We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
User:Elizabeth Yowell/ SandboxFinal
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
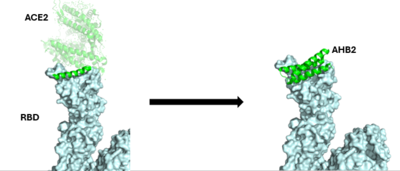
The first mini-binder to be created to combat COVID-19 is called AHB2. In order to ensure that the mini-binder would bind to the same RBD that the ACE2 was bound to, AHB2 was designed by looking at sequence of ACE2 alpha-helix that makes interactions with spike receptor binding domain. This design process is referred to as the Rosetta Blueprint protein design <ref name="Cao">DOI:10.1126/science.abd9909</ref>. | The first mini-binder to be created to combat COVID-19 is called AHB2. In order to ensure that the mini-binder would bind to the same RBD that the ACE2 was bound to, AHB2 was designed by looking at sequence of ACE2 alpha-helix that makes interactions with spike receptor binding domain. This design process is referred to as the Rosetta Blueprint protein design <ref name="Cao">DOI:10.1126/science.abd9909</ref>. | ||
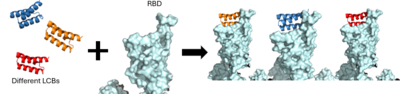
| + | [[Image:LCB1_Methodology.png|400 px|right|thumb|The use of the De Novo protein design to create the LCB1 and LCB3 inhibitors.]] | ||
As the AHB2 inhibitors were tested and found to be effective, it was then time to manipulate the mini-binders to create a more effective vaccine. A rotamer interaction field docking with in silico mini-proteins were used by using a scaffold library to generate binders to more distinct regions of the RBD surface <ref name="Cao">DOI:10.1126/science.abd9909</ref>. This method is known as the de novo protein design and it is how the LCB1 and LCB3 mini-binders were created. | As the AHB2 inhibitors were tested and found to be effective, it was then time to manipulate the mini-binders to create a more effective vaccine. A rotamer interaction field docking with in silico mini-proteins were used by using a scaffold library to generate binders to more distinct regions of the RBD surface <ref name="Cao">DOI:10.1126/science.abd9909</ref>. This method is known as the de novo protein design and it is how the LCB1 and LCB3 mini-binders were created. | ||
| - | + | ||
Revision as of 21:14, 2 April 2025
Contents |
SARS CoV-2 Protein Inhibitors (AHB2 and LCB1/LCB3)
| |||||||||||
References
Cao, L., Goreshnik, I., Coventry, B., Case, J.B., Miller, L., Kozodoy, L., Chen, R.E., Carter, L., Walls, A.C., Park, Y., Strauch, E., Stewart, L., Diamond, M.S., Veesler, D., & Baker, D. De novo design of picomolar SARS-CoV-2 mini protein inhibitors. Science 370, 426-431 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1126/science.abd9909
https://www.who.int/europe/emergencies/situations/covid-19
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41580-021-00418-x#citeas
https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/science.abd9909
PDB Files
[1]https://www.rcsb.org/structure/7UHB
Student Contributors
- Giavanna Yowell
- Shea Bailey
- Matthew Pereira