User:Camille Gaudet/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
=== Biological Role === | === Biological Role === | ||
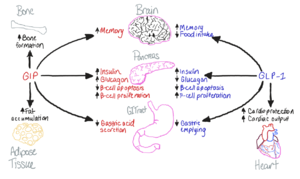
| - | [[Image:GIP-GLP1-Purpose.png|300 px|right|thumb|Figure 1. The biological roles of GIP and and GLP-1, incretin hormones.]] The GIP receptor (GIPR) helps facilitate the transport of glucose into/out of the cell through the stimulation of insulin secretion. <ref name='Sun'>PMID:35333651</ref>. GIPR is a type of [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/G_protein-coupled_receptor G-Protein Coupled Receptor] (GPCR), and its natural ligand, GIP, serves as an initiator of a cellular signaling cascade, thereby activating adenylyl cyclase and increasing cAMP levels. Subsequently, insulin secretion is stimulated. [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Insulin Insulin], a peptide hormone, is secreted by the pancreas in response to glucose ingestion, allowing intake of glucose into the cell via the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/GLUT2 Glut2] transporter. | + | [[Image:GIP-GLP1-Purpose.png|300 px|right|thumb|Figure 1. The biological roles of GIP and and GLP-1, incretin hormones.]] The GIP receptor (GIPR) helps facilitate the transport of glucose into/out of the cell through the stimulation of insulin secretion. <ref name='Sun'>PMID:35333651</ref>. GIPR is a type of [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/G_protein-coupled_receptor G-Protein Coupled Receptor] (GPCR), and its natural ligand, GIP, serves as an initiator of a cellular signaling cascade, thereby activating adenylyl cyclase and increasing cAMP levels. Subsequently, insulin secretion is stimulated. [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Insulin Insulin], a peptide hormone, is secreted by the pancreas in response to glucose ingestion, allowing intake of glucose into the cell via the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/GLUT2 Glut2] transporter. |
| - | + | ||
| Line 17: | Line 16: | ||
=== Glucose-dependent Insulinotropic Polypeptide === | === Glucose-dependent Insulinotropic Polypeptide === | ||
| - | The <scene name='10/1037488/Gip-bound/4'>GIP ligand</scene> binds to its receptor extracellularly, inserting itself [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/N-terminus N-terminus] down into the transmembrane and extracellular domains of the GIP receptor. The polypeptide is 42 residues in length and | + | The <scene name='10/1037488/Gip-bound/4'>GIP ligand</scene> binds to its receptor extracellularly, inserting itself [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/N-terminus N-terminus] down into the transmembrane and extracellular domains of the GIP receptor. The polypeptide is 42 residues in length and takes on a helical structure. |
| Line 24: | Line 23: | ||
== Associated Diseases == | == Associated Diseases == | ||
| + | In individuals with [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Diabetes diabetes], insulin is improperly under-secreted or unresponsive to elevated blood glucose levels. Considering its role as the initial metabolite in [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Glycolysis glycolysis], when glucose is not effectively transported into the cell, it renders the body unable to successfully execute energy production through [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cellular_respiration cellular respiration] (Glycolysis --> the Krebs Cycle --> the Electron Transport Chain --> ATP synthesis). | ||
| + | |||
== Medical Relevance == | == Medical Relevance == | ||
Revision as of 21:08, 28 April 2024
Glucose-dependent Insulinotropic Polypeptide Receptor
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Sun B, Willard FS, Feng D, Alsina-Fernandez J, Chen Q, Vieth M, Ho JD, Showalter AD, Stutsman C, Ding L, Suter TM, Dunbar JD, Carpenter JW, Mohammed FA, Aihara E, Brown RA, Bueno AB, Emmerson PJ, Moyers JS, Kobilka TS, Coghlan MP, Kobilka BK, Sloop KW. Structural determinants of dual incretin receptor agonism by tirzepatide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022 Mar 29;119(13):e2116506119. PMID:35333651 doi:10.1073/pnas.2116506119
Student Contributors
- Camille Gaudet
- Sara Kalkhoff