Introduction
Background
Figure 1. Iron transport and release for bacterial metabolic processes (Image created in BioRender.com).
is a de novo ferric enterobactin esterase designed to highlight the potential of synthetic biology in creating simpler protein structures capable of performing complex functions [1]. Syn-F4 is also the first de novo protein catalytically active in vitro and biologically functional in vivo [1]. Ferric enterobactin esterases are a type of endogenous bacterial enzyme that break ester bonds of small metabolites bound to iron, allowing iron to be released into and utilized by bacterial cells (Fig. 1) [2] [3]. Iron plays crucial roles in various physiological processes in bacteria, including cellular respiration, oxidative stress responses, and DNA and protein synthesis (Fig. 1) [3].
is one such native esterase responsible for releasing Fe3+ from iron-chelating compounds, such as ferric enterobactin, within the cell, making it critical for bacterial survival [2] [4]. In order to mimic evolutionary selection of proteins for specific biological functions, Syn-IF was a de novo bifunctional protein designed to perform iron release, similar to Fes. Syn-IF was subjected to a series of random mutagenesis to individually select for its iron-releasing function, leading to the creation of Syn-F4 [5]. While Syn-F4 catalysis is 1000-fold slower than that of a native Fes enzyme, it is still sufficient in rescuing function in ∆fes E.coli [1] [5].
Whereas most ferric enterobactin esterases are serine hydrolases that function via a catalytic triad, such as Fes, Syn-F4 performs its function via a catalytic dyad without the involvement of a serine active site residue (Fig. 2) [1] [4]. One other serine hydrolase, , also performs catalysis through a catalytic dyad but still uses a serine residue as the nucleophile (Fig. 2) [4] [6]. The unassuming design of Syn-F4 was modeled after the de novo protein , which was originally designed to be used as a "building block" for other synthetic proteins and nanotechnology designs [7]. The crystallization of WA20 reveals an alpha-helix bundle structure, which served as the basis for the design of Syn-F4 [1] [7] .
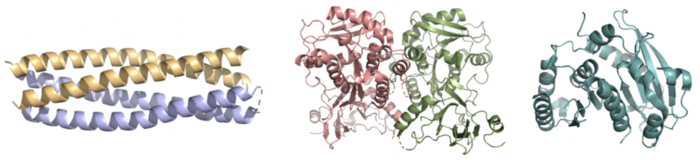
Figure 2. Pictured left-to-right: Structures of the ferric enterobactin esterases Syn-F4 (PDB: 8H7C), Fes (PDB: 3C87), and IroE (PDB: 2GZR), respectively.
Ligand
Ferric enterobactin is a metabolite that is part of a larger family of siderophores, which are low-molecular-weight, high-affinity, iron-chelating compounds that facilitate the transport of iron across the cell membrane [2] [3]. (FeEnt) is characterized by three catecholamine groups linked together by a trilactone ring and an exceptionally high affinity for Fe3+ (Kd = 10−52 M) [2] [8]. It is easily degraded when not bound to iron, which is coordinated to FeEnt by six hydroxyl groups and released by the hydrolysis of an ester bond [2] [8].
Structure
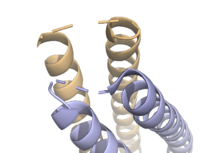
Figure 3. Unresolved residues of "loop left" structure (PDB: 8H7C).
Alpha-Helix Bundle
The crystallization of the
de novo protein, WA20, revealed a an homodimer structure, which served as the foundation for the design of Syn-F4
[7]. While structurally similar, Syn-F4 features a novel active site characterized by the presence of a
[1]. Despite its simple appearance, the structure is highly coordinated and efficient due to this active site.
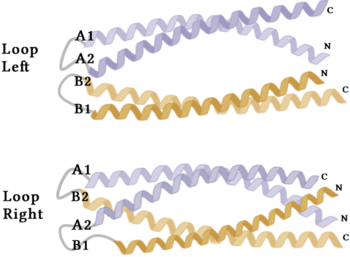
Figure 4. A schematic representing the differential conformations of the "loop-left" and "loop-right" Syn-F4 structures (Image created in BioRender.com).
The symmetry of the four-helix bundle, combined with the configuration of the central hole, facilitates catalytic activity by effectively cleaving the ester bond in ferric enterobactin
[1].
Stabilizing Factors
The on either side of the bundles largely contribute to the stability of Syn-F4. Due to the symmetry of the chains, both chain A and chain B display the same residues and are linked by unresolved residues (Fig. 3) [1]. The accumulated negative charge on the C-termini is stabilized by positively-charged residues (H10, H45, H46, R102), and conversely, the accumulated positive charge on the N-termini is stabilized by negatively-charged residues (D59). Additionally, the within the core of Syn-F4 interact via Van der Waals to promote association between the helices.
The orientation of the alpha helices and their associated interactions could not be definitively determined due to the absence of loop residues in the crystallized structure of Syn-F4 [1]. To address this, molecular dynamics (MD) simulations were performed to estimate the predominant conformation of the helices [1]. Two potential conformations were identified: "loop left" and "loop right" (Fig. 4) [1]. Among these, the "loop left" conformation demonstrated greater stability and was therefore considered the preferred structure (Fig. 4) [1].
Function
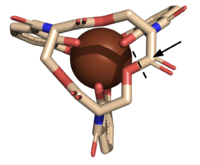
Figure 5. The scissile bond of ferric enterobactin is denoted by a dotted line, and the electrophile is indicated by the arrow (PDB: 2XUZ).
Active Site
The of Syn-F4 lies within the central hole of the structure, made up of five catalytic residues (E26, H74, R77, K78, and R85) that facilitate binding to ferric enterobactin and catalyze hydrolysis of the scissile (ester) bond, which is indicated by the dotted line (Fig. 5) [1]. The mutation of any of these five resides completely abrogates the function of the enzyme [1].
Mechanism
The mechanism of Syn-F4 was proposed to function at pH 6.0 via a catalytic dyad with histidine (H74) and glutamate (E26) residues and water attacking as the nucleophile [1]. The electrophile is an oxygen making up one of the ester bonds of the ligand, denoted by an arrow (Fig. 5). A representation of the possible mechanism of Syn-F4 performing hydrolysis of the scissile bond of ferric enterobactin follows:
Step 1
E26 first deprotonates H74, which then deprotonates H2O in turn (Fig. 6). The newly-formed hydroxide attacks the ester electrophile, kicking electron density up onto the carboxyl group in the first transition state (Fig. 6).
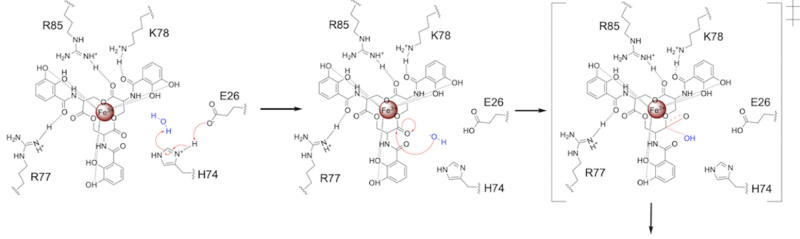
Figure 6. Step 1. Activation of water as the nucleophile and attack of the ester electrophile. The first transition state is depicted.
Step 2
The second transition state is characterized by the electron density on the carboxyl group collapsing and kicking off the leaving group (Fig. 7). As the ferric enterobactin structure linearizes, Fe3+ is released, and the enzyme is reset by the re-protonation of H74 by E26 (Fig. 7).
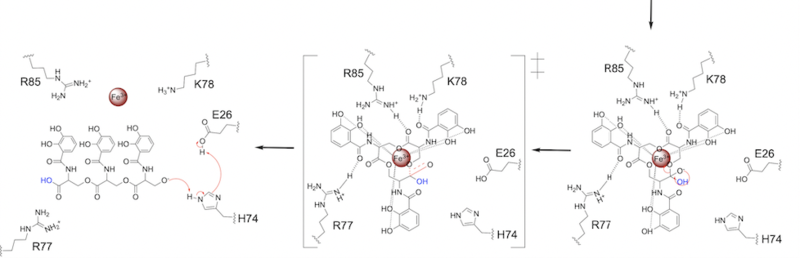
Figure 7. Step 2. The second transition state and linearization of ferric enterobactin are depicted. Iron is released and the enzyme resets itself.
Related Structures
Both the structure and mechanism of Syn-F4 differ from other native ferric enterobactin esterases whose structures have been previously determined. Native Fes and IroE enzymes are both serine hydrolases, which means a serine residue acts as their nucleophile [4] [6] [9]. Native is a homodimer that acts via a catalytic triad (S281, E345, and H375), whereas acts via a catalytic dyad (S189 and H287), similar to Syn-F4 (Fig. 8) [4] [6] [9].
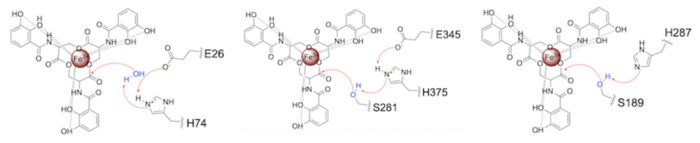
Figure 8. Pictured left-to-right: Mechanisms of the ferric enterobactin esterases Syn-F4, Fes, and IroE, respectively.
Relevance
Synthetic Biology
De novo proteins are at the forefront of biochemical and industrial applications, designed to mimic the evolutionary selection of proteins for highly specific functions. These engineered proteins show significant promise in enhancing antibiotic therapies, particularly in light of rising antibiotic resistance. For example, targeting bacterial iron acquisition pathways may offer an effective alternative to traditional antibiotic treatments [10] [11]. Furthermore, as our understanding of cellular signaling pathways advances, de novo proteins present new opportunities for cancer therapy. Through synthetic biology, it is possible to increase drug efficacy by designing agents that selectively target malignant cells while preserving healthy tissue [12]. Additionally, programming bacteria through synthetic compounds could enable bacteriotherapy approaches, in which engineered bacteria express specific proteins that bind to tumor-associated antigen markers, offering a novel strategy for cancer targeting and treatment [13]. Synthetic biology holds vast potential across a multitude of fields, with applications that span far beyond initial application. Its development is set to become integral to the future of biomedical research and innovation. As the field of synthetic biology continues to advance, its potential applications appear boundless [14] [15].
References
- ↑ 1.00 1.01 1.02 1.03 1.04 1.05 1.06 1.07 1.08 1.09 1.10 1.11 1.12 1.13 1.14 Kurihara K, Umezawa K, Donnelly AE, Sperling B, Liao G, Hecht MH, Arai R. Crystal structure and activity of a de novo enzyme, ferric enterobactin esterase Syn-F4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023 Sep 19;120(38):e2218281120. PMID:37695900 doi:10.1073/pnas.2218281120
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 Abergel RJ, Warner JA, Shuh DK, Raymond KN. Enterobactin protonation and iron release: structural characterization of the salicylate coordination shift in ferric enterobactin. J Am Chem Soc. 2006 Jul 12;128(27):8920-31. PMID:16819888 doi:10.1021/ja062046j
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Peuckert F, Ramos-Vega AL, Miethke M, Schworer CJ, Albrecht AG, Oberthur M, Marahiel MA. The siderophore binding protein FeuA shows limited promiscuity toward exogenous triscatecholates. Chem Biol. 2011 Jul 29;18(7):907-19. PMID:21802011 doi:10.1016/j.chembiol.2011.05.006
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 Lin H, Fischbach MA, Liu DR, Walsh CT. In vitro characterization of salmochelin and enterobactin trilactone hydrolases IroD, IroE, and Fes. J Am Chem Soc. 2005 Aug 10;127(31):11075-84. PMID:16076215 doi:10.1021/ja0522027
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Smith BA, Mularz AE, Hecht MH. Divergent evolution of a bifunctional de novo protein. Protein Sci. 2015 Feb;24(2):246-52. PMID:25420677 doi:10.1002/pro.2611
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 Larsen NA, Lin H, Wei R, Fischbach MA, Walsh CT. Structural characterization of enterobactin hydrolase IroE. Biochemistry. 2006 Aug 29;45(34):10184-90. PMID:16922493 doi:10.1021/bi060950i
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 Arai R, Kobayashi N, Kimura A, Sato T, Matsuo K, Wang AF, Platt JM, Bradley LH, Hecht MH. Domain-Swapped Dimeric Structure of a Stable and Functional De Novo 4-Helix Bundle Protein, WA20. J Phys Chem B. 2012 Mar 8. PMID:22397676 doi:10.1021/jp212438h
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Moynie L, Milenkovic S, Mislin GLA, Gasser V, Malloci G, Baco E, McCaughan RP, Page MGP, Schalk IJ, Ceccarelli M, Naismith JH. The complex of ferric-enterobactin with its transporter from Pseudomonas aeruginosa suggests a two-site model. Nat Commun. 2019 Aug 14;10(1):3673. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-11508-y. PMID:31413254 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-11508-y
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 Timofeeva AM, Galyamova MR, Sedykh SE. Bacterial Siderophores: Classification, Biosynthesis, Perspectives of Use in Agriculture. Plants (Basel). 2022 Nov 12;11(22):3065. PMID:36432794 doi:10.3390/plants11223065
- ↑ Stelitano G, Cocorullo M, Mori M, Villa S, Meneghetti F, Chiarelli LR. Iron Acquisition and Metabolism as a Promising Target for Antimicrobials (Bottlenecks and Opportunities): Where Do We Stand? Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 24;24(7):6181. PMID:37047161 doi:10.3390/ijms24076181
- ↑ Rivera M. Mobilization of iron stored in bacterioferritin, a new target for perturbing iron homeostasis and developing antibacterial and antibiofilm molecules. J Inorg Biochem. 2023 Oct;247:112306. PMID:37451083 doi:10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2023.112306
- ↑ Lim B, Yin Y, Ye H, Cui Z, Papachristodoulou A, Huang WE. Reprogramming Synthetic Cells for Targeted Cancer Therapy. ACS Synth Biol. 2022 Mar 18;11(3):1349-1360. PMID:35255684 doi:10.1021/acssynbio.1c00631
- ↑ Sedighi M, Zahedi Bialvaei A, Hamblin MR, Ohadi E, Asadi A, Halajzadeh M, Lohrasbi V, Mohammadzadeh N, Amiriani T, Krutova M, Amini A, Kouhsari E. Therapeutic bacteria to combat cancer; current advances, challenges, and opportunities. Cancer Med. 2019 Jun;8(6):3167-3181. PMID:30950210 doi:10.1002/cam4.2148
- ↑ Thevenin BJ, Crandall I, Ballas SK, Sherman IW, Shohet SB. Band 3 peptides block the adherence of sickle cells to endothelial cells in vitro. Blood. 1997 Nov 15;90(10):4172-9 PMID:9354688
- ↑ Yan X, Liu X, Zhao C, Chen GQ. Applications of synthetic biology in medical and pharmaceutical fields. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023 May 11;8(1):199. PMID:37169742 doi:10.1038/s41392-023-01440-5








