We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
End-binding protein
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
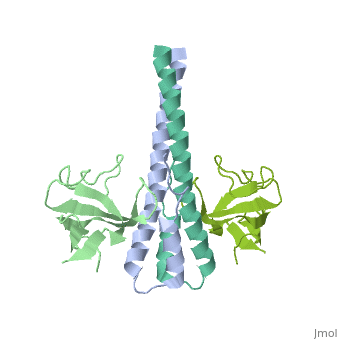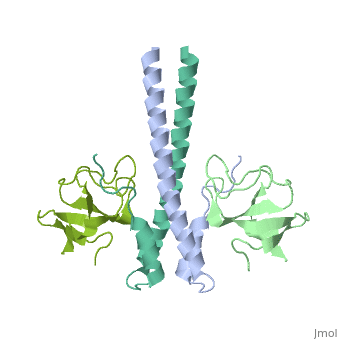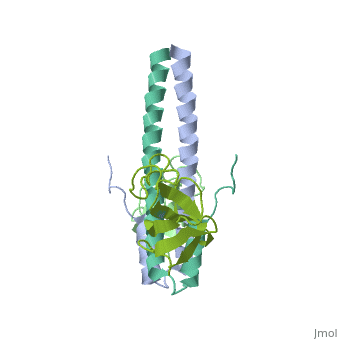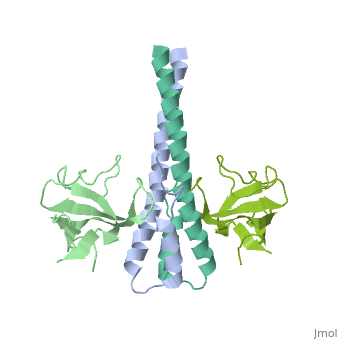
**[[2qjz]] – hEB1 CH domain 12-133<br /> | **[[2qjz]] – hEB1 CH domain 12-133<br /> | ||
**[[5n74]] – hEB1 + KAR9 <br /> | **[[5n74]] – hEB1 + KAR9 <br /> | ||
| + | **[[9co5]] – hEB1 + FKBP12 <br /> | ||
**[[1v5k]] – mEB1 CH domain (mutant) – mouse - NMR<br /> | **[[1v5k]] – mEB1 CH domain (mutant) – mouse - NMR<br /> | ||
**[[6evi]] – mEB1 C-terminal 191-260 - NMR<br /> | **[[6evi]] – mEB1 C-terminal 191-260 - NMR<br /> | ||
| Line 34: | Line 35: | ||
**[[1wyo]] – hEB3 CH domain - NMR<br /> | **[[1wyo]] – hEB3 CH domain - NMR<br /> | ||
**[[3jak]], [[7sj9]] – hEB3 + tubulin – Cryo EM <br /> | **[[3jak]], [[7sj9]] – hEB3 + tubulin – Cryo EM <br /> | ||
| + | **[[9f3r]], [[9f3s]] – hEB3 + tubulin + GTP – Cryo EM <br /> | ||
**[[3jal]] – hEB3 + tubulin + GMPCPP – Cryo EM <br /> | **[[3jal]] – hEB3 + tubulin + GMPCPP – Cryo EM <br /> | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
3D Structures of end-binding protein
Updated on 21-May-2025
References
- ↑ Nakamura M, Zhou XZ, Lu KP. Critical role for the EB1 and APC interaction in the regulation of microtubule polymerization. Curr Biol. 2001 Jul 10;11(13):1062-7. PMID:11470413
- ↑ Nehlig A, Molina A, Rodrigues-Ferreira S, Honoré S, Nahmias C. Regulation of end-binding protein EB1 in the control of microtubule dynamics. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2017 Jul;74(13):2381-2393. PMID:28204846 doi:10.1007/s00018-017-2476-2
- ↑ Goldspink DA, Gadsby JR, Bellett G, Keynton J, Tyrrell BJ, Lund EK, Powell PP, Thomas P, Mogensen MM. The microtubule end-binding protein EB2 is a central regulator of microtubule reorganisation in apico-basal epithelial differentiation. J Cell Sci. 2013 Sep 1;126(Pt 17):4000-14. PMID:23813963 doi:10.1242/jcs.129759