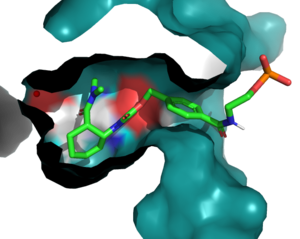
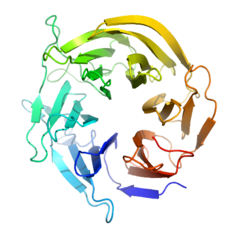Introduction
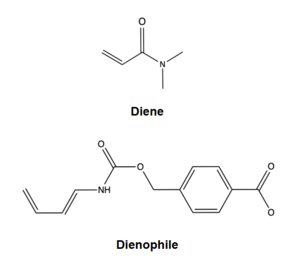
Figure 1. Diels-Alderase substrates
The Diels-Alderase protein aims to create optimal reacting conditions between the diene and dienophile in a Diels-Alder reaction. It accomplishes this by decreasing the energy gap between the dienophile’s lowest unoccupied molecular orbital (LUMO)and the diene’s highest occupied molecular orbital (HOMO)in the transition state.[1] The binding pocket of 4O5T is selective for two substrates, 4-carboxybenzyl trans-1,3-butadiene-1-carbamate (diene) and N,N- dimethylacrylamide (dienophile). The binding site contains a hydrogen bond donor (Y134) which lowers the LUMO energy and stabilizes the negative charge on the dienophile and a hydrogen bond acceptor (Q208) that increases the HOMO energy and stabilizes the positive charge on the diene.[1] Both of these H-bonding interactions work to stabilize the transition state, while also orienting the substrates in optimal conformations for reacting.
The Diels-Alderase enzyme was built using de novo enzyme design, which relies on computational modeling that is refined through programming and collaborative problem-solving from online users. The original protein was made using the Rosetta computational design program, where a potential active site was built and tested against a library of scaffold proteins. Later, as the active site was perfected, future generations of the Diels-Alderase were made using an online protein folding game called Foldit, where players competed to improve binding efficiency by completing various challenges.[2]
General Structure
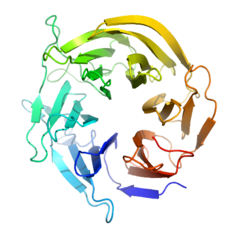
Figure 2. Beta-propeller scaffold
Scaffold
After early Rosetta computational modelling, an ideal protein scaffold was found in the 6-bladed beta-propeller of Loligo vulgalis, or the Europoean Squid. [1][3] The protein is relatively simple, with only one chain, one unit, 324 residues, and no extra ligands, metal ions, or small molecules bound.
Active Site
In the active state, there are that aim to stabilize the transition state of the Diels-Alder reaction. The Y134 acts as a to the oxygen on the . Q208 acts as a to the nitrogen on the ligand. These interactions help reduce the energetic gap between orbitals allowing the reaction to proceed, outlined in HOMO/LUMO.
Helix Cap
In the evolution process, researchers added a 16-residue alpha-helix motif to the top of the binding site. The hydrophobic helix “functions as a lid to constrain the substrates in a productive orientation for reaction,” decreasing the Km of the enzyme and increasing the catalytic efficiency, as seen in the measured kinetics of the enzyme.[2]
Mechanism
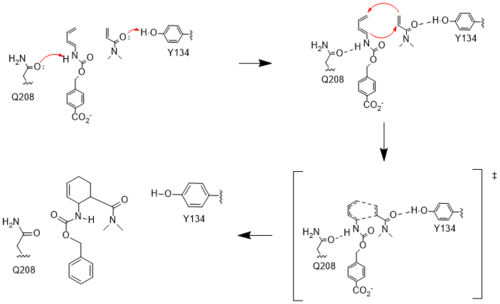
Figure 4. Active site mechanism
HOMO and LUMO
The two active site residues, Y134 and Q208, use hydrogen bonding to close the energy gap between the HOMO diene and the LUMO dienophile. The goal of closing the energy gap allows the diene and dienophile to readily switch roles for the mechanism to progress and complete the formation of the product. Due to the conserved nature of this mechanism, the diels-alderase is stereoselective for the 3R, 4S endo product.
Hydrogen Binding
Rather than using acid-base catalysislike many enzymes, the Diels-Alderase utilizes hydrogen bonding to alter the HOMO and LUMO energies of the diene and dienophile. Y134 donates a hydrogen bond to the dieneophile, increasing the electron density and lowering the LUMO. Q208 accepts a hydrogen bond from the diene, decreasing the electron density and lowering the HOMO.
Development and Evolution
DA_20_00
During initial computer modelling, over one million potential Diels-Alderase active sites could be matched to potential protein scaffolds.[1] Computer optimization narrowed this down to 84 potential models, and researchers attempted to grow and purify those proteins within an E. coli host. Of the 50 proteins that were successfully purified, only 2 proteins proved to be sufficiently active after LC-MSscreening. DA_20_00, which used a beta-propeller scaffold, had the most success in further mutations and therefore became the Diels-Alderase of choice.[1] However, this initial enzyme's active site had very little catalytic activity, seen in its low catalytic efficiency after kinetic screening.[1][4]
DA_20_10
DA_20_10 provided key mutations in and around the active site that increased the hydrophobicity, provided structural stability, and increased interactions between the ligand and surrounding residues.
Q162R
- Residue 162, a , resides near the top of the binding entrance to the enzyme, and is outside 3 Angstroms in most models on the enzyme. It can act as a hydrogen bond donor to the terminal phosphate on the ligand when in proximity. To increase this interaction, the group chose to mutate this Q to an , which decreased the length of the potential hydrogen bond to within 2.5 Angstroms, increasing the strength of the interaction.[1]
S284A
- Residue 284 resides deep within the binding pocket of the enzyme. The group chose a to mutation to increase the hydrophobicity of the binding pocket and reduce reactivity, without also changing any steric characteristics in the region unintentionally near the catalytic residues.[1]
A285N
- , as follows, is also buried within the binding pocket. The group introduced this mutation to increase steric hindrance with the catalytic tyrosine, reducing the number of rotamers the residue has to increase the reactivity of the enzyme by lowering the distance between Y134 and the ligand.[1]
CE6
The DA_20_10 model of the Diels Alderase was further enhanced by players of the online game "Foldit." Building on preliminary early data, players were asked to optimize various helical structures that would surround and support the ligand. After over 100,000 designs were tested, the top-scoring CE6 model was finalized, containing as that favorably constrains ligand orientation. This "cap" consists of two helices--helix one spans from residues 36-44, and helix two spans from residues 48-56.[2]
CE20
In this generation, it was found that the most catalytically efficient models had mutated T34, P48, and R56 to . These mutations further tightened the binding pocket and create a more hydrophobic environment.[4]
Kinetics

Figure X. Catalytic efficiencies of key Diels-Alderase generations. Kinetic data was measured at 25 degrees Celsius, in PBS, at pH 7.4
[4]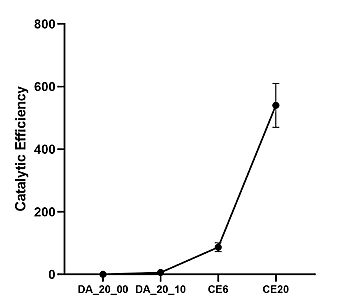
Figure X. Improvement of catalytic efficiency
[4]Classic Michaelis-Menten kineticswere determined for each generation of the enzyme. As the Diels-Alderase relies on a catalyzed interaction between both the diene and dienophile, a Michaelis binding constant (Km value) was determined for each substrate separately before catalytic efficiency was calculated. The CE20 model of the enzyme is over 300-fold more efficient than the first enzyme model due to increasing active site specificity.[4]
Applications
The CE20 model is the most efficient Diels-Alderase yet, surpassing many other biological (antibody) and artificial (ribozyme, metalloenzyme) attempts at catalyzing the Diels-Alder reaction. Even then, the CE20 model has a catalytic efficiency value at least 4 orders of magnitude lower than those seen in other moderately-efficient natural enzymes, demonstrating the innate slowness of the Diels-Alder reaction.[4]
Though the rate of product formation using this enzyme is not significantly different from that found when reactants reflux free in solution, the Diels-Alderase shows a vast improvement in product stereoselectivity. When refluxed in a room temperature aqueous solution containing the necessary substrates, the enzyme catalyzed an over 90% conversion rate, producing only the 3R,4S endo cyclohexane product isomer. By comparison, refluxing the substrates free in solution for a similar duration of time yields a racemic (66:34) mixture of endo and exo products. It is primarily for these stereoselective benefits that this enzyme is valuable for synthetic purposes. [4]
Future improvement of the Diels-Alderase will likely revolve around the improvement of catalytic efficiency, further constriction of the active site, and selective production of varying stereoisomers.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 1.8 Siegel JB, Zanghellini A, Lovick HM, Kiss G, Lambert AR, St Clair JL, Gallaher JL, Hilvert D, Gelb MH, Stoddard BL, Houk KN, Michael FE, Baker D. Computational design of an enzyme catalyst for a stereoselective bimolecular Diels-Alder reaction. Science. 2010 Jul 16;329(5989):309-13. PMID:20647463 doi:329/5989/309
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Eiben CB, Siegel JB, Bale JB, Cooper S, Khatib F, Shen BW, Players F, Stoddard BL, Popovic Z, Baker D. Increased Diels-Alderase activity through backbone remodeling guided by Foldit players. Nat Biotechnol. 2012 Jan 22;30(2):190-2. doi: 10.1038/nbt.2109. PMID:22267011 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nbt.2109
- ↑ Scharff EI, Koepke J, Fritzsch G, Lucke C, Ruterjans H. Crystal structure of diisopropylfluorophosphatase from Loligo vulgaris. Structure. 2001 Jun;9(6):493-502. PMID:11435114
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 4.5 4.6 Preiswerk N, Beck T, Schulz JD, Milovnik P, Mayer C, Siegel JB, Baker D, Hilvert D. Impact of scaffold rigidity on the design and evolution of an artificial Diels-Alderase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014 May 20. pii: 201401073. PMID:24847076 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1401073111
Student Contributors
Taylor Donahue, Kate Thuma, Micah Zile