ||
| + | |||
[[Image:Chimera_pic_2.png]] | [[Image:Chimera_pic_2.png]] | ||
| Line 75: | Line 79: | ||
[[Image:Chimera_pic_3.png]] | [[Image:Chimera_pic_3.png]] | ||
| + | |||
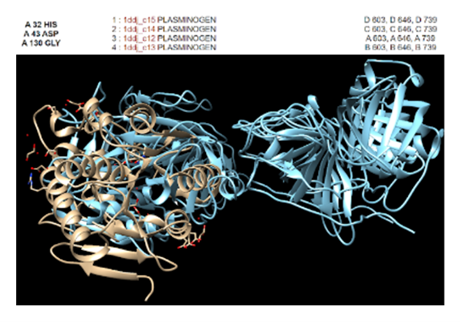
Figure 4: In Chimera, protein 2QRU matched the most with enzymes such as trypsins, proteases, and chymotrypsins. However, the best RMSD value of 2.328 Angstroms was found to be with this plasminogen. | Figure 4: In Chimera, protein 2QRU matched the most with enzymes such as trypsins, proteases, and chymotrypsins. However, the best RMSD value of 2.328 Angstroms was found to be with this plasminogen. | ||
| + | |||
[[Image:Dali_4.png]] | [[Image:Dali_4.png]] | ||
| Line 93: | Line 99: | ||
Figure 7: RCSB PDB Result Page for 2QRU. This page shows an overview of information about protein 2QRU including several classifications. | Figure 7: RCSB PDB Result Page for 2QRU. This page shows an overview of information about protein 2QRU including several classifications. | ||
| + | |||
[[Image:InterPro_2.png]] | [[Image:InterPro_2.png]] | ||
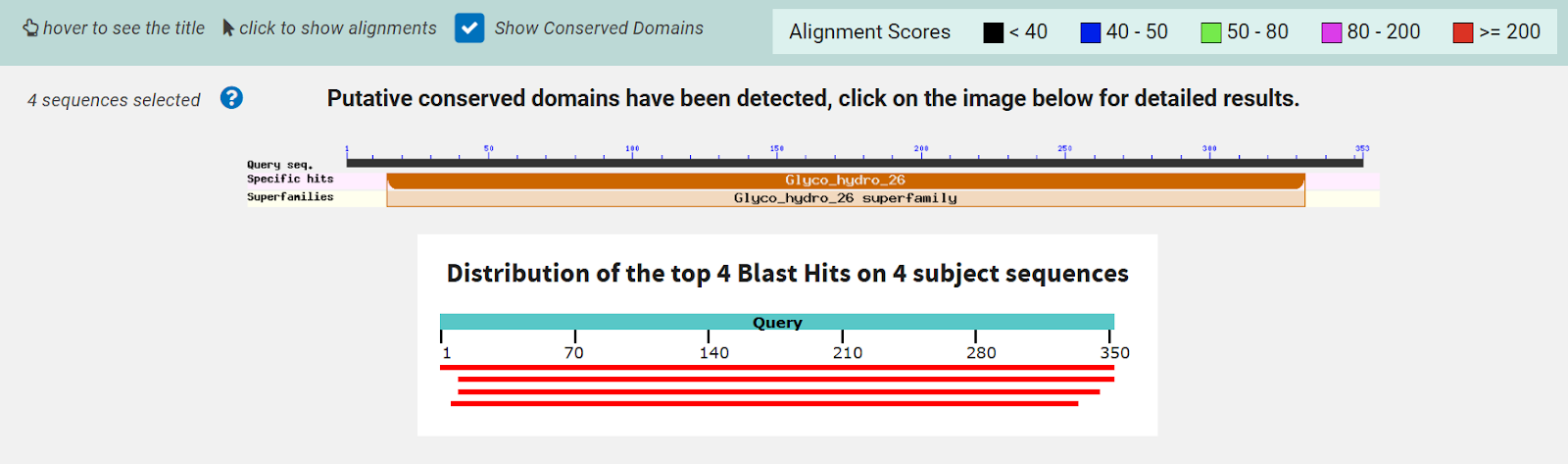
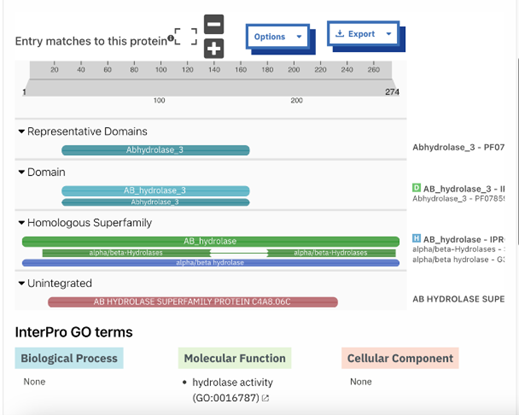
Figure 8: InterPRO results 2QRU. This shows the main page of InterPRO when searching 2QRU and it includes information such as the possible protein family membership (although there was no match for this particular protein). It also shows several domains that are similar matches to 2QRU, all of which are types of hydrolases, suggesting that 2QRU is a type of hydrolase as well. It gives the results for the biological process (none), the molecular function (hydrolase), and the cellular component (none). Some information is missing in this page which is what our research aimed to help fill in. | Figure 8: InterPRO results 2QRU. This shows the main page of InterPRO when searching 2QRU and it includes information such as the possible protein family membership (although there was no match for this particular protein). It also shows several domains that are similar matches to 2QRU, all of which are types of hydrolases, suggesting that 2QRU is a type of hydrolase as well. It gives the results for the biological process (none), the molecular function (hydrolase), and the cellular component (none). Some information is missing in this page which is what our research aimed to help fill in. | ||
| + | |||
[[Image:InterPro_3.png]] | [[Image:InterPro_3.png]] | ||
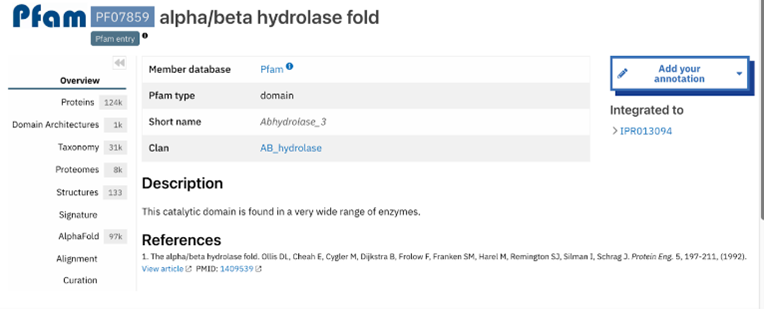
Figure 9: Abhydrolase_3 - PF07859: alpha/beta hydrolase fold profile. This result was found by selecting the domain from the InterPro overview page shown in figure 8. This gives more information about that domain specifically. The information includes several classifications as well as options on the side bar to investigate the result further. | Figure 9: Abhydrolase_3 - PF07859: alpha/beta hydrolase fold profile. This result was found by selecting the domain from the InterPro overview page shown in figure 8. This gives more information about that domain specifically. The information includes several classifications as well as options on the side bar to investigate the result further. | ||
| + | |||
[[Image:InterPro_4.png]] | [[Image:InterPro_4.png]] | ||
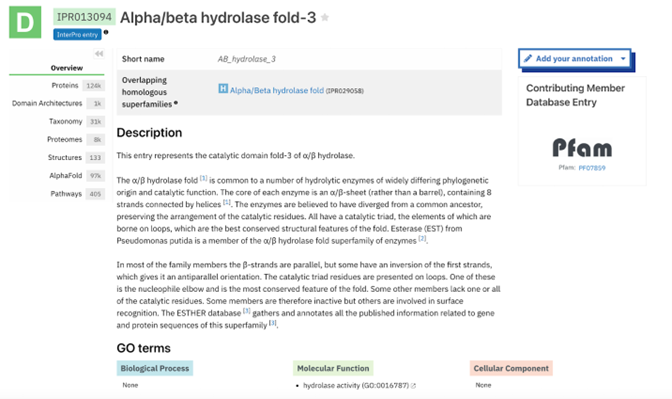
Figure 10: AB_hydrolase_3 - IPR013094: alpha/beta hydrolase fold-3 profile. This result was found by selecting another one of the domains from the InterPro overview page shown in figure 8 and this gives more information about that domain specifically. The information includes several classifications as well as options on the side bar to investigate the result further. | Figure 10: AB_hydrolase_3 - IPR013094: alpha/beta hydrolase fold-3 profile. This result was found by selecting another one of the domains from the InterPro overview page shown in figure 8 and this gives more information about that domain specifically. The information includes several classifications as well as options on the side bar to investigate the result further. | ||
| + | |||
[[Image:InterPro_5.png]] | [[Image:InterPro_5.png]] | ||
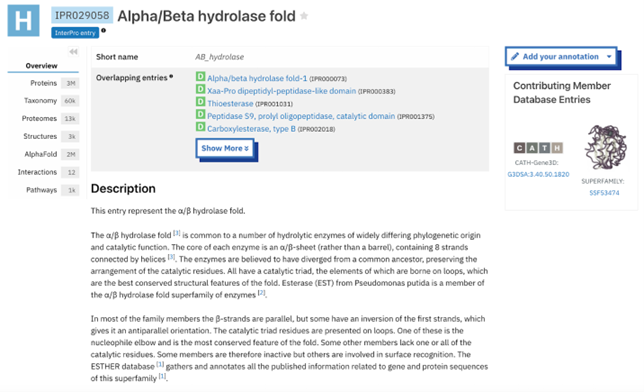
Figure 11: AB_hydrolase - IPR029058: alpha.beta hydrolase fold profile. This result was found by selecting another one of the domains from the InterPro overview page shown in figure 8 and this gives more information about that domain specifically. The information includes several classifications as well as options on the side bar to investigate the result further. | Figure 11: AB_hydrolase - IPR029058: alpha.beta hydrolase fold profile. This result was found by selecting another one of the domains from the InterPro overview page shown in figure 8 and this gives more information about that domain specifically. The information includes several classifications as well as options on the side bar to investigate the result further. | ||
| + | |||
[[Image:InterPro_7.png]] | [[Image:InterPro_7.png]] | ||
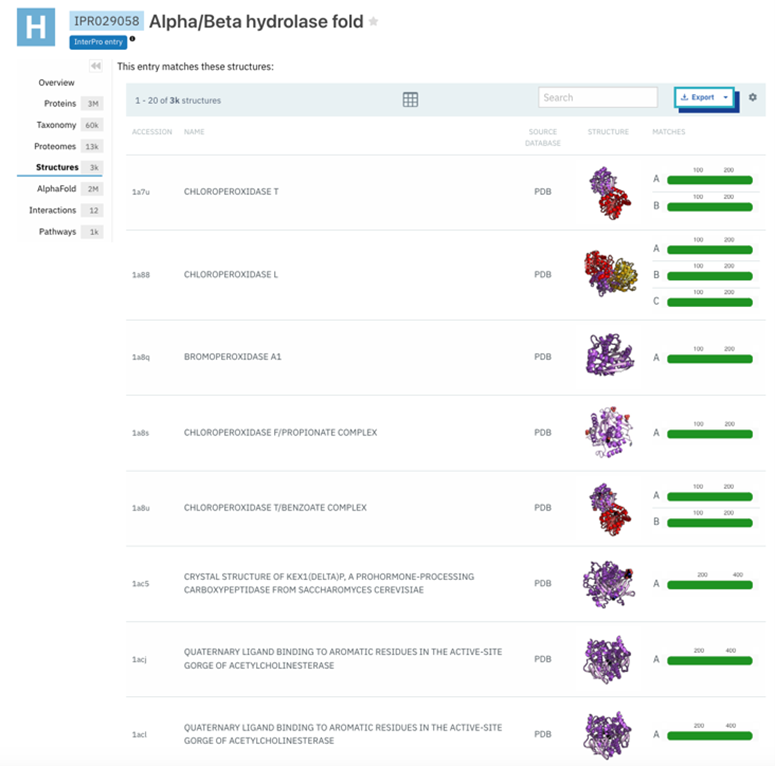
Figure 12: Structure results of IPR029058- alpha/beta hydrolase fold. This was found by selecting the side bar option of structure in Interpro. This provided information about the structural qualities of proteins in that domain. | Figure 12: Structure results of IPR029058- alpha/beta hydrolase fold. This was found by selecting the side bar option of structure in Interpro. This provided information about the structural qualities of proteins in that domain. | ||
| + | |||
[[Image:InterPro_9.png]] | [[Image:InterPro_9.png]] | ||
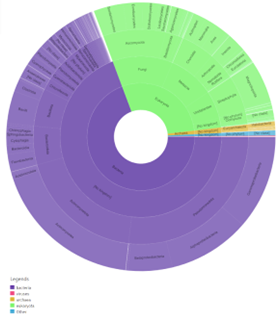
Figure 13: Taxonomy results of IPR029058- alpha/beta hydrolase fold. This was found by selecting the side bar options of taxonomy in Interpro. This provided information about the taxonomic background of proteins in that domain. (KEY: purple- bacteria, pink- viruses, yellow- archaea, green- eukaryote, blue- other). | Figure 13: Taxonomy results of IPR029058- alpha/beta hydrolase fold. This was found by selecting the side bar options of taxonomy in Interpro. This provided information about the taxonomic background of proteins in that domain. (KEY: purple- bacteria, pink- viruses, yellow- archaea, green- eukaryote, blue- other). | ||
| + | |||
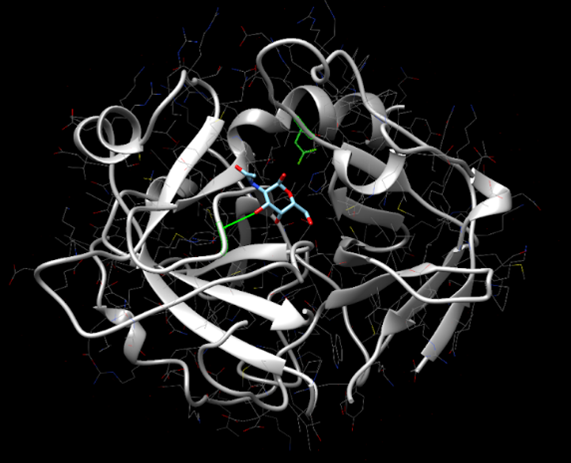
[[Image:SwissDock.png]] | [[Image:SwissDock.png]] | ||
Figure 14: SwissDock results showing Alanine-p-nitroanilide interacting with the active site of protein 2QRU. | Figure 14: SwissDock results showing Alanine-p-nitroanilide interacting with the active site of protein 2QRU. | ||
| + | |||
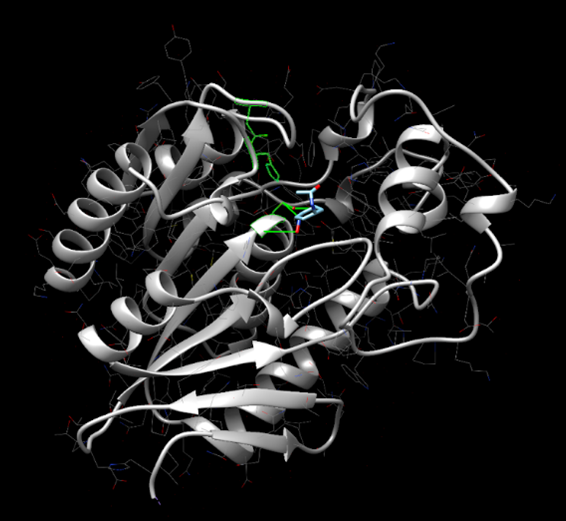
[[Image:SwissDock_2.png]] | [[Image:SwissDock_2.png]] | ||
Figure 15: SwissDock results showing 4-nitroacetanilide interacting with the active site of protein 2QRU. | Figure 15: SwissDock results showing 4-nitroacetanilide interacting with the active site of protein 2QRU. | ||
| + | |||
[[Image:BA_calcss.png]] | [[Image:BA_calcss.png]] | ||
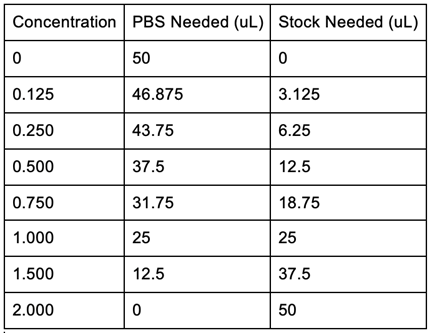
Figure 16: Bradford Assay Standards Preparation. | Figure 16: Bradford Assay Standards Preparation. | ||
| + | |||
[[Image:BA_2.jpg]] [[Image:BA_3.jpg]] [[Image:BA_4.jpg]] | [[Image:BA_2.jpg]] [[Image:BA_3.jpg]] [[Image:BA_4.jpg]] | ||
Figure 17: Bradford Assay Calculations. | Figure 17: Bradford Assay Calculations. | ||
| + | |||
[[Image:SC1.png]] [[Image:SC2.png]] | [[Image:SC1.png]] [[Image:SC2.png]] | ||
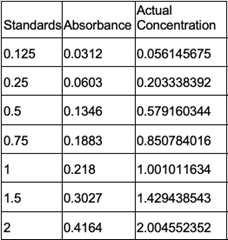
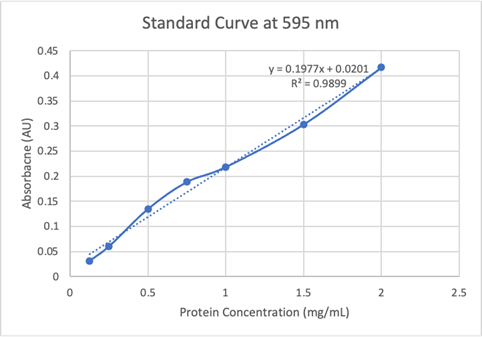
Figure 18: Bradford Assay Standard Curve. | Figure 18: Bradford Assay Standard Curve. | ||
| + | |||
[[Image:BA_5.png ]] | [[Image:BA_5.png ]] | ||
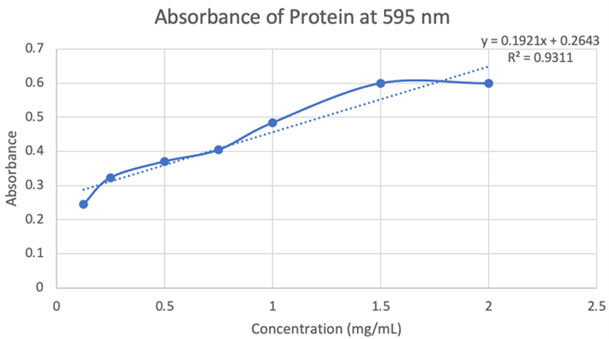
Figure 19: Absorbance of protein at 595nm. | Figure 19: Absorbance of protein at 595nm. | ||
| + | |||
[[Image:BA_6.png ]] | [[Image:BA_6.png ]] | ||
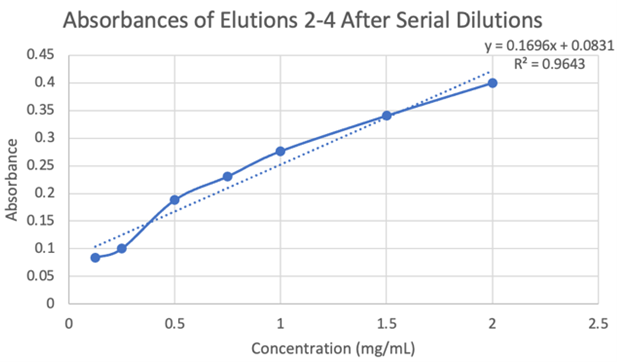
Figure 20: Absorbances of elutions 2-4 after serial dilutions. | Figure 20: Absorbances of elutions 2-4 after serial dilutions. | ||
| + | |||
[[Image:Gel_2.jpg]] | [[Image:Gel_2.jpg]] | ||
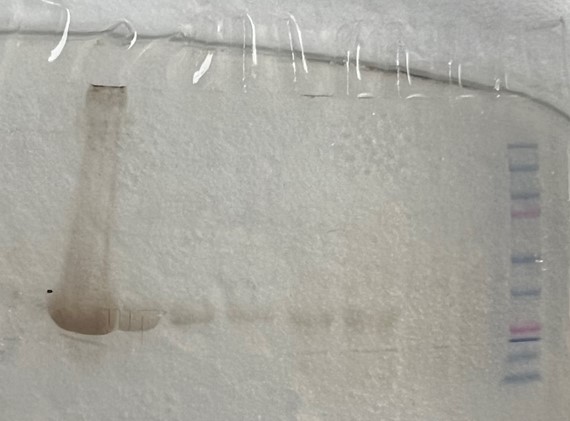
Figure 21: SDS-PAGE results showing bands at ~30 kD, indicating hydrolase activity. Well 1 to 10 (left to right): elutions 1-5, before sonication, before column, flowthrough, wash, ladder (molecular-weight size markers). | Figure 21: SDS-PAGE results showing bands at ~30 kD, indicating hydrolase activity. Well 1 to 10 (left to right): elutions 1-5, before sonication, before column, flowthrough, wash, ladder (molecular-weight size markers). | ||
| + | |||
[[Image:PH_6.4.png]] | [[Image:PH_6.4.png]] | ||
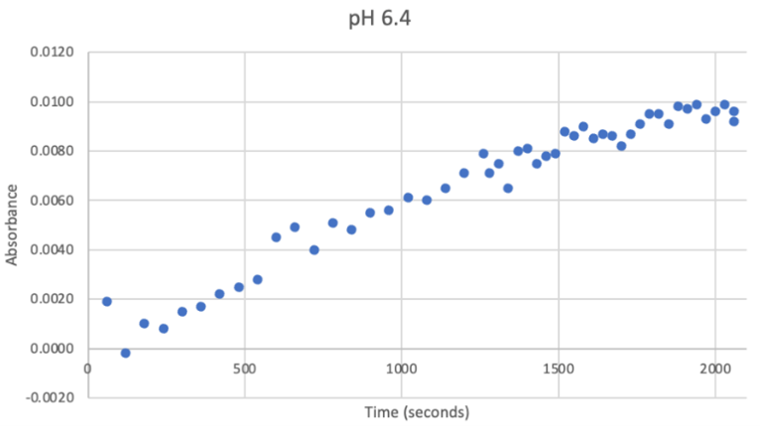
Figure 22: UV-vis results at pH 6.4. There was a very strong and steady increase in enzyme activity. The best enzymatic function was observed at this pH. | Figure 22: UV-vis results at pH 6.4. There was a very strong and steady increase in enzyme activity. The best enzymatic function was observed at this pH. | ||
| + | |||
[[Image:PH_7.2.png]] | [[Image:PH_7.2.png]] | ||
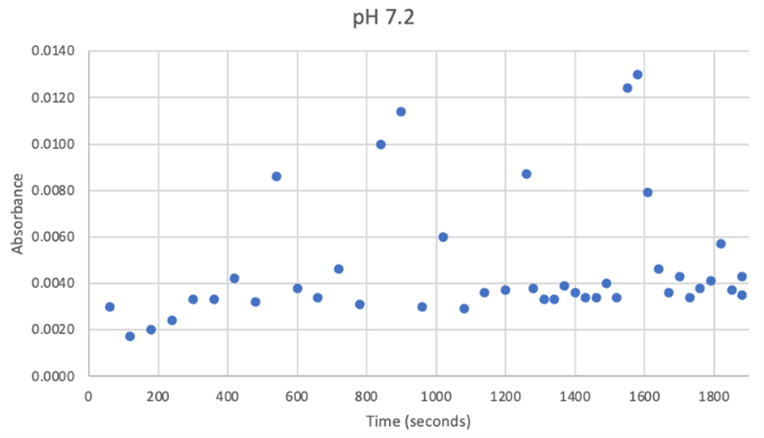
Figure 23: UV-vis results at pH 7.2. There was no steady increase in enzyme activity. Instead, it remained within a range despite a few random spikes which can clearly be seen as outliers. | Figure 23: UV-vis results at pH 7.2. There was no steady increase in enzyme activity. Instead, it remained within a range despite a few random spikes which can clearly be seen as outliers. | ||
| + | |||
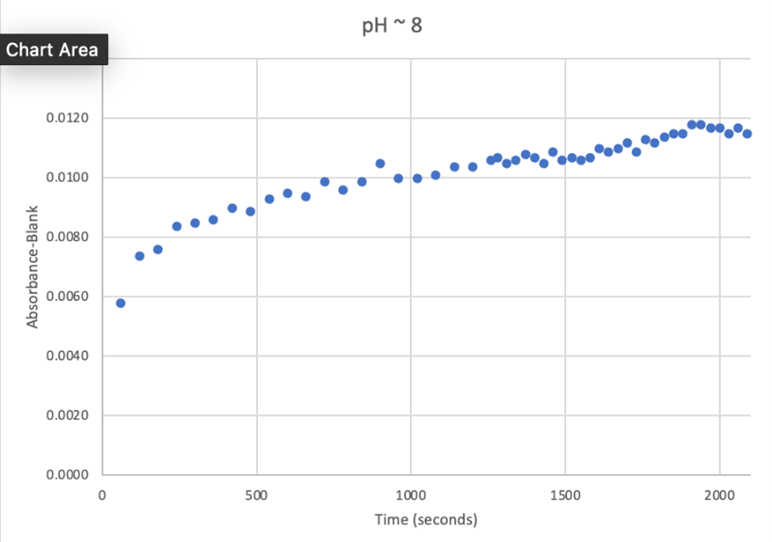
[[Image:PH_8.png]] | [[Image:PH_8.png]] | ||
| Line 184: | Line 207: | ||
== '''Conclusion''' == | == '''Conclusion''' == | ||
Overall, the hypothesis that the protein 2QRU is a type of hydrolase was determined through testing with a general hydrolase-recognized substrate p-nitrophenyl acetate. After testing at three different pH environments, the best pH level for this enzyme seemed to be at a more neutral, between 6.4 and 7.2. After computational testing, the best matched substrates are suspected to be 4-nitroacetanilide and alanine-p-nitroanilide. Enzyme activity testing has not been completed thus far with these substrates, but that work could indicate what specific substrates would be best matched with the enzyme providing more specifics into the structure and function of 2QRU. | Overall, the hypothesis that the protein 2QRU is a type of hydrolase was determined through testing with a general hydrolase-recognized substrate p-nitrophenyl acetate. After testing at three different pH environments, the best pH level for this enzyme seemed to be at a more neutral, between 6.4 and 7.2. After computational testing, the best matched substrates are suspected to be 4-nitroacetanilide and alanine-p-nitroanilide. Enzyme activity testing has not been completed thus far with these substrates, but that work could indicate what specific substrates would be best matched with the enzyme providing more specifics into the structure and function of 2QRU. | ||
| + | |||
Revision as of 15:59, 26 April 2024
Identification of Unknown Protein 2QRU
| |||||||||||