We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 1852
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
==General Structure== | ==General Structure== | ||
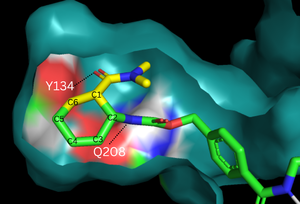
| - | [[Image:Diels-AlderaseSurfaces.png|300px|left|thumb|Figure | + | [[Image:Diels-AlderaseSurfaces.png|300px|left|thumb|Figure 2. Binding pocket and substrate. Shown is the binding pocket of the enzyme shown as surface, highlighting the electrostatics of the two catalytic residues, Tyr134 and Glu208. The ligand is color coded based on original structure: the dieophile is in yellow and the diene is in green. The reaction proceeds via attack of the C6 on the C5, shifting electron density to C2, which attacks C1.]] |
====Scaffold==== | ====Scaffold==== | ||
After early Rosetta computational modelling, an ideal protein <scene name='10/1075254/Squidscaffold/2'>scaffold</scene> was found in the 6-bladed [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Beta-propeller beta-propeller] of ''Loligo vulgalis,'' or the European Squid. <ref name="Siegel"/><ref name="Scharff">PMID:11435114</ref> The protein is relatively simple, with only one chain, one unit, 324 residues, and no extra ligands, metal ions, or small molecules bound. | After early Rosetta computational modelling, an ideal protein <scene name='10/1075254/Squidscaffold/2'>scaffold</scene> was found in the 6-bladed [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Beta-propeller beta-propeller] of ''Loligo vulgalis,'' or the European Squid. <ref name="Siegel"/><ref name="Scharff">PMID:11435114</ref> The protein is relatively simple, with only one chain, one unit, 324 residues, and no extra ligands, metal ions, or small molecules bound. | ||
====Active Site==== | ====Active Site==== | ||
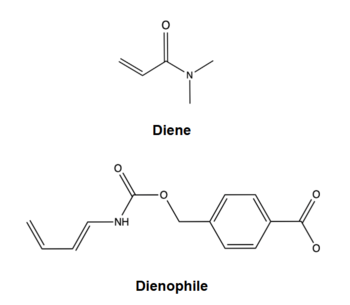
| - | In the designed active site, <scene name='10/1075254/Active_site/6'>two catalytic residues</scene> stabilize the transition state of the Diels-Alder reaction. The Tyr134 acts as a <scene name='10/1075253/Y134_h_donation/ | + | In the designed active site, <scene name='10/1075254/Active_site/6'>two catalytic residues</scene> stabilize the transition state of the Diels-Alder reaction. The Tyr134 acts as a <scene name='10/1075253/Y134_h_donation/3'>hydrogen bond donor</scene> to the oxygen on the dienophile (see Fig. 2). Q208 acts as a <scene name='10/1075254/208_bond_donor/3'>hydrogen bond acceptor</scene> to the nitrogen on the diene. These interactions help reduce the energetic gap between orbitals allowing the reaction to proceed. |
====Helix Cap==== | ====Helix Cap==== | ||
In the evolution process, a 16-residue [https://proteopedia.org/wiki/index.php/Alpha_helix alpha-helix] <scene name='10/1075252/Alpha_helix_highlighted/4'>motif</scene> to the top of the binding site. The hydrophobic helix “functions as a lid to constrain the substrates in a productive orientation for reaction,” decreasing the ''K<sub>m</sub>'' of the enzyme and increasing the catalytic efficiency, as seen in the measured kinetics of the enzyme.<ref name="Eiben">PMID:22267011</ref> | In the evolution process, a 16-residue [https://proteopedia.org/wiki/index.php/Alpha_helix alpha-helix] <scene name='10/1075252/Alpha_helix_highlighted/4'>motif</scene> to the top of the binding site. The hydrophobic helix “functions as a lid to constrain the substrates in a productive orientation for reaction,” decreasing the ''K<sub>m</sub>'' of the enzyme and increasing the catalytic efficiency, as seen in the measured kinetics of the enzyme.<ref name="Eiben">PMID:22267011</ref> | ||
== Mechanism == | == Mechanism == | ||
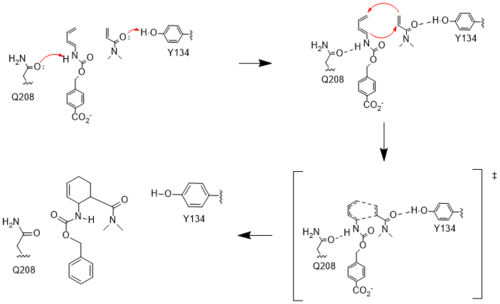
| - | [[Image:Resizedmechanism.png|500px|left|thumb|Figure | + | [[Image:Resizedmechanism.png|500px|left|thumb|Figure 3. Active site mechanism]] |
====HOMO and LUMO==== | ====HOMO and LUMO==== | ||
The two active site residues, Y134 and Q208, use hydrogen bonding to close the energy gap between the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Diels%E2%80%93Alder_reaction HOMO diene and the LUMO dienophile]. The goal of closing the energy gap allows the diene and dienophile to readily switch roles for the mechanism to progress and complete the formation of the product. Due to the conserved nature of this mechanism, the diels-alderase is stereoselective for the 3R, 4S endo product. | The two active site residues, Y134 and Q208, use hydrogen bonding to close the energy gap between the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Diels%E2%80%93Alder_reaction HOMO diene and the LUMO dienophile]. The goal of closing the energy gap allows the diene and dienophile to readily switch roles for the mechanism to progress and complete the formation of the product. Due to the conserved nature of this mechanism, the diels-alderase is stereoselective for the 3R, 4S endo product. | ||
| Line 52: | Line 52: | ||
==Kinetics== | ==Kinetics== | ||
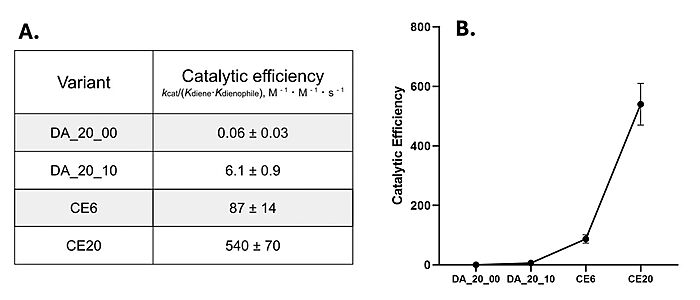
| - | [[Image:DAcombinedkineticdata Large.jpeg|700px|left|thumb|Figure | + | [[Image:DAcombinedkineticdata Large.jpeg|700px|left|thumb|Figure 4. A) Catalytic efficiencies of key Diels-Alderase generations. Kinetic data was measured at 25°C, in PBS, at pH 7.4. B) Improvement of catalytic efficiency across generations.<ref name="Preiswerk">PMID:24847076</ref>]] |
Classic [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Michaelis%E2%80%93Menten_kinetics Michaelis-Menten kinetics]were determined for each generation of the enzyme. As the Diels-Alderase relies on a catalyzed interaction between both the diene and dienophile, a Michaelis binding constant (''K<sub>m</sub>'' value) was determined for each substrate separately before catalytic efficiency was calculated. The CE20 model of the enzyme is over 300-fold more efficient than the first enzyme model due to increasing active site specificity.<ref name="Preiswerk"/> | Classic [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Michaelis%E2%80%93Menten_kinetics Michaelis-Menten kinetics]were determined for each generation of the enzyme. As the Diels-Alderase relies on a catalyzed interaction between both the diene and dienophile, a Michaelis binding constant (''K<sub>m</sub>'' value) was determined for each substrate separately before catalytic efficiency was calculated. The CE20 model of the enzyme is over 300-fold more efficient than the first enzyme model due to increasing active site specificity.<ref name="Preiswerk"/> | ||
Revision as of 01:09, 24 April 2025
| This Sandbox is Reserved from March 18 through September 1, 2025 for use in the course CH462 Biochemistry II taught by R. Jeremy Johnson and Mark Macbeth at the Butler University, Indianapolis, USA. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1828 through Sandbox Reserved 1846. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
Diels-Alderase
| |||||||||||