Background
Plastic pollution is a major problem in our modern world. Many strategies have been employed to recycle plastics instead of creating more and adding further pollution to the environment.
One of the most commonly used plastics is a polymer called Polyethylene Terephthalate, also known as PET. PET is commonly used to make plastic bottles or food containers due to its thermal stability, transparency, and impermeability to liquids and gases. Unfortunately, these properties that make it desirable also make it non-biodegradable, meaning that we must recycle PET to avoid polluting the environment with it. Traditional methods, such as melting and reforming the plastic, destroy the mechanical properties of PET, eliminating the ability to recycle it and necessitating a new strategy for recycling PET.
Enzyme hydrolysis
One solution that researchers have been studying is using a naturally occurring enzyme that has PET degrading activity, PET hyrdolase, to break down the polymer into its monomers. This would allow the PET to be reformed from its monomers into a new piece of plastic.
A class of enzymes that has been a focus is Cutinase.
One simple way to break PET down is through the hydrolysis of the ester bond between each monomer. There are already known enzymes that can perform hydrolysis on ester bonds of polymers, so applying one of these enzymes to PET provides a good starting point for the engineering of a PET hydrolase enzyme, like .
Leaf-branch compost cutinase (LCC)
The study done by Tournier et al. (2020) identified a good template enzyme for creating a PET hydrolase as the LCC enzyme. This enzyme was discovered through metagenomics of a leaf-branch compost. Its target substrate is the polymer cutin, found in the cuticle of plants. LCC breaks down Cutin to separate the monomers at the ester bond between them. The LCC enzyme was compared to several other enzymes and was selected as it showed the best rate of PET depolymerization
Mechanism
Overview of Active Site
LCC is a serine hydrolase. The mechanism uses a : S165 (which was made into an alanine for crystallization purposes), D210, and H242. S165 is the nucleophile attacking the electrophilic carbonyl carbon with the to stabilize the translation state. Theze key residues of the catalytic triad and oxyanion hole help to make up the .
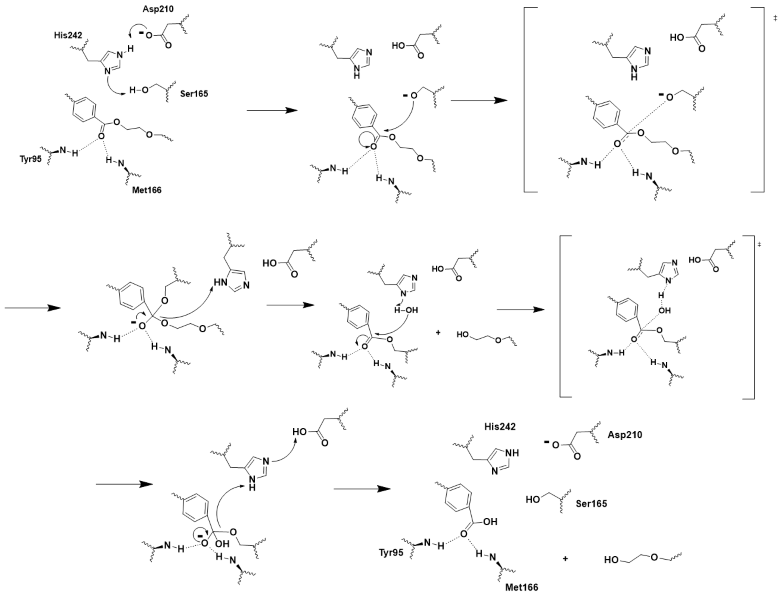
Figure 2 - Push-mechanism for the cutinase reaction
2-HE(MHET)3 substrate
The model substrate for the reaction was .
Mutations
After selection, LCC was mutated in order to improve its efficiency and thermal stability. Tournier et al. (2020) identified from the wildtype and made hundreds of different mutation commutations. Two of these 11 were chosen for the final mutant enzyme, . These mutations were paired with two separately identified thermostability specific mutations (D238C and S283C) to make the final enzyme.
Efficiency improvement
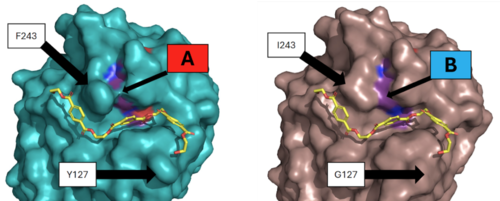
Figure 3 - Protein surface images displaying the impact on the active site
Two of the mutations were selected as they showed the best improvement in catalytic efficiency. The mutation of residue 127 from a to a and the mutation of residue 243 from a to an improved the specific activity of the PET depolymerization of the enzyme by around 27%. This increase in catalytic activity was likely due to the decreased average distance between the catalytic residues in the mutant enzyme. This change can be seen in the surface view of the enzyme’s active site, which shows the loss of the “bridge” over the active site created by the interaction between F243 and its nearby residues. The loss of these interactions when changed to I243 most likely allows for the relaxation of the active site residues and the decrease in the distance between them. Molecular simulations showed that the distance between the carbonyl carbon of the substrate, oxygen of S165, and the nitrogen of H242 was decreased.
Thermostability improvement
To allow the enzyme to be effective in the recycling of PET, it needed to be stable in the high temperature environments used during the recycling process. Because of this, improvements needed to be made to the thermostability of the enzyme. The researchers went about this by searching for divalent metal binding sites, which had been seen to improve the thermal stability of other PET hydrolase enzymes. They found this site formed by the residues of E208, D238, and S283. These residues formed a similar structure that had been seen in other PET hydrolase enzymes, and when calcium ions were added to the enzyme the thermal stability improved. In order to avoid issues with purification, the team opted to avoid the addition of calcium salts and to instead create a disulfide bridge at the location of the divalent metal binding site. They chose to replace the with cysteine residues to form a . This mutation improved the melting temperature of the enzyme by 9.8℃.


