We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox323
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==4Q7Q Structure and Proposed Functionality== | ==4Q7Q Structure and Proposed Functionality== | ||
| - | (NOTE TO ALL EDITORS: This page is part of a final project for a biochemistry lab at Elizabethtown College. Please do not edit this.) | + | (NOTE TO ALL EDITORS: This page is part of a final project for a biochemistry lab at Elizabethtown College. Please do not edit this. -Neil Divins) |
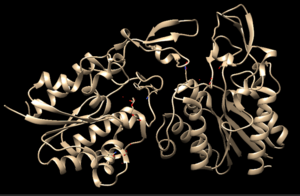
4Q7Q is a homodimeric protein complex that originates from the bacterial species Chitinophaga Pinensis and has a mass of 58.5 kDa. It is a member of the SGNH Hydrolase Superfamily with structural and sequential similarities to esterases and lipases. Current evidence suggests it causes the hydrolysis of esters and/or acetyl groups on lipids/lipid-like molecules via a serine protease-like active site. | 4Q7Q is a homodimeric protein complex that originates from the bacterial species Chitinophaga Pinensis and has a mass of 58.5 kDa. It is a member of the SGNH Hydrolase Superfamily with structural and sequential similarities to esterases and lipases. Current evidence suggests it causes the hydrolysis of esters and/or acetyl groups on lipids/lipid-like molecules via a serine protease-like active site. | ||
| Line 73: | Line 73: | ||
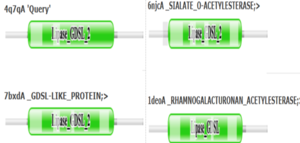
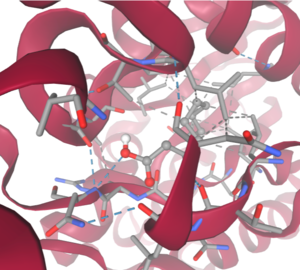
We also believe 4Q7Q undergoes several significant structural changes during enzymatic activities. Analysis into other members of its family reveal mechanisms wherein serine and histidine residues shift during substrate binding. <ref name="GDSL" /> | We also believe 4Q7Q undergoes several significant structural changes during enzymatic activities. Analysis into other members of its family reveal mechanisms wherein serine and histidine residues shift during substrate binding. <ref name="GDSL" /> | ||
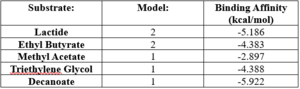
| - | + | == Experimental Data == | |
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
Revision as of 21:39, 25 April 2025
4Q7Q Structure and Proposed Functionality
(NOTE TO ALL EDITORS: This page is part of a final project for a biochemistry lab at Elizabethtown College. Please do not edit this. -Neil Divins)
4Q7Q is a homodimeric protein complex that originates from the bacterial species Chitinophaga Pinensis and has a mass of 58.5 kDa. It is a member of the SGNH Hydrolase Superfamily with structural and sequential similarities to esterases and lipases. Current evidence suggests it causes the hydrolysis of esters and/or acetyl groups on lipids/lipid-like molecules via a serine protease-like active site.
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 4Q7Q. Protein Database, 2014. https://www.rcsb.org/structure/4Q7Q
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 Nadzirin, N.; Gardiner, E.; Willett, P.; Artymiuk, P. J.; Firdaus-Raih, M. 2012. SPRITE and ASSAM: web servers for side chain 3D-motif searching in protein structures. Nucleic Acids Res., 40(Web Server Issue), W380-6.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Rio, T. G. D.; et al. Complete genome sequence of Chitinophaga pinensis type strain (UQM 2034). Stand. Genomic. Sci., 2010, 2(1), 87-95. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3035255/
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 SGNH hydrolase superfamily. InterPro, 2017. https://www.ebi.ac.uk/interpro/entry/InterPro/IPR036514/
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 Rio, T. G. D.; et al. Complete genome sequence of Chitinophaga pinensis type strain (UQM 2034). Stand. Genomic. Sci., 2010, 2(1), 87-95. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3035255/
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 Molgaard, A.; Kauppinen, S.; Larsen, S. Rhamnogalacturonan acetylesterase elucidates the structure and function of a new family of hydrolases. Struct., 2000, 8(4), 373-383. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0969212600001180?via%3Dihub
- ↑ UCSF Chimera--a visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. Pettersen EF, Goddard TD, Huang CC, Couch GS, Greenblatt DM, Meng EC, Ferrin TE. J Comput Chem. 2004 Oct;25(13):1605-12.
- ↑ Akoh, C. C.; Lee, G.; Liaw, Y.; Huang, T.; Shaw, J. GDSL family of serine esterases/lipases. Prog. Lipid Res., 2004, 43(6), 534-552. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15522763/
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 9.3 9.4 9.5 9.6 Holm L, Laiho A, Toronen P, Salgado M (2023) DALI shines a light on remote homologs: one hundred discoveries. Protein Science 23, e4519
- ↑ Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedMolaard - ↑ 11.0 11.1 11.2 11.3 Bugnon M, Röhrig UF, Goullieux M, Perez MAS, Daina A, Michielin O, Zoete V. SwissDock 2024: major enhancements for small-molecule docking with Attracting Cavities and AutoDock Vina. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024, 52 (W1), W324-W332. DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkae300.
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 12.2 12.3 Grosdidier A, Zoete V, Michielin O. SwissDock, a protein-small molecule docking web service based on EADock DSS. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39 (Web Server issue), W270-W277. DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkr366
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 13.2 13.3 Eberhardt J, Santos-Martins D, Tillack AF, Forli S. AutoDock Vina 1.2.0: New Docking Methods, Expanded Force Field, and Python Bindings. J. Chem. Inf. Model., 2021, 61 (8), 3891–3898, DOI: 10.1021/acs.jcim.1c00203
- ↑ Trott O, Olson AJ. AutoDock Vina: Improving the Speed and Accuracy of Docking with a New Scoring Function, Efficient Optimization, and Multithreading. J. Comput. Chem., 2010, 31 (2), 455–461, DOI: 10.1002/jcc.21334
- ↑ Miesfeld, R. L.; McEvoy, M. M. Biochemistry, 2nd ed.; W. W. Norton & Company, 2021
- ↑ Xia, L.; Qian, M.; Cheng, F.; Wang, Y.; Han, J.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, K.; Tian, J.; Jin, Y. The effect of lactic acid bacteria on lipid metabolism and flavor of fermented sausages. Food Biosci., 2023, 56, 103172.