Introduction
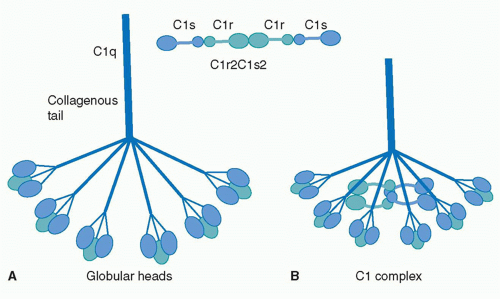
Complement component 1q, or , is the first component of the classical pathway of the complement system. C1q is a subcomponent of the Complement component 1 (C1), along with C1r and C1s. C1q consists of six globular-head regions all connected to a collagen-like region (), with each globular head consisting of 3 separate , having a total mass of roughly 460 kDa. The globular heads entirely consist of β-sheets. The activation of C1q through the binding of the globular head to a variety of epitopes induces structural changes in the collagen-like region of C1q. This activates C1r, which cleaves C1s, which splits into other complement proteins to further activate other aspects of the classical complement system pathway. C1q binds to a variety of different antigens, such as phagocytes to induce phagocytosis, apoptotic cells through phosphatidylserine and DNA to induce apoptosis, and the Fc region of IgG and IgM to activate the complement system as described. C1q acts as a crucial protein that bridges the adaptive and innate immune system.
Function
Innate Immunity
C1q plays a major role in the innate part of the immune system. It is the first complement protein to be activated in the classical complement pathway. This pathway of complement activation is dependent on the detection of antibody-antigen complexes, which creates a cascade of complement protein activation to ultimately promote inflammation, enhance the performance of various immune cells, and attack the pathogen's cell membrane. This acts as an irreplicable aspect of the innate immune system and is one of the body's primary defense against invaders.
C1q is also known to be a kind of opsonin, which is a protein that tags a foreign cell to be engulfed and destroyed by phagocytes, such as neutrophils and macrophages. This process is a very important aspect of the innate immune system to eliminate foreign bacteria and viruses to keep the host healthy. It has been shown that both neutrophils and macrophages posses receptors capable of binding the globular head and CLR of C1q, named gC1q and cC1q respectively, emphasizing their crucial role for phagocytes to identify and eliminate foreign pathogens. Immature dendritic cells have also been shown to contain a large amounts of gC1q and cC1q. This acts as an important bridge between the innate and adaptive immune systems; dendritic cells can survey certain areas based on the amount of present C1q in order to activate and begin digesting antigens to present to T-cells, which is a crucial step in adaptive immunity activation.
Adaptive Immunity
As iterated above, C1q is important in the activation phase of the adaptive immune response. In addition, C1q plays a major role in the solubilization of certain immune complexes, mainly the antibody-antigen complex. One of the main roles of C1q is to bind to these complexes at the Fc region of Immunoglobulin (Ig) G and IgM when bonded to an antigen. This activates the classical cascade of the complement system but also prevents the immune complex from becoming insoluble, which could lead to further unnecessary inflammation as they can no longer be detected by phagocytes for destruction. C1q, especially the globular head region, is known to be profoundly and is a key component in the prevention of preformed immune precipitation, along with other components of the classical complement pathway.
C1q has been shown to partially facilitate the function of T-cells. The receptors gC1q and cC1q are both present on T-cells and serve as both activators and inhibitors. In the presence of immune complexes, C1q has shown to activate T-cells, acting as a bridge between the innate and adaptive immune system. In terms of inhibition, C1q is observed to suppress the activity of T-cells in certain environments to regulate the immune system and prevent autoimmune disease. C1q is known to bind to various phospholipids, namely phosphatidylserine, which is largely present on the surface of apoptotic cells. This promotes opsonization by complement proteins such as C1q which leads to macrophage activation while also inhibiting T-cells to interact with the apoptotic cells. Over-activation of T-cells can lead to unnecessary harm within the body when their presence is not necessary and phagocytes are favored.
Active Site
Globular Head
C1q is observed to have many active sites depending on what it is interacting with, with most of these active sites being located on the globular head regions. The most researched interaction concerning C1q active site is its interaction with the antibody-antigen complex. C1q largely depends on ionic residues to create salt bridges and ionic bonds with the Cγ2 domain of IgG or the Cμ3 domain of IgM. The Cγ2 of IgG is located on the Fc region, which becomes aggregated upon complexing with antigens, allowing for increased affinity to C1q. Residues Glu198 -X- Asp200 -X- Lys202 on the A chain of the C1q globular head have been shown to be a consistent active site motif on C1q. This region forms an antiparallel ß-sheet, promoting stability. Another active site has been observed on the B chain of the globular head region (ghB) at residues 114-129. The principle residues involved in binding are the Arg114 and Arg129. These residues interact with negatively charged residues on IgG, mostly Asp and Glu, such as residues Glu195 and Glu287. A common motif seen on IgG that these active sites interact with is Glu - X - Lys - X - Lys, located at residues 318, 320, and 322 respectively. This is a common motif seen on many proteins associated with the immune system, which enforces the observation that C1q can interact with many different proteins in many different contexts. One study showed that an arginine or lysine is required at positions 320 and 322 and a glutamic acid or threonine is required at position 318 in order for C1q to successfully bind. This suggests that a hydrogen bond at position 318 and an ionic interaction at positions 320 and 322 are required for C1q to bind to IgG and other epitopes.
Collagen-Like Region
The collagen-like region (CLR) is the location of a binding site associated with a variety of non-complement related interactions, such as the binding of phagocytes to C1q as mentioned above. However, one of the most important functions of the CLR of C1q is the activation through protease of the remainder of C1; C1r and C1s. Two equivalences of C1r and C1s are bonded C1s - C1r - C1r - C1s to comprise a tetramer that, when cleaved after the bonding of C1q to an epitope, activates the classical pathway of complement activity, promoting inflammation and phagocytosis. The active site on the CLR of C1q is proposed to be lysine residues located at position 61 on the B chain and position 58 on the A chain. These basic residues create salt bridges with associated residues on C1r, generally a glutamic acid or aspartic acid. These residues are coordinated with the Ca2+ ion present in C1q through single carboxyl oxygens, which is available for mediating through an electrostatic bond with a basic residue. Through activation, the C1r - C1r bond is broken, which induces conformational changes in C1r that subsequently cleaves C1s.
Disease
A variety of diseases have been tied to an overabundance and lack of C1q in a person's body, most of which involve the presence of anti-C1q autoantibodies. Anti-C1q autoantibodies are antibodies that target one's own C1q, specifically the collagen-like tail of C1q. These are mistakenly generated through a misdirected immune response, and have the potential to develop into an autoimmune disease, although tests have shown that as much as 2-8% of healthy individuals still contain this antibody. Low levels of C1q and the presence of anti-C1q autoantibodies has been correlated with Hypocomplementemic Urticarial Vasculitis Syndrome (HUVS) or McDuffie syndrome. The main symptoms of this disease are chronic urticarial vasculitic lesions that persist more than 24 hours or are recurring. When these autoantibodies complex with C1q, they cause serum precipitins that contribute to swelling of the blood vessels. This can further lead to organ malfunction, various inflammatory diseases, arthritis, and a plethora of other diseases.
Another disease associated with the presence of anti-C1q autoantibodies is Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE), or just simply lupus. SLE is a disease where the body's own antibodies attack healthy tissue and cause inflammation. This disease, in the cause of SLE caused specifically by anti-C1q autoantibodies, is seen to cause Proliferative Lupus Nephritis (LN), a type of glomerulonephritis, which is inflammation and damage to the kidneys. This causes scarring of the tissue and malfunction of the blood vessels within the kidney and ultimately lead to kidney failure if not treated properly. Studies have been preformed that show that the presence of autoantibodies, including anti-C1q, in the kidneys is capable of producing limited disposition of the kidneys but not nephritis. Only when these anti-C1q autoantibodies are presented with C1q-containing immune complexes do they cause LN. It is unknown why anti-C1q autoantibodies predominantly enhance tissue damage in the kidneys and not in other tissues known to contain C1q immune complexes.
An overabundance of C1q has shown to correlate with the development of neurodegenerative diseases and loss of cognitive function. Higher age groups are seen to have larger levels of C1q, especially in their brain. This buildup mainly occurs because of poorer activity in synaptic clearing of C1q bound to neuronal RNA-binding proteins called neuronal ribonucleoprotein complexes, affecting protein homeostasis in the brain and decreasing cognitive function. C1q is involved in pruning synapses in developing brains by tagging the synapses for phagocytosis by microglia. Elevated concentrations of C1q in the synapses has been correlated with overactivity of microglia when provoked by brain injury or a series of strokes. Most cells in the body have complement inhibiting agents to regulate complement activity, whereas nerve cells lack these complement inhibitors. Astrocytes are known to secrete C1q when provoked by infections or damage to the central nervous system, and an overproduction of these can lead to over inflammation in the brain by the complement cascade and synapses loss, both fundamental components of Alzheimer's disease and various other neurodegenerative diseases.
Structural Highlights
Additional Resources
Classical Pathway Activation animation of C1q binding to IgG.

