User:Vinícius M. Neto/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
== Basic structure == | == Basic structure == | ||
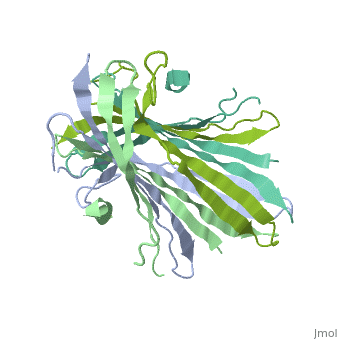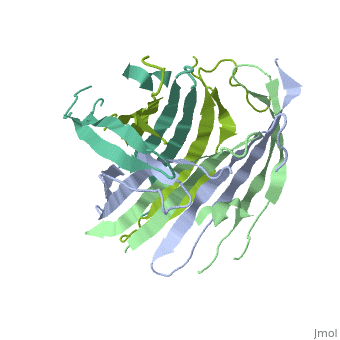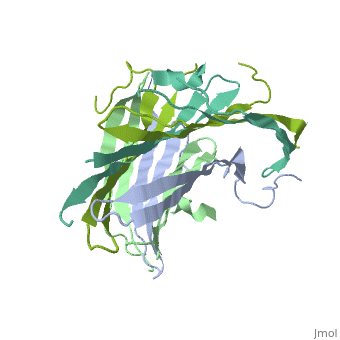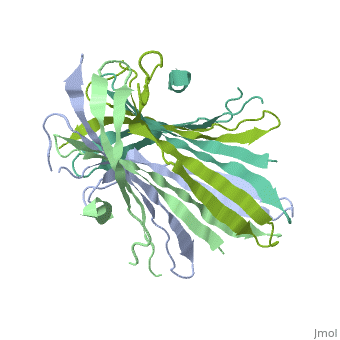
| - | The N-terminal domain of the fibroin heavy chain (FibNT [https://www.rcsb.org/structure/3UA0 3UA0]) is a '''homo-tetramer''' composed of 268 residues, most of which are <scene name='10/1082417/ | + | The N-terminal domain of the fibroin heavy chain (FibNT [https://www.rcsb.org/structure/3UA0 3UA0]) is a '''homo-tetramer''' composed of 268 residues, most of which are <scene name='10/1082417/Hydrophilic-phobic_aas/1'>hydrophilic</scene> (<font color="maroon">'''hydrophilic amino acids in marron'''</font> and <font color="mediumblue">'''hydrophobic in medium blue'''</font>). FibNT's asymmetric unit is a homodimer with eight alternating β-sheets and a disordered C-terminus (Gly109-Ser126). Its two chains (A and B) are nearly identical except for the N-terminal segments (Phe26-Val35): |
* '''Chain A''': Forms a short α-helix. | * '''Chain A''': Forms a short α-helix. | ||
* '''Chain B''': Adopts a loop conformation. | * '''Chain B''': Adopts a loop conformation. | ||
| - | The FibNT homodimer | + | The FibNT homodimer exhibits the following topology: β1<sub>A</sub>–β2<sub>A</sub>–β4<sub>B</sub>–β3<sub>B</sub>–β3<sub>A</sub>–β4<sub>A</sub>–β2<sub>B</sub>–β1<sub>B</sub>, where the β-sheets are connected via two β-hairpins (Thr36–Asn65 and Glu78–Ser107) and two type I β-turns (Asp49–Gly52 and Asp89–Gly92). The entire assembly is stabilized by an extensive network of hydrogen bonds between adjacent β-strands. |
<scene name='10/1082417/Hbondsv2/1'>TextToBeDisplayed</scene> | <scene name='10/1082417/Hbondsv2/1'>TextToBeDisplayed</scene> | ||
Revision as of 14:03, 18 June 2025
Your Heading Here (maybe something like 'Structure')
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Hanson, R. M., Prilusky, J., Renjian, Z., Nakane, T. and Sussman, J. L. (2013), JSmol and the Next-Generation Web-Based Representation of 3D Molecular Structure as Applied to Proteopedia. Isr. J. Chem., 53:207-216. doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/ijch.201300024
- ↑ Herraez A. Biomolecules in the computer: Jmol to the rescue. Biochem Mol Biol Educ. 2006 Jul;34(4):255-61. doi: 10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644. PMID:21638687 doi:10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644