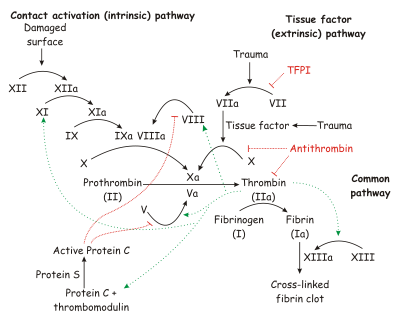
Factor Xa
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 87: | Line 87: | ||
**[[1c5m]] - hFX heavy chain catalytic domain + light chain (residues 84-179)<br /> | **[[1c5m]] - hFX heavy chain catalytic domain + light chain (residues 84-179)<br /> | ||
**[[1whe]], [[1whf]] – bFX GLA + EGF-like domains – bovine – NMR<br /> | **[[1whe]], [[1whf]] – bFX GLA + EGF-like domains – bovine – NMR<br /> | ||
| - | **[[ | + | **[[1apo]], [[1ccf]] - bFX EGF-like domain – NMR<br /> |
*Factor Xa complex with inhibitor | *Factor Xa complex with inhibitor | ||
| - | **[[ | + | **[[1v3x]], [[1wu1]], [[2d1j]], [[2ei6]], [[2ei7]], [[2ei8]], [[2p93]], [[2p94]], [[2p95]] – hFX heavy chain residues 16-243 + light chain EGF-like domain + inhibitor<br /> |
| - | + | **[[1fax]], [[1fjs]], [[1g2l]], [[1g2m]], [[1ioe]], [[1iqe]], [[1iqf]], [[1iqg]], [[1iqh]], [[1iqi]], [[1iqj]], [[1iqk]], [[1iql]], [[1iqm]], [[1iqn]], [[1mq5]], [[1mq6]], [[1xka]], [[1xkb]], [[1z6e]], [[2bq6]], [[2bq7]], [[2bqw]], [[2bmg]], [[2bok]], [[2fzz]], [[2g00]], [[2jkh]], [[2p16]], [[2p3t]], [[2p3u]], [[2phb]], [[2pr3]], [[2q1j]], [[2ra0]], [[2vh0]], [[2vh6]], [[2vvc]], [[2vvu]], [[2vvv]], [[2vwl]], [[2vwm]], [[2vwn]], [[2vwo]], [[2w3i]], [[2w3k]], [[2w26]], [[2wyg]], [[2wyj]], [[2xbv]], [[2xbw]], [[2xbx]], [[2xby]], [[2xc0]], [[2xc4]], [[2xc5]], [[2y5f]], [[2y5g]], [[2y5h]], [[2y7x]], [[2y7z]], [[2y80]], [[2y81]], [[2y82]], [[3cs7]], [[3cen]], [[3ens]], [[3ffg]], [[3hpt]], [[3iit]], [[3k9x]], [[3kl6]], [[3kqb]], [[3kqc]], [[3kqd]], [[3kqe]], [[3liw]], [[3m36]], [[3m37]], [[3q3k]], [[3tk5]], [[3tk6]], [[4a7i]], [[4y6d]], [[4y71]], [[4y76]], [[4y79]], [[4y7a]], [[4y7b]] - hFX heavy chain catalytic domain + light chain EGF-like domain + inhibitor<br /> | |
| - | **[[ | + | |
**[[2boh]] - hFX heavy chain catalytic domain (mutant) + light chain EGF-like domain (mutant) + inhibitor<br /> | **[[2boh]] - hFX heavy chain catalytic domain (mutant) + light chain EGF-like domain (mutant) + inhibitor<br /> | ||
| - | **[[ | + | **[[1ezq]], [[1f0r]], [[1f0s]], [[1ksn]], [[1lpg]], [[1lpk]], [[1lpz]], [[1lqd]], [[2cji]], [[2j2u]], [[2j34]], [[2j38]], [[2j4i]], [[2j94]], [[2j95]], [[2uwl]], [[2uwo]], [[2uwp]], [[4zh8]], [[4zha]], [[5k0h]] - hFX heavy chain catalytic domain 235-488 + light chain GLA and EGF-like domains 46-179 + inhibitor<br /> |
**[[1nfu]], [[1nfw]], [[1nfx]], [[1nfy]] - hFX heavy chain catalytic domain + light chain residues 46-240 + inhibitor<br /> | **[[1nfu]], [[1nfw]], [[1nfx]], [[1nfy]] - hFX heavy chain catalytic domain + light chain residues 46-240 + inhibitor<br /> | ||
**[[3sw2]], [[4bti]], [[4btt]], [[4btu]] - hFX heavy chain catalytic domain + light chain residues 84-179 + inhibitor<br /> | **[[3sw2]], [[4bti]], [[4btt]], [[4btu]] - hFX heavy chain catalytic domain + light chain residues 84-179 + inhibitor<br /> | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
3D structures of factor Xa
Updated on 08-June-2025
Additional Resources
For additional information, see: Hemophilia
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Greer, John (2008). Wintrobe's Clinical Hematology, p. 545-546. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. ISBN 0781765072.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Department of Chemistry, University of Maine, Orono, ME. http://chemistry.umeche.maine.edu/CHY252/Peptidase3.html
- ↑ Padmanabhan K, Padmanabhan KP, Tulinsky A, Park CH, Bode W, Huber R, Blankenship DT, Cardin AD, Kisiel W. Structure of human des(1-45) factor Xa at 2.2 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1993 Aug 5;232(3):947-66. PMID:8355279 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1006/jmbi.1993.1441
- ↑ Friedman PA, Przysiecki CT. Vitamin K-dependent carboxylation. Int J Biochem. 1987;19(1):1-7. PMID:3106112
- ↑ Vermeer C. Gamma-carboxyglutamate-containing proteins and the vitamin K-dependent carboxylase. Biochem J. 1990 Mar 15;266(3):625-36. PMID:2183788
- ↑ Price PA, Fraser JD, Metz-Virca G. Molecular cloning of matrix Gla protein: implications for substrate recognition by the vitamin K-dependent gamma-carboxylase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8335-9. PMID:3317405
- ↑ Freedman SJ, Furie BC, Furie B, Baleja JD. Structure of the metal-free gamma-carboxyglutamic acid-rich membrane binding region of factor IX by two-dimensional NMR spectroscopy. J Biol Chem. 1995 Apr 7;270(14):7980-7. PMID:7713897
- ↑ Freedman SJ, Blostein MD, Baleja JD, Jacobs M, Furie BC, Furie B. Identification of the phospholipid binding site in the vitamin K-dependent blood coagulation protein factor IX. J Biol Chem. 1996 Jul 5;271(27):16227-36. PMID:8663165
- ↑ Morita T, Jackson CM. Preparation and properties of derivatives of bovine factor X and factor Xa from which the gamma-carboxyglutamic acid containing domain has been removed. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 25;261(9):4015-23. PMID:3512564
- ↑ Muskavitch MA, Hoffmann FM. Homologs of vertebrate growth factors in Drosophila melanogaster and other invertebrates. Curr Top Dev Biol. 1990;24:289-328. PMID:2116263
- ↑ Ohlin AK, Linse S, Stenflo J. Calcium binding to the epidermal growth factor homology region of bovine protein C. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 25;263(15):7411-7. PMID:3259233
- ↑ Selander-Sunnerhagen M, Ullner M, Persson E, Teleman O, Stenflo J, Drakenberg T. How an epidermal growth factor (EGF)-like domain binds calcium. High resolution NMR structure of the calcium form of the NH2-terminal EGF-like domain in coagulation factor X. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 25;267(27):19642-9. PMID:1527084
- ↑ Persson E, Hogg PJ, Stenflo J. Effects of Ca2+ binding on the protease module of factor Xa and its interaction with factor Va. Evidence for two Gla-independent Ca(2+)-binding sites in factor Xa. J Biol Chem. 1993 Oct 25;268(30):22531-9. PMID:8226763
- ↑ Persson E, Selander M, Linse S, Drakenberg T, Ohlin AK, Stenflo J. Calcium binding to the isolated beta-hydroxyaspartic acid-containing epidermal growth factor-like domain of bovine factor X. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 5;264(28):16897-904. PMID:2789221
- ↑ Hopfner KP, Kopetzki E, Kresse GB, Bode W, Huber R, Engh RA. New enzyme lineages by subdomain shuffling. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998 Aug 18;95(17):9813-8. PMID:9707558
- ↑ Factor X. Wikipedia
- ↑ Serine Protease. Wikipedia
- ↑ 18.0 18.1 Hedstrom L. Serine protease mechanism and specificity. Chem Rev. 2002 Dec;102(12):4501-24. PMID:12475199
- ↑ 19.0 19.1 Rai R, Sprengeler PA, Elrod KC, Young WB. Perspectives on factor Xa inhibition. Curr Med Chem. 2001 Feb;8(2):101-19. PMID:11172669
- ↑ www.bmolchem.wisc.edu/
- ↑ 21.0 21.1 Bachovchin, W. Contributions of NMR spectroscopy to the study of hydrogen bonds in serine protease active sites. Magnetic Resonance in Chemistry; (2001); 39(Spec. Issue); 199-213.
- ↑ Bachovchin WW. 15N NMR spectroscopy of hydrogen-bonding interactions in the active site of serine proteases: evidence for a moving histidine mechanism. Biochemistry. 1986 Nov 18;25(23):7751-9. PMID:3542033
- ↑ Brady K, Wei AZ, Ringe D, Abeles RH. Structure of chymotrypsin-trifluoromethyl ketone inhibitor complexes: comparison of slowly and rapidly equilibrating inhibitors. Biochemistry. 1990 Aug 21;29(33):7600-7. PMID:2271520
- ↑ Frey PA, Whitt SA, Tobin JB. A low-barrier hydrogen bond in the catalytic triad of serine proteases. Science. 1994 Jun 24;264(5167):1927-30. PMID:7661899
- ↑ Frey, Perry A. Strong hydrogen bonding in chymotrypsin and other serine proteases. Journal of Physical Organic Chemistry (2004), 17(6-7), 511-520.
- ↑ 26.0 26.1 Fuhrmann CN, Daugherty MD, Agard DA. Subangstrom crystallography reveals that short ionic hydrogen bonds, and not a His-Asp low-barrier hydrogen bond, stabilize the transition state in serine protease catalysis. J Am Chem Soc. 2006 Jul 19;128(28):9086-102. PMID:16834383 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/ja057721o
- ↑ Kuhn P, Knapp M, Soltis SM, Ganshaw G, Thoene M, Bott R. The 0.78 A structure of a serine protease: Bacillus lentus subtilisin. Biochemistry. 1998 Sep 29;37(39):13446-52. PMID:9753430 doi:10.1021/bi9813983
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Jacqueline Gertz, Michal Harel, Alexander Berchansky, David Canner, Jaime Prilusky